 Electrical System Defects List & Home Inspection Education
Electrical System Defects List & Home Inspection Education
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about home & building inspection courses, standards, & defect checklists for electrical inspections
This article lists significant Electrical System defects, definitions, and home inspection education topics. This article series, beginning at BUILDING DEFECTS LISTS, provides lists of common building defects and basic defect knowledge that also outline recommended curriculum content for home inspector education.
The building defects and inspection points listed in these articles also guide homeowners and home buyers to building areas that merit careful attention and often point areas of safety concern or important maintenance and repair tasks. Page top sketch provided courtesy of Carson Dunlop Associates, a Toronto home inspection, education & report writing tool company [ carsondunlop.com ].
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
Home Inspection Education Curriculum - Electrical
3.0 ELECTRICAL System Inspection Requirements & Defects List
3.1 Service Drop and Service Entrance
3.1.1 Knowledge Base
1. Describe the function of the electrical system in the home.
2. Describe the location and function of the service drop and service entrance.
3. Describe two types of service drops (overhead and underground).
4. Describe two types of service entrance (conduit and cable).
5. List the common materials used for service entrance conductors (copper, aluminum).
6. Describe the features of adequate installation and repair technique for service drops and service entrance conduit or cable.
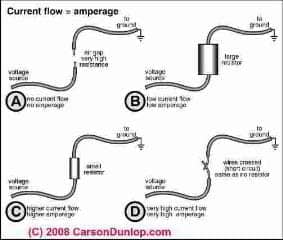
7. Define the following terms:
Service drop, service lateral, service entrance conductor, over-current device (over-current protection device), amp (amperes), volt (voltage), electrical potential (electromotive force), ohms (resistance), ungrounded conductor (black, hot, red, hot), grounded conductor (white, neutral, identified conductor), grounding conductor (green, bare, ground), bonding conductor, alternating current versus direct current, insulator versus conductor, 120 versus 240 volts, impedance, resistor, watt, kilowatt, kilowatt-hour ( kWh), electrical circuit, short circuit, fuse, breaker, ground fault, overload, parallel circuit, series circuit, drip loop, masthead (service cap, entrance cap, pothead?? Not home inspectors!, weather head, service head), three phase electrical system (does three phase matter to home inspectors?) On rare occasions these can be found. JDG\, service capacity, service panel, distribution panel, combination panel.
8. Write the formula for voltage as a function of current and resistance. Write the formula for power as a function of voltage and current, and be able to rearrange both formulas to solve for any variable. This is really not required to be a home inspector, but the RDS includes theory Conversion fomula for KW to BTU..JDG
9. Understand the term load calculation with respect to sizing house electrical services (performing load calculations is not part of a home inspection).
10. Identify the codes and standards which apply to electrical service drop and service entrance in your area.
3.1.2 Inspection Skills:
1. Describe the inspection procedure for service drop and service entrance systems.
2. Describe the procedure for identifying service capacity and evaluating service adequacy.
3. Identify the common defects listed on the next page.
4. Describe the implication of each of the defects above.
5. Identify the safety issues for the inspector and the occupant of the house (electrical shock, fire).
6. Communicate findings to client verbally and in writing, recommending corrective action where needed.
Electrical Service Drop & Electrical Service Entry Typical Defects List
Electrical Service Drop or Service Lateral Defects List
• Branches, vines interfering with wires
• Damaged, frayed wires
• Excessive height
• Clearance over roofs
• Clearance over walking areas
• Clearance over roadways
• Clearance over driveways
• Clearance over decks, balconies and pools
• Inadequate window or door clearance
• Poor connection to service conductors
Electric Meter & Meter Base
The electric meter base may or may not include a main electrical power switch.
External, visible defects at the electric meter such as
- Electric meter or base loose, not secured to building (fire, shock hazard)
- Electric meter base shows signs of overheating
- Leaks at service entry cable connectors
- SEC between meter and panel not sealed at wall
See details at
- ELECTRIC METERS & METER BASES - start of this article
Electrical Service Capacity Defects
- Fuse, breaker size in service box
- Inadequate service size
- Marginal service size
- Rating of service box
- Service conductor size
- Mismatch among SEC, Meter, Service Box, Service entry components
Electrical Service Conductors, SEC, or Entrance Wires & Cables Defects List
• Conduit or cable damaged
• Conduit or cable covered by siding or roof penetrations for additions. JDG
• Conduit or cable not weathertight
• Drip loop too low (touching roof)
- Frayed, damaged SEC
• Mast rust
• Mast bent
• Mast rot
• Mast loose
• Mast not weathertight
• Masthead not weathertight
• No masthead
• No drip loop
• Wires too close to roof
3.2 Electrial Service Panel, Grounding & Panel Inspection
3.2.1 Knowledge Base for Electrical Panels
1. Describe the function of the service panel
2. Describe the function of the grounding system.
3. Describe the function of distribution panels.
4. Describe three types of service panels (fuse, breaker, combination).
5. List the materials and components of service panels.
6. Describe the features of adequate installation and repair techniques for service boxes.
7. Describe the materials and components of an electrical grounding system.
8. Describe the features of adequate installation and repair techniques for house grounding systems including systems that terminate at ? water pipes, metal rods in ground, UFER ground (concrete encased grounding electrode), grounding plates or rings, metal building frames, well casings.
Note: The omission of UFER grounding may be particularly serious in areas of dry soils.
See UFER explained
at ELECTRICAL DEFINITIONS and see a discussion of grounding connection in the footing or slab omission in
at ELECTRICAL GROUND REQUIREMENTS.
9. Describe the types of distribution panels (fuses, breakers, combination).
10. List the typical materials and components of distribution panels.
11. Differentiate between main distribution panels and sub-panels.
12. Describe the features of good installation and repair techniques for main and sub-panels.
13. Define the following terms:
Service box (service equipment, main panel, service panel these are all the same to me??), distribution panel, combination panel, grounding equipment, over-current device, electrical meter, line and load, carrier current controller, bonding, dielectric connector, type S fuse, type D fuse, type P fuse, distribution panel (service panel, , subpanel, fuse box, fuse panel, , ), pull-out fuse box, overfusing, cartridge fuse, fused neutral, double tap (double lugging), pig tailing, multi-wire branch circuit, bus bar, linked fuse, linked breaker, single throw and double throw breaker, single pole and double pole breaker.
14. When is a service panel not required?
15. Identify the codes or standards which apply to electrical service boxes, grounding systems and panels in your area.
3.2.2 Inspection Skills for Electrical Panels
1. Describe the inspection procedure for:
- the service panel
- grounding system
- auxiliary panels
2. Identify the common defects listed on the next page.
3. Describe the implication of each defect.
4. Identify the safety issues for the inspector and occupant of the house (electrical shock, fire).
5. Communicate findings to client verbally and in writing, recommending corrective action where needed.
Electrical Service Panel (Main Panel) Defects List
- Electrical Panel rating too small
- location improper
- not weathertight
- Damaged parts
- ELECTRICAL PANEL FUSED NEUTRAL WIRE HAZARDS
- Fuses upstream of disconnect switch
- Improper taps
- Inappropriate mounting surface
- Multiple disconnects
- Neutral wire bypasses service
- Not well secured
- Obsolete service box
- Overheating
- Poor access
- Poor connections
- Rust Corrosion JDG
- Service entrance wires exposed in house
- Single main disconnect ?? isn't one disc. OK?
- Unprotected openings
- Unsafe electrical service box: known problem brands or models (FPE, Zinsco, Recalled items)
- Wrong fuse or breaker size or brand
- Also see Distribution Panel Defects List below
Electrical Distribution Panel Defects List
- Circuits not labeled
- Damaged electrical panel or components
- Double taps at a fuse, breaker, or mains connection lug
See DOUBLE TAPPED CIRCUIT BREAKERS - Fuse holder loose or broken
- Fused neutrals - more likely to be found in obsolete elecgrical panels
- Fuses loose
- Fuses or breakers too big - over-fusing
- Fuses bypassed
- Inappropriate mounting surface
- Loose circuit breakers
- Loose or missing door to the electrical panel
- Loose panel box or enclosure
- Loose or poorly-connected breakers (falling out of box)
- Multi-wire circuit on same bus
- Neutral and ground wires bonded at subpanel
- No fuses or breakers for subpanel and feeder
- No links for multi-wire circuits (only required if they terminate at the same device)
- Not rated for aluminum, aluminum wiring used
- Obsolete electrical panels
- Openings in panel
- Overheating
- Panel crowded
- Panel upside-down
- Rust Corrosion. JDGor water in panel
- Subpanel not grounded
- Undersized panel
- Unsafe electrical panel or sub-panel known problem brands or models (FPE, Zinsco, Recalled items)
- Wrong fuses or breakers for subpanel and feeder
- Wrong breaker for panel
Electrical Grounding System Defects List
- Aluminum ground wire, bare, corroded, loose, damaged
- Box not bonded to ground
• Connections not accessible
• Corroded grounding conductor
• Grounding electrode rod cut or disconnected..JDG
• Missing
• Neutral bonded to grounding conductor wire downstream of service box
• Neutral not bonded to ground at box
• No jumper for meters and valves
• No ground for subpanel
• Poor connections
• Spliced grounding conductor wire
• Undersized grounding conductor wire
• Wire attached to plastic pipe
• Wire attached to abandoned pipe
Electrical Wire Defects & Damage Checklist
- Abandoned wires in panel
- Aluminum branch circuit wires in use, incomplete repairs or evidence of not properly repaired (e.g. twist-on connector spliced pigtailing)
- Damaged
- Loose connections
- Not well secured
- Overheating
- Sheathing not removed
- Wire crossing bus connections
3.3 The Electrical Distribution System - Wiring Defects
3.3.1 Knowledge Base
1. Describe the function of the electrical distribution system in a house.
2. List the materials and components of the electrical distribution system including the common conductor types (conventional copper, aluminum and knob-and-tube).
3. Describe the features of adequate installation and repair technique for the distribution system including wiring, lights, outlets, switches, and junction boxes.
4. Define the following terms: branch circuit conductor, polarity, ground fault circuit interrupter, NMW cable, NMD cable, BX cable, solder-dipped wire, wire insulation versus sheathing , solid and stranded wire (including typical sizes for each), wire gauge (including AWG and MCM), dedicated circuits, anti-oxidant, CuAl JDG, CO/ALR, COPALUM, wire nut, (solderless connector, twist-on connector), creep with respect to aluminum wire, potlight (recessed light fixture, high-hat light fixture), three way switch, four way switch, two-pin receptacle, three-pin receptacle.
5. Identify the codes or standards which apply to the electrical distribution system in your area.
3.3.2 Inspection Skills for Building Electrical Wiring
1. Describe the inspection procedure for the distribution system including the conductors, lights, outlets, switches and junction boxes, including central air-conditioner circuits.
2. Describe the special inspection issues related to aluminum wiring.
3. Identify the common defects listed on the next page.
4. Describe the implication of each defect .
5. Identify the safety issues for the inspector and the occupant of the house(electric shock and fire).
6. Communicate findings to client verbally and in writing, recommending corrective action where needed.
Electrical DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM, Wiring, Receptacles, Lights & Fixtures, TYPICAL DEFECTS
Electrical Lights, Lighting Defects
- Damaged
- Heat lamps over doors
- Improper closet lighting
- Improper spotlights ? JDG
- Inoperative nonresponsive ? JDG
- Isolating links needed on pull chains wiring
- Loose
- Not grounded
- Obsolete
- Overheating
- Poor stairway lighting, improper location, dim, not switched properly
- Lights needed at exterior doors
- Multi-way light switches needed at stairs
Electrical Switch Defects List
- Damaged, loose, rust
- Faulty 3-way dimmer switch
- Inoperative, obsolete
- No shut off
- Overheated
- Poor location in bathroom
- Poor garbage disposal switch location
- Poor location at furnace
Electrical Wiring Defects
• Abandoned wire
- Aluminum branch circuit solid conductor wiring, evidence of improper or incomplete repair
• Buried cable
• Damaged
• Exposed on walls or ceilings
• Exposed in attics
• Improper color coding
• In steel studs without protection
• Indoor cable used outdoors
• Loose connections
• Missing
• Not well secured
• Open splices
• Overhead wires not stranded
• Permanent wiring used as extension cord
• Too close to ducts, pipes, chimneys, etc.
• Too close to edge of studs or joists
• Under carpets
• Undersized wire
• Wrong type
Electrical Junction Box Defects List
- Concealed boxes
- Cover loose or missing
- Damaged, rust
- Missing, loose
- Not grounded
- Overcrowded
- Overheating
Knob & Tube Electrical Wiring Defects List
• Buried in insulation
• Connections need boxes
• Conventional lights in wet areas
• Fused neutrals
• Wire insulation or sheathing brittle
Aluminum Electrical Wiring Defects List
- ALUMINUM WIRING REPAIR FIELD NOTES - separate article gives detailed practical advice & field experience using the AlumiConn™ connector, such as pigtail wire lengths, and aluminum wiring repair installation time for different boxes & devices.
- ALUMINUM WIRE REPAIR SPLICE SPACE - how to get more wiring space when retrofitting existing electrical devices & wiring in existing or old work electrical boxes
- AlumiConnTM Status Update - CPSC Recommended, is discussed separately here
- ALUMINUM to ALUMINUM SPLICE Connections are discussed separately here
- BINDING SCREW PROBLEMS - Technical notes on binding and poor wire connections in aluminum terminal blocks & aluminum wire repairs
- Aronstein, Jess, Reducing the Fire Hazards in Aluminum-Wired Homes - 5/21/07 [PDF] (AlumiConn™ information is on p. 9)
- ALUMINUM WIRING HAZARDS & REPAIRS - home
- AlumiConn INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
- AlumiConn TORQUE TESTS
- ALUMINUM WIRING BIBLIOGRAPHY
- ALUMINUM WIRE FAILURE REPORTS
- ALUMINUM WIRE GROUNDS
- ALUMINUM-WIRED HOMES, REDUCE THE HAZARD - PDF
- ALUMINUM WIRING IDENTIFICATION
- ALUMINUM WIRING RENTAL HOME ADVICE
- ALUMINUM WIRING REPAIR COALR & CU-AL
- ALUMINUM WIRING REPAIR METHODS
- ALUMINUM WIRING REPAIR ELECTRICIANS
- ALUMINUM WIRING REPAIR FIELD NOTES
- ALUMINUM WIRING REPAIRS NOT-RECOMMENDED
- ALUMINUM WIRE REPAIR SPLICE SPACE
- ALUMINUM WIRING REPAIRS NOT-RECOMMENDED
- ALUMINUM WIRING SAFETY ASSESSMENT - CPSC
- ALUMINUM WIRING GUIDE for HOME INSPECTORS
- ALUMINUM WIRIING SUMMARY free to copy page
- COPPER-CLAD ALUMINUM WIRE
- REDUCE THE AL WIRE RISK: DETAILS
Electrical Receptacle Defects Checklist
- Above electric baseboard heaters
- Broken pin or blade in slots
- Broken receptacle parts, plastic face &c
- Damaged
- Dedicated circuits needed
- In floors or countertops
- Inoperative
- In floors or countertops
- Loose
- No AFCI
- No GFCI
- Open neutral
- Open hot
- Overheated neutral
- Overheating
- Reverse polarity
- Too close to bathtubs
- Too few outlets
- Too far from basin
- Ungrounded
- Within 18 inches of garage floor
- Worn receptacles
- Wrong type
Outdoor Electrical Wiring Defects Checklist
• Buried wire
• Extension cords powering exterior outlets
• Garage door opener connected to extension cord
• Indoor wire used outdoors
• Not suitable for use
• Solid wire run overhead
• Wires not well secured to walls
• Wires too close to grade
• Wires run on roof surfaces
• Wires through gutters or downspouts
Use the Search Box at the top or bottom of these pages to find in-depth information about building, energy savings, and indoor environment inspection, diagnosis and repair at this website. Watch out: these inspection lists do not list all possible defects for the systems discussed, and ot all home or building inspectors will examine all of the items listed here. CONTACT us to suggest corrections or additions to articles at this website.
These curriculae and building defect lists are based on smilar curriculum documents first prepared by Joe Scaduto, an ASHI member who prepared course material for Northeastern University's Building Inspection Certificate program in 1988, subsequently by DF, InspectApedia's editor, for New York University ca 1988 and later, with others, recommended to ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
ASHI did not adopt this material though currently that association as well as others offer extensive HOME INSPECTOR EDUCATION material. The curriculum and lists of defects are informed by additional analysis of the process of home inspection that was developed beginning Calgary, AB for Canadian and U.S. home inspector education and certification examinations in 1997.
Other early contributors to home inspection education in the U.S. and Canada include Dr. Jess Aronstein, Alan Carson, Mike Casey, Mark Cramer, John Cox, Dwight Barnett, Douglas Hansen, Rick Heyl, Larry Hoytt, Bill Merrill, Kevin O'Malley, Dennis Robitalille, Keith Peddie, Pat Porzio, Roger Robinson.
...
Continue reading at ELECTRICAL INSPECTION, DIAGNOSIS, REPAIR - topic home, or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- ARTICLE INDEX to ELECTRICAL INSPECTION & TESTING
- ARTICLE INDEX to BUILDING LIGHTING
- BUILDING DEFECTS LISTS - home
- ELECTRICAL INSPECTION, DIAGNOSIS, REPAIR - home for a complete list of electrical inspection, diagnosis, & repair topics & articles.
- ELECTRICAL INSPECTION, DIAGNOSIS, REPAIR - home
- ALUMINUM WIRING HAZARDS
- AFCI GFCI WIRING, TESTING & SAFETY
- AMPS MEASUREMENT AUTOMOTIVE DC
- AMPS MEASUREMENT METHODS
- AMPS VOLTS DETERMINATION
- CAPACITORS for HARD STARTING MOTORS
- DEFINITIONS of ELECTRICAL TERMS
- DEFINITION of HEATING, COOLING & INSULATION TERMS
- DIRECTORY OF ELECTRICIANS
- DMM DIGITAL MULTIMETER HOW TO USE
- DMMs VOMs SAFE USE OF
- DO IT YOURSELF ELECTRICAL WORK
- DOUBLE TAPPED CIRCUIT BREAKERS
- ELECTRIC MOTOR DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE
- ELECTRIC MOTOR HORSEPOWER & CIRCUIT WIRE SIZE
- ELECTRIC MOTOR NOISE DIAGNOSIS
- ELECTRIC MOTOR OVERLOAD RESET
- ELECTRIC PANEL INSPECTION - home
- ELECTRIC PANEL INSPECTION SAFETY
- ELECTRICAL BASICS
- ELECTRICAL GROUND SYSTEM INSPECTION
- ELECTRICAL WIRING COLOR CODES
- FEDERAL PACIFIC FPE HAZARDS
- FPE ELECTRIC METER BASE & BREAKERS
- HOME & BUILDING INSPECTORS & INSPECTION METHODS.
- KNOB & TUBE WIRING
- LIGHTING, EXTERIOR GUIDE
- LIGHTING, INTERIOR GUIDE
- LIGHTNING PROTECTION SYSTEMS
- LOW VOLTAGE BUILDING WIRING
- MAIN ELECTRICAL DISCONNECT
- OLD HOUSE ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS
- OLD ELECTRICAL WIRING TYPES
- SAFETY for ELECTRICAL INSPECTORS
- SEER RATINGS & OTHER DEFINITIONS
- SERVICE AMPACITY
- TEST EQUIPMENT, ELECTRICAL
- THERMISTORS
- THERMOSTAT INSTALLATION STEPS
- VISUALLY DETERMINE AMPS & VOLTS
- VOLTAGE at the SEC
- VOLTS / AMPS MEASUREMENT EQUIP
- VOLTS MEASUREMENT METHODS
- ZINSCO / SYLVANIA HAZARDS
Suggested citation for this web page
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM DEFECTS LIST at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to BUILDING & HOME INSPECTION
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- Mark Cramer Inspection Services Mark Cramer, Tampa Florida, Mr. Cramer is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors and is a Florida home inspector and home inspection educator. Mr. Cramer serves on the ASHI Home Inspection Standards. Contact Mark Cramer at: 727-595-4211 mark@BestTampaInspector.com
- John Cranor [Website: /www.house-whisperer.com ] is an ASHI member and a home inspector (The House Whisperer) is located in Glen Allen, VA 23060. He is also a contributor to InspectApedia.com in several technical areas such as plumbing and appliances (dryer vents). Contact Mr. Cranor at 804-873-8534 or by Email: johncranor@verizon.net
- Mark Cramer Inspection Services Mark Cramer, Tampa Florida, Mr. Cramer is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors and is a Florida home inspector and home inspection educator. Contact Mark Cramer at: 727-595-4211 mark@BestTampaInspector.com 11/06
- Roger Hankey is principal of Hankey and Brown Inspections, Winter Park, CO. Mr. Hankey is a past chairman of the ASHI Standards Committee and served in other ASHI chapter and national leadership roles. Mr. Hankey is a National Radon Proficiency Program certified measurement professional and a Level II infrared thermographer. Contact Roger Hankey at: 970-393-6604 - rogerhankey47@gmail.com . Website: www.HankeyandBrown.com Mr. Hankey is a frequent contributor to InspectAPedia.com.
- Arlene Puentes [Website: www.octoberhome.com ] , an ASHI member and a licensed home inspector in Kingston, NY, and has served on ASHI national committees as well as HVASHI Chapter President. Ms. Puentes can be contacted at ap@octoberhome.com
- Our recommended books about building & mechanical systems design, inspection, problem diagnosis, and repair, and about indoor environment and IAQ testing, diagnosis, and cleanup are at the InspectAPedia Bookstore. Also see our Book Reviews - InspectAPedia.
- Building Pathology, Deterioration, Diagnostics, and Intervention, Samuel Y. Harris, P.E., AIA, Esq., ISBN 0-471-33172-4, John Wiley & Sons, 2001 [General building science-DF] ISBN-10: 0471331724 ISBN-13: 978-0471331728
- Building Pathology: Principles and Practice, David Watt, Wiley-Blackwell; 2 edition (March 7, 2008) ISBN-10: 1405161035 ISBN-13: 978-1405161039
- Historic Preservation Technology: A Primer, Robert A. Young, Wiley (March 21, 2008) ISBN-10: 0471788368 ISBN-13: 978-0471788362
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.

