 Foundation Damage Reports - How to Describe Foundation Damage
Foundation Damage Reports - How to Describe Foundation Damage
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about foundation inspection reports
Foundation damage reporting:
This document describes how visually observed foundation damage should be reported and what general advice makes sense for building owners or buyers where foundation damage is found and/or where further foundation inspection, testing, diagnosis, or repair appear warranted based on a general field inspection. We include discussion of methods used to perform ongoing monitoring of building foundations for cracking and movement.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
Foundation DAMAGE REPORTS - How to Report Foundation Damage
 In the most concise summary, any report of the condition of a building foundation following a visual inspection of its condition
should include a description of the type of foundation and foundation
materials, the explicit observations of defects or other conditions that led the inspector to his or her opinions about the condition of the foundation,
an opinion about the urgency of need for further action, and if it can be determined, an opinion on whether or not significant costs are likely
to be involved.
In the most concise summary, any report of the condition of a building foundation following a visual inspection of its condition
should include a description of the type of foundation and foundation
materials, the explicit observations of defects or other conditions that led the inspector to his or her opinions about the condition of the foundation,
an opinion about the urgency of need for further action, and if it can be determined, an opinion on whether or not significant costs are likely
to be involved.
If the inspector elects to use simple methods and materials commonly used by masons or general contractors, such as use of a tape measure and plumb line to observe conditions, that information should also be provided. [For an example of simple foundation measurements see FOUNDATION BULGE or LEAN MEASUREMENTS.
Explicit description of observations of the condition of a building foundation or floor slab should be provided with sufficient detail such that a qualified expert on reading the report, and on assuming that the report author did not miss other site clues, could agree that the inspector's conclusions were reasonable and prudent.
Evidence of Foundation Damage or Movement Should Be Reported
- Observed wall lean, bulge, sign of settlement or movement
- Crack sizes observed (approximate: hairline 1/16 1/8 1/4 larger)
- Crack locations on the building and the location of cracking with respect to other building or site conditions such as the location top of exterior grade
- Crack Pattern - horizontal, vertical, step
Report Other Site or Structural Clues Observed Which are Likely to Relate to the Condition of the Foundation or Slab
- Signs of ongoing movement in the building, such as interior cracks, repeated crack repairs, sagged or humped floors, or separation of framing members were observed or were not seen
- Signs of repairs inside, outside, to building surfaces, windows, doors, or other components likely to be affected were observed or not. If evidence of repair was observed, did the evidence suggest that the repair was recent or old, and has the repair been performed only once or repeatedly - indicating chronic, episodic, or ongoing building or foundation movement.
NOTE: this documentation can aid future evaluations should the owner or others decide to monitor the structure for further evidence of movement.
Making Foundation Crack or Movement Monitoring/Action Recommendations
Possible outcomes and advice following a foundation inspection include:
- Do Nothing (cosmetic, minor) - the inspection did not detect evidence of significant foundation movement.
- Monitor the foundation or other structural areas and component for signs of new or ongoing movement
- Evaluate the foundation or structure further, using an expert engineer who is familiar with foundation diagnosis and repair, or a foundation repair company
- Foundation repair, replacement, improvement, or provision of missing components is obviously needed or likely to be needed based on simple site visual observations *
- Foundation Repair or Investigation Priority: is the next step urgent or can it be deferred *
- Cost estimates: is the cost of foundation repair, based on limited visual inspection, likely to be major or minor * (More or less than $500, or any other amount that the inspector specifies)
- References to authoritative sources for foundation information, and if possible, for the conclusions made during the inspection*
- References to foundation repair experts*
Items marked * are or may be beyond scope of ASHI Standards of Practice but may be performed by inspectors, engineers, architects, masons, or foundation repair company representatives who have appropriate education and/or experience.
Methods for Monitoring Foundations for Evidence of Ongoing or Episodic Movement
Please see CRACK MONITORING Methods for the complete article on this topic.
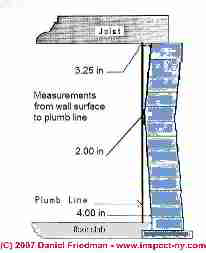
 Building foundations may be moving, either continuously or episodically. Most movement is episodic, that is, the movement is not a simple and continuous creep but rather foundation movement or cracking occurs in fits and starts. Our sketch (left) shows a bulged masonry block foundation wall that has bowed in two inches at its innermost point.)
Building foundations may be moving, either continuously or episodically. Most movement is episodic, that is, the movement is not a simple and continuous creep but rather foundation movement or cracking occurs in fits and starts. Our sketch (left) shows a bulged masonry block foundation wall that has bowed in two inches at its innermost point.)
Usually foundation movement and further cracking occurs in response to occurrences of what has caused the cracking in the first place.
See FOUNDATION DAMAGE SEVERITY and then FOUNDATION MOVEMENT ACTIVE vs. STATIC for distinguishing severe and also ongoing foundation movements.
Proper Foundation Inspection Report Language - "Structural Soundness"
Engineering analysis (structural requirements, load calculations, design and specification of components and/or repairs) is not part of a normal home inspection, even if the inspection has been performed by a licensed professional engineer or architect.
All professional home inspectors are expected to recognize when expert advice or further evaluation are needed. Foundation Experts: have special training, methods, costs. Refer problems to qualified foundation engineer/repair people who specialize in this area. It is proper for an inspector to report whether or not s/he observed indications of damage to the structure. Such basic observations are the normal purview of anyone working in and experienced in new construction, construction repair, and home inspection as well as foundation repair.
An inspector who is not qualified should make no pronouncements of "structural soundness" of building components. Even a home inspector who is qualified to perform structural analysis, (such as a licensed professional structural or civil engineer) should distinguish between stating that there was no evidence of structural damage and a blanket statement that the construction is "structurally sound."
Where conventional construction practices and materials have been used there is implicit engineering work which determined the original specifications for sizes, spans, connections, fasteners, etc. A technical pronouncement of structural soundness is normally not appropriate nor required and would require measurement and engineering analysis of all structural components including ones which are not visible for examination; for example, how would one determine visually whether or not an un-damaged foundation wall has proper steel reinforcement?
There is a reasonable presumption of "structural soundness" of original design at properties which are constructed using accepted, conventional materials and methods. This does not mean that changes in conditions may not require repairs.
What about buildings constructed to standards less demanding than modern contemporary practices and codes? In the absence of evidence of damage to a structure which was designed to standards which were accepted at the time of construction, it is possible that a prudent consumer or inspector would have the opinion that:
- Repair or reinforcement are optional: not presently cost-justified nor required as an immediate major repair even though such repair or reinforcement might be desirable to increase the safety, durability, and life of the structure.
- Repair and reinforcement are likely to be required: presently may be cost justified if marginal materials have been used, regardless of whether or not there is present damage or evidence of movement. An example might be an intact foundation built without footings where local area drainage conditions appear to put the building at risk of undermining and collapse.
Finally, a report about foundation damage should make clear to the client what action, if any, is necessary. The explanation, in lay terms, must indicate what does the damage means to the client. That is, that damage was found, that unsafe conditions or risk of collapse are present (IF that is the opinion of the inspector), and that repair is necessary (or not), that it will be a significant expense (or not). This report is not an explanation of cause/effect/engineering - unless the inspector is qualified & chooses to provide this extra service
Exclusions from "foundation damage" reports:
Basement or Crawl Space Water entry as a Foundation Defect
Some owners consider water entry defects to be foundation defects. This is incorrect. Building foundations are intended to hold back earth and to support the structure. Control of moisture and water entry is not normally the function of these components. (See foundation waterproofing, site work and site drainage topics.) This topic is, however, appropriate to include within the scope of a professional home inspection.
Finding Experts & Examples of Foundation Expert Procedures
- Geotechnical engineering: sketch, borings, analysis, report, recommended solutions
- Boring with drill rig standard penetration test, 140# hammer free-falls 30" to id soil density boring
- provides soil composition info
- Ground penetrating radar signal depth to non-penetrating layer (clay & rock),
- profiles the sub surface, to plan boring locations
Note: consumers should beware of "general practitioner" contractors, architects and engineers who sign-up to diagnose and repair foundation failures. Use an expert who has experience and training in this specific field to assure that various options available for repair are known-to and evaluated by the consultant. A general practitioner may be able to design a repair that will work but if s/he is not familiar with the best practices of the industry and if s/he is unfamiliar with special products which are available, the repair may be far more costly and possibly less effective than desired.
Structural Damage Insurance Recommended for Home Owners/Buyers
- All houses in Florida (and some other locations in the U.S. such as portions of Pennsylvania are or should be insured for sink hole damage.
- Clay soil problem insurance is available, maybe low cost in some states as Colorado, Florida, Missouri.
Authority
Opinions herein are the responsibility of the author. Most of this material has been subject to ongoing peer review but is without any professional engineering analysis. Home inspections may include the discovery of defects involving life, safety, and significant costs. Home inspectors who are not both qualified and certain of the authoritative basis of their conclusions should obtain their own expert advice from qualified experts.
This work is also based on the author's construction & inspection experience, training, research, and survey of material from ASHI, and from N. Becker, R. Burgess, J. Bower, D. Breyer, A. Carson, J. Cox, A. Daniel, M. Lennon, R. Peterson, J. Prendergast, W. Ransom, D. Rathburn, E. Rawlins, E. Seaquist, and D. Wickersheimer. Some useful citations are at the end of this paper.
...
Continue reading at FOUNDATION CRACKS & DAMAGE GUIDE- topic home, or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- FOUNDATION CRACKS & DAMAGE GUIDE - home
- BLOCK FOUNDATION & WALL DEFECTS
- BRICK FOUNDATIONS & WALLS
- BULGE or LEAN MEASUREMENTS
- CONCRETE FOUNDATION, WALL, SLAB DEFECTS - home
- CONCRETE SLAB CRACK EVALUATION
- CONCRETE SHRINKAGE CRACKS
- CONTROL JOINT CRACKS in CONCRETE
- CRACK MONITORING METHODS
- DIAGONAL CRACKS in BLOCK FOUNDATIONS, WALLS
- DIAGONAL CRACKS in CONCRETE FOUNDATIONS, WALLS
- EARTHQUAKE DAMAGED FOUNDATIONS
- FLOOD DAMAGED FOUNDATIONS
- FOUNDATION CRACK DICTIONARY - what is the severity of foundation damage, what is its effect on the stability of the structure, and how urgently are foundation repairs needed?
- FOUNDATION DAMAGE by MATERIAL or INCLUSIONS
- FOUNDATION FAILURES by MOVEMENT TYPE: is the movement active or not, how is the foundation moving: bulging, leaning, settling, etc. ?
- FOUNDATION FAILURES by TYPE & MATERIAL: how does damage show up in different types of foundation material & what are the implications for collapse risk or repair need?
- FOUNDATION DAMAGE on SHALE
- FOUNDATION MOVEMENT ACTIVE vs. STATIC
- FOUNDATION SHRINKAGE vs EXPANSION vs SETTLEMENT
- FROST HEAVES, FOUNDATION, SLAB
- HORIZONTAL FOUNDATION CRACKS
- PYRRHOTITE INCLUSION CRACKING
- SHRINKAGE vs EXPANSION vs SETTLEMENT
- SINKHOLES & BUILDING DAMAGE
- THERMAL EXPANSION CRACKS in BRICK
- VERTICAL CRACKS in BLOCK WALLS
- VERTICAL FOUNDATION CRACKS
- FOUNDATION DAMAGE & REPAIR GUIDE - home page foundation damage assessment & repair procedures.
- FOUNDATION INSPECTION METHODS
- FOUNDATION REPAIR METHODS discusses alternative ways to fix a damaged foundation or floor slab crack or movement
Suggested citation for this web page
FOUNDATION DAMAGE REPORTS at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to BUILDING STRUCTURES
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- "Concrete Slab Finishes and the Use of the F-number System", Matthew Stuart, P.E., S.E., F.ASCE, online course at www.pdhonline.org/courses/s130/s130.htm
- Avongard crack monitors, Santa Monica, CA 90406, 800-244-7241 can be reached by email to info@avongard.com
- Slope Indicator Company, 12123 Harbour Reach Dr., Mukilteo, WA, USA 98275 425-493-6200 can be reached by email to solutions@slope.com
- Sal Alfano - Editor, Journal of Light Construction*
- Thanks to Alan Carson, Carson Dunlop, Associates, Toronto, for technical critique and some of the foundation inspection photographs cited in these articles
- Terry Carson - ASHI
- Mark Cramer - ASHI
- JD Grewell, ASHI
- Duncan Hannay - ASHI, P.E. *
- Mark Cramer Inspection Services Mark Cramer, Tampa Florida, Mr. Cramer is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors and is a Florida home inspector and home inspection educator. Mr. Cramer serves on the ASHI Home Inspection Standards. Contact Mark Cramer at: 727-595-4211 mark@BestTampaInspector.com
- John Cranor [Website: /www.house-whisperer.com ] is an ASHI member and a home inspector (The House Whisperer) is located in Glen Allen, VA 23060. He is also a contributor to InspectApedia.com in several technical areas such as plumbing and appliances (dryer vents). Contact Mr. Cranor at 804-873-8534 or by Email: johncranor@verizon.net
- Bob Klewitz, M.S.C.E., P.E. - ASHI
- Ken Kruger, P.E., AIA - ASHI
- Aaron Kuertz aaronk@appliedtechnologies.com, with Applied Technologies regarding polyurethane foam sealant as other foundation crack repair product - 05/30/2007
- Bob Peterson, Magnum Piering - 800-771-7437 - FL*
- Arlene Puentes, ASHI, October Home Inspections - (845) 216-7833 - Kingston NY
- Greg Robi, Magnum Piering - 800-822-7437 - National*
- Dave Rathbun, P.E. - Geotech Engineering - 904-622-2424 FL*
- Ed Seaquist, P.E., SIE Assoc. - 301-269-1450 - National
- Dave Wickersheimer, P.E. R.A. - IL, professor, school of structures division, UIUC - University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign School of Architecture. Professor Wickersheimer specializes in structural failure investigation and repair for wood and masonry construction. * Mr. Wickersheimer's engineering consulting service can be contacted at HDC Wickersheimer Engineering Services. (3/2010)
- *These reviewers have not returned comment 6/95
ADDITIONAL READING about Foundation Failure Diagnosis & Repair
- Diagnosing & Repairing House Structure Problems, Edgar O. Seaquist, McGraw Hill, 1980 ISBN 0-07-056013-7 (obsolete, incomplete, missing most diagnosis steps, but very good reading; out of print but used copies are available at Amazon.com, and reprints are available from some inspection tool suppliers). Ed Seaquist was among the first speakers invited to a series of educational conferences organized by D Friedman for ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors, where the topic of inspecting the in-service condition of building structures was first addressed.
- Design of Wood Structures - ASD, Donald E. Breyer, Kenneth Fridley, Kelly Cobeen, David Pollock, McGraw Hill, 2003, ISBN-10: 0071379320, ISBN-13: 978-0071379328
This book is an update of a long-established text dating from at least 1988 (DJF); Quoting:
This book is gives a good grasp of seismic design for wood structures. Many of the examples especially near the end are good practice for the California PE Special Seismic Exam design questions. It gives a good grasp of how seismic forces move through a building and how to calculate those forces at various locations. THE CLASSIC TEXT ON WOOD DESIGN UPDATED TO INCLUDE THE LATEST CODES AND DATA. Reflects the most recent provisions of the 2003 International Building Code and 2001 National Design Specification for Wood Construction. Continuing the sterling standard set by earlier editions, this indispensable reference clearly explains the best wood design techniques for the safe handling of gravity and lateral loads. Carefully revised and updated to include the new 2003 International Building Code, ASCE 7-02 Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures, the 2001 National Design Specification for Wood Construction, and the most recent Allowable Stress Design. - Building Failures, Diagnosis & Avoidance, 2d Ed., W.H. Ransom, E.& F. Spon, New York, 1987 ISBN 0-419-14270-3
- Forensic Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering, Robert W. Day, McGraw-Hill Professional, 1998, ISBN 0070164444, 9780070164444, 460 pp. Mr. Day discusses the Avongard crack monitors and other foundation monitoring methods - p. 48-49.
- Domestic Building Surveys, Andrew R. Williams, Kindle book, Amazon.com
- Defects and Deterioration in Buildings: A Practical Guide to the Science and Technology of Material Failure, Barry Richardson, Spon Press; 2d Ed (2001), ISBN-10: 041925210X, ISBN-13: 978-0419252108. Quoting:
A professional reference designed to assist surveyors, engineers, architects and contractors in diagnosing existing problems and avoiding them in new buildings. Fully revised and updated, this edition, in new clearer format, covers developments in building defects, and problems such as sick building syndrome. Well liked for its mixture of theory and practice the new edition will complement Hinks and Cook's student textbook on defects at the practitioner level. - Guide to Domestic Building Surveys, Jack Bower, Butterworth Architecture, London, 1988, ISBN 0-408-50000 X
- "Avoiding Foundation Failures," Robert Marshall, Journal of Light Construction, July, 1996 (Highly recommend this article-DF)
- "A Foundation for Unstable Soils," Harris Hyman, P.E., Journal of Light Construction, May 1995
- "Backfilling Basics," Buck Bartley, Journal of Light Construction, October 1994
- "Inspecting Block Foundations," Donald V. Cohen, P.E., ASHI Reporter, December 1998. This article in turn cites the Fine Homebuilding article noted below.
- "When Block Foundations go Bad," Fine Homebuilding, June/July 1998
- InspectAPedia.com - The Free Home Inspection & Construction Diagnosis Public Information Website
- Journal of Light Construction articles are available on CD ROM from the Journal of Light Construction, www.bginet.com, 802-434-4747
- Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction, by Steven Bliss. John Wiley & Sons, 2006. ISBN-10: 0471648361, ISBN-13: 978-0471648369, Hardcover: 320 pages, available from Amazon.com and also Wiley.com. See our book review of this publication.
- Decks and Porches, the JLC Guide to, Best Practices for Outdoor Spaces, Steve Bliss (Editor), The Journal of Light Construction, Williston VT, 2010 ISBN 10: 1-928580-42-4, ISBN 13: 978-1-928580-42-3, available from Amazon.com
- The Journal of Light Construction has generously given reprint permission to InspectAPedia.com for certain articles found at this website. All rights and contents to those materials are ©Journal of Light Construction and may not be reproduced in any form.
- Appliances and Home Electronics, - energy savings, U.S. Department of Energy
- Avongard FOUNDATION CRACK PROGRESS CHART [PDF] - structural crack monitoring
- BASEMENT MOISTURE CONTROL [PDF] U.S. Department of Energy
- Building Failures, Diagnosis & Avoidance, 2d Ed., W.H. Ransom, E.& F. Spon, New York, 1987 ISBN 0-419-14270-3
- Building Pathology, Deterioration, Diagnostics, and Intervention, Samuel Y. Harris, P.E., AIA, Esq., ISBN 0-471-33172-4, John Wiley & Sons, 2001 [General building science-DF] ISBN-10: 0471331724 ISBN-13: 978-0471331728
- Building Pathology: Principles and Practice, David Watt, Wiley-Blackwell; 2 edition (March 7, 2008) ISBN-10: 1405161035 ISBN-13: 978-1405161039
- The Circular Staircase, Mary Roberts Rinehart
- Construction Drawings and Details, Rosemary Kilmer
- CRAWL SPACE MOISTURE CONTROL [PDF] U.S. Department of Energy
- Design of Wood Structures - ASD, Donald E. Breyer, Kenneth Fridley, Kelly Cobeen, David Pollock, McGraw Hill, 2003, ISBN-10: 0071379320, ISBN-13: 978-0071379328
This book is an update of a long-established text dating from at least 1988 (DJF); Quoting:
This book is gives a good grasp of seismic design for wood structures. Many of the examples especially near the end are good practice for the California PE Special Seismic Exam design questions. It gives a good grasp of how seismic forces move through a building and how to calculate those forces at various locations. THE CLASSIC TEXT ON WOOD DESIGN UPDATED TO INCLUDE THE LATEST CODES AND DATA. Reflects the most recent provisions of the 2003 International Building Code and 2001 National Design Specification for Wood Construction. Continuing the sterling standard set by earlier editions, this indispensable reference clearly explains the best wood design techniques for the safe handling of gravity and lateral loads. Carefully revised and updated to include the new 2003 International Building Code, ASCE 7-02 Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures, the 2001 National Design Specification for Wood Construction, and the most recent Allowable Stress Design. - Diagnosing & Repairing House Structure Problems, Edgar O. Seaquist, McGraw Hill, 1980 ISBN 0-07-056013-7 (obsolete, incomplete, missing most diagnosis steps, but very good reading; out of print but used copies are available at Amazon.com, and reprints are available from some inspection tool suppliers). Ed Seaquist was among the first speakers invited to a series of educational conferences organized by D Friedman for ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors, where the topic of inspecting the in-service condition of building structures was first addressed.
- Domestic Building Surveys, Andrew R. Williams, Kindle book, Amazon.com
- Defects and Deterioration in Buildings: A Practical Guide to the Science and Technology of Material Failure, Barry Richardson, Spon Press; 2d Ed (2001), ISBN-10: 041925210X, ISBN-13: 978-0419252108. Quoting:
A professional reference designed to assist surveyors, engineers, architects and contractors in diagnosing existing problems and avoiding them in new buildings. Fully revised and updated, this edition, in new clearer format, covers developments in building defects, and problems such as sick building syndrome. Well liked for its mixture of theory and practice the new edition will complement Hinks and Cook's student textbook on defects at the practitioner level. - Guide to Domestic Building Surveys, Jack Bower, Butterworth Architecture, London, 1988, ISBN 0-408-50000 X
- "Avoiding Foundation Failures," Robert Marshall, Journal of Light Construction, July, 1996 (Highly recommend this article-DF)
- "A Foundation for Unstable Soils," Harris Hyman, P.E., Journal of Light Construction, May 1995
- "Backfilling Basics," Buck Bartley, Journal of Light Construction, October 1994
- "Inspecting Block Foundations," Donald V. Cohen, P.E., ASHI Reporter, December 1998. This article in turn cites the Fine Homebuilding article noted below.
- "When Block Foundations go Bad," Fine Homebuilding, June/July 1998
- Historic Preservation Technology: A Primer, Robert A. Young, Wiley (March 21, 2008) ISBN-10: 0471788368 ISBN-13: 978-0471788362
- LOG HOMES: MINIMIZING AIR LEAKAGE [PDF] U.S. Department of Energy
- Manual for the Inspection of Residential Wood Decks and Balconies, by Cheryl Anderson, Frank Woeste (Forest Products Society), & Joseph Loferski, October 2003, ISBN-13: 978-1892529343,
- Masonry Design for Engineers and Architects, M. Hatzinikolas, Y. Korany, Canadian Masonry (2005), ISBN-10: 0978006100, ISBN-13: 978-0978006105
- Masonry Structures: Behavior and Design, Robert G. Drysdale, Ahmid A. Hamid, Lawrie R. Baker, The Masonry Society; 2nd edition (1999), ISBN-10: 1929081014, ISBN-13: 978-1929081011
- Masonry, Engineered: Using the Canadian Code, J. I. Gainville, Cantext publications (1983), ASIN: B0007C37PG
- Masonry, Non-reinforced masonry design tables, Hans J. Schultz, National Concrete Producers Association and the Canadian Masonry Contractors Association (1976), ASIN: B0007C2LQM
- MOISTURE CONTROL in BUILDINGS [PDF] U.S. Department of Energy
- MOISTURE CONTROL in WALLS [PDF] U.S. Department of Energy
- Quality Standards for the Professional Remodeling Industry, National Association of Home Builders Remodelers Council, NAHB Research Foundation, 1987.
- Quality Standards for the Professional Remodeler, N.U. Ahmed, # Home Builder Pr (February 1991), ISBN-10: 0867183594, ISBN-13: 978-0867183597
- Slab on Grade Foundation Moisture and Air Leakage, U.S. Department of Energy
- Straw Bale Home Design, U.S. Department of Energy provides information on strawbale home construction - original source at http://www.energysavers.gov/your_home/designing_remodeling/index.cfm/mytopic=10350
- More Straw Bale Building: A Complete Guide to Designing and Building with Straw (Mother Earth News Wiser Living Series), Chris Magwood, Peter Mack, New Society Publishers (February 1, 2005), ISBN-10: 0865715181 ISBN-13: 978-0865715189 - Quoting:
Straw bale houses are easy to build, affordable, super energy efficient, environmentally friendly, attractive, and can be designed to match the builder’s personal space needs, esthetics and budget. Despite mushrooming interest in the technique, however, most straw bale books focus on “selling” the dream of straw bale building, but don’t adequately address the most critical issues faced by bale house builders. Moreover, since many developments in this field are recent, few books are completely up to date with the latest techniques.
More Straw Bale Building is designed to fill this gap. A completely rewritten edition of the 20,000-copy best--selling original, it leads the potential builder through the entire process of building a bale structure, tackling all the practical issues: finding and choosing bales; developing sound building plans; roofing; electrical, plumbing, and heating systems; building code compliance; and special concerns for builders in northern climates. - VAPOR BARRIERS or VAPOR DIFFUSION RETARDERS [PDF] U.S. DOE - how vapor barriers work, types of vapor diffusion barriers, installing vapor barrier
- VENTILATION for ENERGY-EFFICIENT BUILDINGS [PDF] Purpose of ventilation, ventilateion strategies, etc.
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
Sinkholes and Sudden Land Subsidence References, Products, Consultants
- "A Hole in the Ground Erupts, to Estonia's Delight", New York Times, 9 December 2008 p. 10.
- History of water usage in Estonia: (5.7 MB PDF) jaagupi.parnu.ee/freshwater/doc/the_history_of_water_usage_systems_in_estonia.pdf
- "Quebec Family Dies as Home Vanishes Into Crater, in Reminder of Hidden Menace", Ian Austen, New York Times, 13 May 2010 p. A8. See http://www.nytimes.com/
- "Quick Clay", Wikipedia search 5/13/2010 - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quick_clay
- Florida DEP - Department of Environmental Protection, & Florida Geological survey (http://www.dep.state.fl.us/geology/default.htm) on Florida sinkholes: Effects of Sinkholes on Water Conditions Hernando County, Florida, Brett Buff, GIS in Water Resources, 2008, Dr. David R. Maidment, Photos - Tom Scott, Florida Geographic Survey - Web Search 06/09/2010 - http://www.dep.state.fl.us/geology/geologictopics/jacksonsink.htm
and - http://www.dep.state.fl.us/geology/geologictopics/sinkhole.htm
also see
Lane, Ed, 1986, Karst in Florida: Florida Geological Survey Special Publication 29, 100 p. - Foundation Engineering Problems and Hazards in Karst Terranes, James P. Reger, Maryland Geological Survey, web search 06/05/2010, original source: http://www.mgs.md.gov/esic/fs/fs11.html
Maryland Geological Survey, 2300 St. Paul Street, Baltimore, MD 21218 - "Frost Heaving Forces in Leda Clay", Penner, E., Division of Building Research, National Research Council of Canada, Canadian Geotechnical Journal, NRC Research Press, 1970-2, Vol 7, No 1, PP 8-16, National Research Council of Canada, Accession number 1970-023601, Quoting from original source
The frost heaving forces developed under a 1 ft. (30.5 cm) diameter steel plate were measured in the field throughout one winter. The steel plate was fixed at the ground surface with a rock-anchored reaction frame. heave gauges and thermocouples were installed at various depths to determine the position and temperature of the active heaving zone. The general trend was for the surface force to increase as the winter progressed. when the frost line approached the maximum depth the force was in excess of 30,000 lb (13,608 KG). Estimates of the heaving pressure at the frost line ranged from 7 to 12 psi (0.49 to 0.84 KG/cm) square during this period. The variation of surface heaving force was closely associated with weather conditions. Warming trends resulting in a temperature increase of the frozen layer caused the forces to decline.
- "Geoscape Ottowa-Gatineau Landslides", Canada Department of Natural Resources, original source http://geoscape.nrcan.gc.ca/ottawa/landslides_e.php - quoting from that source:
Leda clay slopes in the Ottawa valley are vulnerable to catastrophic landslides. More than 250 landslides, historical and ancient, large and small, have been identified within 60 km of Ottawa. Some of these landslides caused deaths, injuries, and property damage, and their impact extended far beyond the site of the original failure. In spectacular flowslides, the sediment underlying large areas of flat land adjacent to unstable slopes liquefies. The debris may flow up to several kilometres, damming rivers and causing flooding, siltation, and water-quality problems or damaging infrastructure. Geologists and geotechnical engineers can identify potential landslide areas, and appropriate land-use zoning and protective engineering works can reduce the risk to property and people.
Deposits of Leda clay, a potentially unstable material, underlie extensive areas of the Ottawa-Gatineau region. Leda clay is composed of clay- and silt-sized particles of bedrock that were finely ground by glaciers and washed into the Champlain Sea. As the particles settled through the salty water, they were attracted to one another and formed loose clusters that fell to the seafloor. The resulting sediment had a loose but strong framework that was capable of retaining a large amount of water. Following the retreat of the sea, the salts that originally contributed to the bonding of the particles were slowly removed (leached) by fresh water filtering through the ground. If sufficiently disturbed, the leached Leda clay, a weak but water-rich sediment, may liquefy and become a 'quick clay'. Trigger disturbances include river erosion, increases in pore-water pressure (especially during periods of high rainfall or rapid snowmelt), earthquakes, and human activities such as excavation and construction.
After an initial failure removes the stiffer, weathered crust, the sensitive clay liquefies and collapses, flowing away from the scar. Failures continue in a domino-like fashion, rapidly eating back into the flat land lying behind the failed slope. The flowing mud may raft intact pieces of the stiffer surface material for great distances.
- Kochanov, W. E., 1999, Sinkholes in Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania
Geological Survey, 4th ser., Educational Series 11, 33 p., 3rd printing April 2005, Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources / Bureau of Topographic and Geologic Survey, DCNR Educational Series 11, Pennsylvania Geological Survey, Fourth Series, Harrisburg,
1999 - web search 06/05/2010, original source: http://www.dcnr.state.pa.us/topogeo/hazards/es11.pdf - Quoting from the document introduction:
The first 18 pages of this booklet contain an explanation of how sinkholes develop. In order to tell the sinkhole story, it is important to discuss a number of related geologic disciplines. The words used to describe sinkholes and these disciplines may be a bit unfamiliar. However, general explanations are given throughout the booklet to help clarify their meanings. Key words are printed in bold type for emphasis. The more important ones are defined in a Glossary that begins on page 29. The remaining sections, starting with “Sinkholes in the Urban Environment” (page 18), deal with sinkholes and their impact on our environment. This includes recognition of subsidence features and sinkhole repair. - [1] Sarah Cervone, [web page] data from the APIRS database, Graphics by Ann Murray, Sara Reinhart and Vic Ramey, Vic Ramey is the editor. DEP review by Jeff Schardt and Judy Ludlow. The web page is a collaboration of the Center for Aquatic and Invasive Plants, University of Florida, and the Bureau of Invasive Plant Management, Florida Department of Environmental Protection contact: varamey@nersp.nerdc.ufl.edu [A primary resource for this article
- [2] Center for Cave and Karst Studies or the Kentucky Climate Center, both at Western Kentucky University
- Vanity Fair - web search 06/04/2010 http://www.vanityfair.com/online/daily/2010/06/what-caused-the-guatemala-sinkhole-and-why-is-it-so-round.html
- Sinkholes, Virginia Division of Mineral Resources,
- Virginia Department of Mines, Minerals and Energy, www.dmme.virginia.gov Virginia Department of Mines, Minerals and Energy Division of Mineral Resources 900 Natural Resources Drive, Suite 500 Charlottesville, VA 22903 Sales Office: (434) 951-6341 FAX : (434) 951-6365 Geologic Information: (434) 951-6342 http://www.dmme.virginia.gov/ divisionmineralresources.shtml - Web search 06/09/2010
Sink Hole & Related Engineering References
- Newton, J. G., 1987, Development of sinkholes resulting from man's activities in the eastern United States: US Geological Survey Circular 968, 54 p.
- Sinclair, W. C., 1982, Sinkhole development resulting from ground-water withdrawal in the Tampa Area, Florida: U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations 81-50, 19 p.
- White, W. B., 1988, Geomorphology and Hydrology of Karst Terrains: Oxford University Press, New York, 464 p.
- Williams, J. H. and Vineyard, J. D., 1976, Geologic indicators of subsidence and collapse in karst terrain in Missouri: Presentation at the 55th Annual Meeting, Transportation Research Board, Washington, D.C.
- Barry F. Beck, A. J. (1999). Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology of Sinkholes and Karst. Rotterdam, Netherlands: A. A. Balkema.
- Beck, B. F. (2003). Sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst. Huntsville, Alabama: The American Society of Civil Engineers.
- Beck, B. F. (2005). Sinkholes and the Engineering and Envrionmental Impacts of Karst. San Antonio, Texas: The American Society of Civil Engineers.
- Tony Waltham, F. B. (2005). Sinkholes and Subsidence, Karst and Cavernous Rocks in Engineering and Construction. Chichester, United Kingdom: Praxis Publishing.
- Whitman D., G. T. (1999). Spatial Interrelationships Between Lake Elevations, Water Tables, and Sinkhole Occurence in Central Florida: A GIS Approach. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing , 1169-1178.
- Cited References from this article:
- #3. Detecting Sinkholes with Geophysics, Enviroscan, Inc., Lancaster PA 717-396-8922 email@enviroscan.com www.enviroscan.com 2003
- Sinkholes in Guatemala, Guatemala City, Wikipedia - web search 06/04/2010 - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guatemala_City
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.

