 Hand Dug Water Wells
Hand Dug Water Wells
Dig, install, maintain & use hand excavated drinking water wells
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about hand dug water wells, construction, inspection, safety, sanitation, and well collapses
Hand dug wells: their properties, construction & sanitation.
This article offers advice for hand dug water wells and the sanitation and maintenance concerns with this water supply type.
We provide advice about what to do when things go wrong, how to inspect hand dug wells for safety, safe practices for actually digging a well, and how to address hand dug well sanitation
. In our guide to hand dug wells we discuss how a hand dug well is constructed, maintained, and kept sanitary or "safe to drink".
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
Characteristics of hand dug wells, their construction, use, sanitation

The world wide popularity of hand dug wells is accounted for by the ease of construction without specialized equipment, the simplicity of water raising equipment (a bucket on a rope has worked for thousands of years), and the ability of the Dug well to hold a large volume of water in storage for times of peak demand.
[Click to enlarge any image]
- Hand Dug Wells
are usually quite shallow - typically less than 25 feet deep. - The volume of water
on hand (the well's static head) in a hand dug well depends not on the well's overall depth, but the depth and diameter of the column of water in the well when it is at rest and fully recovered from any draw-down.
If you are not sure how to calculate how much water is in your well, we give the formula and some examples
at STATIC HEAD of WATER in the WELL - The amount of water you can get out
of a hand dug well depends on its standby volume or static head, the rate at which water flows into it, and the lift and pumping capacity in gallons per minute or liters per minute of the pump being used.
See WELL FLOW RATE for an explanation of how to determine the rate at which water flows into the well or what water flow rate a well can deliver.
Watch out: Typically, if your dug well has less than a meter of water in it at the most dry season, it is unlikely to be adequate - How water is delivered from a dug well:
Depending on the well depth, flow rate, storage capacity, and usage requirements, any of a variety of devices or pumps might be used to draw water from a dug well, including- large-diameter dug wells that were entered on foot by water carriers,
- the traditional bucket on a winched rope or hand-drawn rope,
- hand pumps using a lever and piston mechanism to lift water from the well, for the properties of hand pumps and the use of hand pumps to deliver water from any well, drilled or hand-dug,
See HAND PUMP for WELLS - windmill-operated lift pumps
- solar-powered electric well pumps
- shallow well jet pumps operated by electricity
- deep well jet pumps or submersible pumps operated by electricity
- See WATER PUMP CAPACITIES TYPES RATES GPM
and also WATER PUMP LIFE EXPECTANCY for description of types of water pumps and their life expectancy

- The deepest hand dug well
we could find is the 1285 ft. deep Woodingdean Well begun in 1858 and completed in 1862 in Woodingdean, a suburb of Brighton and Howe, East Sussex, England.
More commonly hand dug water wells range from about fifteen feet (4.5 meters) in depth, to a practical depth of around 100 feet (30 meters) though 200 foot deep hand dug wells certainly exist. - The widest hand dug well -
well, we're not sure as sources conflict, but The Big Well in Greensburg Kansas is 109 feet in diameter (and 33 feet deep) may be the widest.
Watch out: digging a well by hand is quite dangerous, risking collapse on and death to the excavators. Also, in very deep wells, there may be air quality safety hazards. [2]
Digging & Using Hand Dug Drinking Water Wells

Dug wells are usually constructed during dry weather when the water level is at its lowest, both for safety (less likely wet soils cause well collapse) and to determine the necessary depth of the Dug well to obtain adequate water supply.
Details about how to dig and construct a hand dug well such as the Oaxaca hand dug well shown at left, begin
at HAND DUG WELL PROCEDURE.
[Click to enlarge any image]
You might see an antique hand water pump shown at left of this article, or even a rope and bucket for removing water from the well.
But don't assume this is the only way that water is being delivered from the well.
Often we find a hand dug well whose water is delivered to the building by
a ONE LINE JET PUMP.
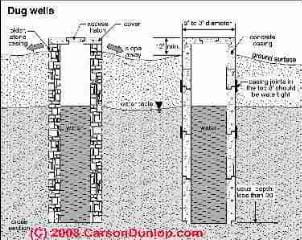
As we show in this sketch at below left, courtesy of Carson Dunlop Associates, Usually a hand dug well is less than 20 feet deep.
Dug wells have the same sanitation difficulties as springs and cisterns: they are easily contaminated by surface runoff and in some cases may have limited ability to deliver water at modern quantity and flow rates.
Hand dug wells range in depth from a few feet to as much as three meters and are used worldwide. Often the Dug-well was lined with dry-laid stone.
Dug or excavated wells are the picturesque wells we see on postcards, with an above-ground wall and a bucket lowered by rope into the well.
But dug wells continue into modern use, often with the installation of either an in-building jet pump draw water from the well into the building. We weren't sure what the little cover in our photo above was hiding - a dug well, a cistern, or a modern well casing extending above ground.
Sources for repair parts and installation instructions for hand pumps on dug wells and shallow wells are provided at our reviewers list at the end of this page.
Safety Procedures & Warnings for Hand Dug Wells

The hazards of hand dug wells include poor sanitation (ground water and surface runoff easily enter the drinking water supply), and cave-ins during construction or injuries to tools dropped into the well during construction.
We are particularly concerned about the safety hazards to children when a dug well does not have a child proof wall and/or cover.
At HAND DUG WELL PROCEDURE we describe all of the detailed steps in the procedure for constructing a hand-dug well with concrete well rings in Mexico.
But do not begin a well digging project without advice from an expert and do not try digging a well without following these and any other recommended safety measures for well excavation:
Hand Dug Well Construction Safety Advice
The following advice is adapted from The Hand Dug Well [instruction manual, by Henk Holtslag & John deWolf, Foundation Connect International. Links to a copy of that free manual are at our references section [2].
- Never work alone.
Watch out: The excavator in the bottom of the well should have a buddy at ground level above, on guard to assist if needed. While someone is working down the well there must always be someone in attendance at the top.
Never leave someone unattended at the bottom of the well.
Watch out: Aside from the risk of a worker being buried alive, killed, or trapped during the process of digging the well, in deep well excavations a lack of oxygen can cause a worker to faint and may require an emergency rescue. - Signaling between well excavator and people at ground level:
A system may need to be developed for signaling between people at the bottom and top of the well for lowering and raising equipment and people. Make sure everyone understands these signals and there is no miscommunication. - Check all ropes
and hand-dug-well digging equipment every day at the start of work - Rope knots:
When using a rope to lower or lift something from the well, knots should be made along the rope at metre intervals to stop the rope slipping through your hands; - Earth lifting buckets:
Ensure that the handle of the bucket is firmly fixed and cannot slip off; - Lowering worker into the dug well:
If possible, always use a windlass to lift and lower materials. Use a windlass with two handles and therefore two people if a digger is lowered or lifted.
If one of the people loses the control of his handle, the digger will not fall back in the well because the other still controls his side. - Protect edges of the top of the well opening during construction:
Put a plank across the edge of the opening to the shaft, so that people and buckets can be lowered over the edge without wearing away the ground at the side and causing it to cave in; - Steps in well shaft sides?
Cut steps into the side of the shaft to make it easier for people going up and down the well.
This is only possible if the soil is strong enough to hold the weight of a person. When you doubt: do not make them!
[When the well digging has been completed and it is being lined, a few well builders provide stepping stones (in a stone lined well) and handles, or steel rungs and handles to permit the well to be accessed by climbing if necessary. Usually people rely on a windlass and rope.] - Well digger head protection:
Always wear a helmet in case something falls down in the well; - Well digger foot protection:
Be careful while loosing the soil in the well with the long chisel. Don’t cute off your toes! If possible wear shoes with a metal nose protection. - Safety of air supply at the bottom of a hand dug well:
In narrow wells more than 15 metres deep, there may be a problem having fresh air at the bottom of the well.
Watch out: This is very dangerous and even poison gasses may appear. Air circulation can be helped by raising and lowering leafy branches in the shaft to ‘stir up’ the air.
The best way is to use a ventilator to get fresh air in the well. This ventilator can easily be made by a local workshop and exists of local available materials. - Handling soil & rocks dug out of the well:
Heap excavated soil more than one metre from the edge of the shaft so that as the pile grows, it will not fall back down the well; - Hand dug well site safety:
Put a fence or some sort of barrier around the digging site to stop people and animals falling in; when the well is completed it should have a child-proof surrounding fence and cover.
Additional Dug Well Safety Advice

- Provide an above-ground wall around the completed well
to prevent children and animals from falling into the well - a drowning hazard.
Photo above: this looks like a hand dug well that has an above-ground protecting wall and a cover over the actual well opening (you can just see the red edges of the cover.
Photos above: Safety grille installed over a dug well in Campeche, Mexico.
- Provide a safety screen over the above-ground wall or over well pits
to prevent children or anyone else from falling in to the well
If there is a concern for people tossing trash or contaminants into a dug well, a screen or grate may not be enough. The solid iron cover over the dug well shown below is installed at Campo St. Maurizio, Venice, Italy. The domed top sheds rainwater and keeps out tossed or other debris and contaminants.
Above: Domed iron well cover, Venice, Italy. Below: an unsafe dug well cover at a New York property.
Dug wells and hand pumps on old water wells are an attractive nuisance, especially to small children. The cover should be secure against entry by children.
Photos above: the thin cover over this dug well was easily kicked aside (after we removed the toddler who was found standing atop the well - Ed.)
- Watch out: Provide a child-safe heavy, secure cover at ground level
for dug wells with no above-ground wall or for any below-ground well pit - such as the well shown in our photos just above.
At a Connecticut home in the U.S. our clients, whose family included small children, was worried about lead paint hazards as their foremost concern. We arrived early and had already made a note of a rotting and unsafe cover over a hand-dug well.
The client arrived. Her seven-year-old son leapt from the family station wagon and made a beeline for the old hand pump atop the well.
As he began jumping up and down, pumping the lever, we ran to him and scooped him off of the well top just before the entire rotting cover fell into the Dug well.
Our view was that this was an immediate and severe safety hazard next to which the lead paint problem was less pressing.
Photo above: author's dog Katie is left on guard at an unsafe rotting-wood dug well cover in Dutchess County, New York.
- Direct surface runoff away from the well
and test the water frequently for potability and for other surface-borne water contaminants.
- Beware of hand dug well collapse hazards -
do not ever enter a hand dug well unless you are properly trained and do not work there alone. - Test hand dug well water regularly for potability -
since these wells commonly have sanitation issues.
See DUG WELL POTABILITY TEST
- Abandoning a hand-dug well -
requires that the well be protected from someone falling into the well; a smart abandonment will also protect the dug well from being used as a refuse or chemical dump - doing so risks contaminating the aquifer and is illegal in most jurisdictions.
Our photo (above-left) illustrates an abandoned hand-dug well in Guanajuato, Mexico. That well has been filled-in.
See details at WELL ABANDONMENT PROCEDURE
Resources & Research on Dug Well Construction & Safety Procedures
"Well safety" in the literature collapses two rather independent areas of concern
- Safety of the well water -
is the well water potable or safe to drink?
discussed at DUG WELL POTABILITY TEST
where we include additional resources on well water safety - Well construction safety -
Safety for workers during well construction as well as safety against someone falling into the well after its construction -
discussed above on this page
at SAFETY WARNINGS for WELL DIGGERS
- U.S. EPA, DUG WELLS [PDF], U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, retrieved 2021/05/31 original source: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-11/documents/dugwell.pdf -
Excerpt
Dug wells are holes in the ground dug by shovel or backhoe. Historically, a dug well was excavated below the groundwater table until incoming water exceeded the digger’s bailing rate. The well was then lined (cased) with stones, brick, tile, or other material to prevent collapse. It was covered with a cap of wood, stone, or concrete.
Since it is so difficult to dig beneath the ground water table, dug wells are not very deep. Typically, they are only 10 to 30 feet deep. Being so shallow, dug wells have the highest risk of becoming contaminated. To minimize the likelihood of contamination, your dug well should have certain features. These features help to prevent contaminants from traveling along the outside of the casing or through the casing and into the well.
Note that the word "Safety" does not appear in this one-page EPA document! - USDA, WELL DESIGN & SPRING DEVELOPMENT, Chapter 31, Part 631, [PDF] (2010) National Engineering Handbook, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation service, retrieved 2022/05/29, original source: https://directives.sc.egov.usda.gov/OpenNonWebContent.aspx?content=26985.wba
- WELL SAFETY WALL & COVER - More examples of safety covers and surrounding walls for dug wells
Dug Well Cleaning & Disinfection Resources
- AB, TROUBLESHOOTING WATER WELL PROBLEMS [PDF] Alberta Department of Agriculture, retrieved 2022/07/16 original source: https://www1.agric.gov.ab.ca/$department/ deptdocs.nsf/ba3468a2a8681f69872569d60073fde1/ b235a3f65b62081b87256a5a005f5446/ $FILE/WaterWells_module7.pdf
Excerpt:
There are several basic causes of well problems.
- Improper well design and construction
- Incomplete well development
- Borehole stability problems
- Incrustation build-up
- Biofouling
- Corrosion
- Aquifer problems
- Over-pumping.
The first two causes relate to the expertise and performance of the licensed water well contractor. Borehole stability problems, incrustation, corrosion and aquifer problems are related to characteristics of the aquifer. The last cause, overpumping, is caused by well users. - BC, DUG WELL BEST PRACTICES [PDF] BC, Department of Agriculture, retrieved 2022/07/16 original source: https://www2.gov.bc.ca/ assets/gov/environment/air-land-water/ water/water-wells/best_practices_for_dug_wells.pdf
- New Foundland, GUIDELINES for DISINFECTING DUG & DRILLED WELLS [PDF] NewFoundland, Environment and Climate Change P.O. Box 8700 St. John’s, NL A1B 4J6 Canada, Email: ECCInfo@gov.nl.ca Labrador, Canada, - retrieved 2022/07/16, original source: https://www.gov.nl.ca/ecc/waterres/cycle/groundwater/well/disinfecting/
- OR, WATER WELL OWNERS HANDBOOK [PDF] A Guide to Water Wells in Oregon, Oregon Public Health Division, Oregon Water
Resources Department,
725 Summer St. NE, Suite A,
Salem, OR 97301 USA, retrieved 2022/07/16, original source: https://www.oregon.gov/owrd/WRDPublications1/Well_Water_Handbook.pdf
Excerpt: Vigorously pumping or purging the well to clean out drill cuttings and maximize water production. Development is used to reduce or eliminate clay, silt or sand in the production water. - OXFAM, REPAIRING, CLEANING & DISINFECTING HAND DUG WELLS [PDF] OXFAM-TB6, - retrieved 2022/07/16, original source: https://sswm.info & https://give.oxfamamerica.org/
Excerpt: Oxfam is a global organization that fights inequality to end poverty and injustice - Hurstader, Chris, SIX WAYS to FIX UP A WELL & GET CLEAN WATER [PDF] (2018) OXFAM, - retrieved 2022/07/16 original source: https://firstperson.oxfamamerica.org/six-ways-to-fix-up-a-well-and-get-clean-water/
Excerpt:
Oxfam helps communities around the world fix up their wells and learn how to treat their drinking water to avoid water-borne diseases. It’s particularly important during times when people are short on food, due to bad harvests following drought, floods, or any sort of humanitarian emergency.
This was the case in Senegal in 2011 and 2012, when Oxfam’s program helped farmers recover from a drought and bad harvest in 2011. Oxfam delivered some cash to help farmers buy food, but we also helped them to address water and sanitation and hygiene, all closely linked to malnutrition — because if you have a stomach ailment from drinking bad water, you won’t benefit from the nutrition derived from what food you can find. - SCW, DUG WELL RESTORATION [PDF] South Coast Water, Hapshire, U.K., Email contact form at https://www.southcoastwater.co.uk/contact.html - retrieved 2022/07/16, original source: southcoastwater.co.uk/well-restoration.html
Excerpt:
We can clean a well even if it is completely filled in with rubble so do not think it will never be a usable well again. All it takes is for us to remove all the rubble and debris, clean and restore the walls and the well will be good to naturally refill with water ready for use again. Please visit our well cleaning page for more information. - Swistock, Bryan & Dana Rizzo, M.S., WATER WELL MAINTENANCE & RESTORATION [PDF] PennState Extension,The Pennsylvania State University 323 Agricultural Administration Building University Park, PA 16802 USA, retrieved 2022/07/16 original source: https://extension.psu.edu/water-well-maintenance-and-rehabilitation
Note: this article pertains more-specifically to drilled water wells rather than dug wells. - UT STATE of UTAH WATER WELL HANDBOOK [PDF] (2018) Utah DNR, Department of Natural Resources
Division of Water Rights
PO Box 146300
Salt Lake City UT 84114-6300 - retrieved 2022/07/16, original source: https://www.waterrights.utah.gov/wellinfo/handbook.pdf
Excerpt:
The Utah Division of Drinking Water (UDDW) Administrative Rules apply to wells drilled for public drinking water supply. If you plan to drill public supply wells, you will need to adhere to the State Engineer's well drilling rules and the UDDW’s well drilling rules. - WELL CLEANING PROCEDURES [web page] - for drilled wells, some of these methods will work well for dug wells too.
- WHO, WEDC, CLEANING & REHABILITATING HAND DUG WELLS [PDF] (2013) Loughborough University, UK, for WHO, World Health Organization
Water, Sanitation, Hygiene and Health
Unit, Avenue Appia 20, 1211, Geneva 27,
Switzerland
Phone: + 41 22 791 2111
Phone (direct): + 41 22 791 3555/3590
www.who.int/water_sanitation_health - retrieved 2022/07/16, original source: https://wedc-knowledge.lboro.ac.uk/resources/e/mn/ 031-Cleaning-and-rehabilitating-hand-dug-wells.pdf
Excerpt:
Water taken from hand-dug wells is often of poor quality, mainly due to the poor construction of the above-ground elements and unhygienic methods of collecting water.
The steps described here will not overcome these problems as they are designed to return the well to its original condition. Sources of further information on improving and upgrading wells are given ...
Sanitation Advice for Hand Dug Wells
This topic moved to DUG WELL SANITATION PROTECTION
...
Reader Comments, Questions & Answers About The Article Above
Below you will find questions and answers previously posted on this page at its page bottom reader comment box.
Reader Q&A - also see RECOMMENDED ARTICLES & FAQs
On 2022-10-18 by InspectApedia (Editor) - does climate change cause geothermal system design's water temperature to drop
@Ted Allen,
Thank you for an interesting geothermal system design question. I don't know a solid answer but I suspect you may need to install a small circulating pump to mix the water if you're diagnosis is correct.
On 2022-10-18 by Ted Allen
I have a dug well consisting of a 150 gal cistern with (3) 48" well tiles stacked on top of the cistern. It has a deep well pump at the bottom of the cistern. This well is for my pump and dump geothermal system. This being my ejection well and my injection well ~ 100 ft away is 12ft deep.
The system has been on line since 1996 and up until the past few years no problems, but with the decreasing snowfall rates in the NE I've been noticing the entering water temp dropping below 40 degrees and when this happens the system shuts down. It seems like the snow had insulated the well previously and prevented the cooling effect of the cold air and frost.
So the well is ~48" diameter down 12 ft then the hole in the cisteris 26" and then the cistern is a 7 ft octagon 6'-8" deep.
My theory is the water at the top which can be within a foot of the well cover is cooled by the frost and since it wants to sink because of it's density there is a constant circulation of cold water dropping down to the pump where it gets picked up and fed into the geothermal system. I'm looking at putting a cover on the top of the cistern to break the circuit. Does this sound feasible.
On 2022-10-07 by InspectApedia-911 (mod) - can a 24ft hand dug well to reabsorb 1500gal. over an 8hr period?
@Reg Rogan,
If your dug well is normally filled with water it would be a surprise but certainly possible for the soil conditions or surrounding geology to change such that the well stops giving water and instead drains it away.
We also seen this happen when someone drills or digs another Well nearby tapping into the same aquifer.
But I would be surprised if a well were cycling between providing water and taking it back.
Is it possible that the geometry of the well-piping could have caused water to siphon out of the well?
On 2022-10-07 by Reg Rogan
is it possible for a 24ft hand dug well to reabsorb 1500gal. over an 8hr period ? the pump is shut off,nothing being taken out of the well.
On 2022-09-10 by InspectApedia-911 (mod) - safest way to retrieve the lumber from the well
@Jim Frank,
We list a number of well retrieval tools and approaches at
WELL PIPE RETRIEVAL TOOLS
and some of those may be able to grab lumber - as can a grappling hook and a decent line.
Watch out: don't work alone, don't fall into the well.
Watch out: be sure that your wells have safe covers and that a child (or older person) can NOT fall into the well.
On 2022-09-10 by Jim Frank
Our place has two hand dug wells on it. At this time one is dry. The other is not, but it has quite a bit of fallen-in lumber from an old cover that collapsed. What is the safest way to retrieve the lumber from the well? Would a grapple hook work or is there something better?
We are not looking to go down into the well, it is quite deep. We measured 50 ft before hitting water, and another 20 ft of water.
On 2022-09-07 by InspectApedia-911 (mod) - no well point in hand dug well
@Paul,
Your friend has, perhaps, misunderstood what kind of well you have.
A hand dug well is just that: a large-diameter hole in the ground, dug by hand. There is no "well point" - a well point is used in a driven point well like those shown and discussed at
DRIVEN POINT WELLS
On 2022-09-07 by Paul
I have a hand dug well and every year it runs dry between August and October, comes back between November and January. My property is at 800ft elevation. A friend of mine keeps telling me to dig out the well point... how do I do that and what will it do?
On 2022-07-15 by (mod) - how to clean or remove silt & debris from a hand-dug well
Sure Oceans,
In my opinion, using hand bailers to clean out a silt-laden dug well is not the best approach to removing sediment and silt.
Above on this page we list several excellent guides for cleaning hand-dug wells.
Read through some of the dug well cleaning and restoration articles there to see the range of tricks and tips people use for a faster, more-efficient, and safer way to remove crud from the well bottom.
See HAND DUG WELL CLEANING & RESTORATION PROCEDURES
Separately
more-sophisticated well cleaning methods are described in procedures for drilled wells where there is less working room. There you'll see some interesting well cleaning methods using special siphon pump arrangements that pump water down through a suction device that picks up the silt and returns the glop to the ground level through a second pipe.
But
Watch out: When you've got tree root invasion of the dug well sides, as we see in your photo, there are increased risks of both water contamination - surface runoff following tree roots into the well, and of well collapse.
You might want to find a well company or plumber who has a well inspection camera that may let you take a closer look at the full depth of the well.
See WELL BORE CAMERA SYSTEMS
On 2022-07-15 by Oceansnotion - Need to carefully remove 3 feet of silt from 35 feet down
Need to carefully remove 3 feet of silt from 35 feet down, water level is at 21 feet, I got a rough estimate of 65 feet from linking conduit together, air lift wouldn't seem to work in these ranges. !00 year old well estimate of 65 feet 4 foot diameter, house and old pump house right beside.
Can't tell if there has been collapse of wall below the root levels of two huge sycamore trees. Ground has subsided and both structures leaning into each other for mutual support. West coast drought has dropped it about 20 feet.
6 people on the property, I have replaced the configuration as seen to shallow well pump but need to return to deep well configuration, any ideas for removing silt and sediment?
Do you have any idea for hand bailers for such a need or a better procedure. I was thinking of a two stage arrangement of two sump pumps. One in the well the end of it's hose in a bucket with another sump pump to pump it out the rest of the way.
On 2022-02-19 by Inspectapedia Com Moderator - does water infiltrate in the seams of the casings
@Joseph,
If the concrete well rings or sections are solid, only a small volume of water enters at the sides at the seams - most water will enter at the well bottom.
On 2022-02-19 by Joseph
In a concrete lined dug well, does water infiltrate in the seams of the casings , though the bottom of the well, or both?
On 2022-01-14 by Inspectapedia Com Moderator - Ugandan nonprofit African Educate hand dug well maintenance
@Linda Griesbach,
Someone may have been speaking carelessly but in my lexicon, "bore hole" is the hole created when we DRILL a well. Maybe 6" in diameter.
When we DIG a well, the hole diameter will be much larger as one or more human beings get down into the hole to excavate to make the well.
So if your contractor really said bore-hole, I'm not sure of her level of expertise or care.
But depending on how your hand dug well was constructed, yes, its sides might need maintenance or repair.
If the well sides are lined with stone, that needs to be intact and in place and sound to avoid risk of a well collapse.
And surface runoff from rain ought not be running right into the well.
Perhaps you could post a photo of your well (one image per comment)
and
another of its interior walls.
A dug well might also need periodic cleaning, for example, if soil or silt is accumulating on the dug well bottom, reducing its water volume.
Finally, as the local water table drops - as may well occur in some locations due to global warming, it may be necessary to deepen the well from time to time.
But all that said, it's disappointing if a new dug well needs any significant repair after just two years.
Let's get the details.
On 2022-01-13 by Linda Griesbach
Our nonprofit African Educate has had a hand dug well constructed in rural Uganda for 2 years. The contractor now says the bore hole needs maintenance. Does this seem reasonable?
On 2021-07-03 by inspectapedia.com.moderator - lining a hand-dug well with rock masonry
@Steve,
First take a look at WELL RINGS: WHEN TO USE or OMIT
as that's a faster, easier, safer way to line a dug well.
When a dug well is lined by hand-built masonry, the opening is dug large enough that the finish-opening diameter, when the masonry liner is installed, is the desired dug-well size.
Depending on where the water table is found the mason will use a combination of mortar, stone on a footing, and some dry-laid stone joints to permit water entry through the well sides.
Other than safety precautions appropriate for working in the bottom of a hole (collapse, air, safe entry/exit, not working alone, helpers to lower materials, etc) it's standard stonemasonry.
A thorough answer of your question, much more than I should try re-typing here, is found by reading through the articles in this series, in the sequence given at the
Recommended Articles
found near the end of the article above on this page;
Start with HAND DUG WELL PROCEDURE
If there's a specific question you have in mind and for which you don't see a clear answer, just ask.
On 2021-07-03 by Steve
What is the procedure for lining a hand-dug well with rock masonry?
On 2020-12-29 - by (mod) - I need to dig a well
A good place to start is
On 2020-12-29 by Lisa Ann Conley
My back yard stays saturated year round. I need a system of acquiring the water for use in my home for water only for bathroom, dishes and othe non drinking uses. I need to dig a well and set up system for use. Thank you
On 2020-12-03 - by (mod) -
Shirley
You'll want to find a local well company or possibly an excavation contractor who assures you that they are experienced with dug well repair.
Keep in mind that it is just about impossible to assure that water from a dug well is sanitary - free from surface runoff and bacteria - so at the very least you'd want your well water tested, annually or more-often, at the very least for bacteria.
On 2020-12-03 by Shirley
I have a dug well that was dug in 1980 when we purchased the property. Has been great water and very plentiful. Have not ever had a dry well. Started getting some sand in the water lines and 14 months ago cleaned out the well and added pea gravel. The well is 25ft deep.
While cleaning out the well noted some of the tiles are chipping and some sand getting in. Now water line is dirt and sand. Is there someone who can dig out the silt and replace tiles? What/who would I look for? Husband passed 13 yrs ago and unfortunately for me took his wealth of knowledge. Appreciate any info
On 2020-09-09 - by (mod) -
Billy
Thanks for asking a helpful question.
It is not safe nor durable to use greenboard nor any plasterboard or drywall as the protective surround for a dug well. That material will not endure outdoor exposure to the weather and it also lacks adequate strength to assure a safe barrier.
On 2020-09-05 by Billy
Is it safe to use green board around a dug well?
On 2020-09-09 - by (mod) -
Billy
Thanks for asking a helpful question.
It is not safe nor durable to use greenboard nor any plasterboard or drywall as the protective surround for a dug well. That material will not endure outdoor exposure to the weather and it also lacks adequate strength to assure a safe barrier.
On 2020-09-05 by Billy
Is it safe to use green board around a dug well?
On 2020-06-16 - by (mod) -
Elva
A lot depends on whether the damage is entirely above ground or whether the sides of the dug well below ground are damaged and to caving in. Obviously above ground is easier to repair on site. Perhaps you can post photos, one per comment, so that we can see the situation there.
On 2020-06-15 by Elva Pruden
The well has been from beginning of time I have lived here since 1979. The top of well is falling apart I want to fix it
I have a rock laid well too is concrete and falling apart how do I fix it or build a new on
On 2020-06-07 - by (mod) -
FM
That's an interesting and troubling problem that, if I've got this right, could be described as intermittent loss of water in a dug well.
I don't know for sure what's happening but I suspect that something is temporarily draining the aquifer that is supplying your shallow well. The effect could be weather related, not just dry or wet spells that affect the groundwater level but even more-subtle changes such as in barometric pressure.
At an old well that served for years but now lacks water, we might ask what has changed. Global warming, changes in weather, may lower an aquifer such that the supply to your well is now 'on edge' and is more-obviously impacted by barometric pressure or other variables.
Or if another well, shallow or deep, was built nearby and taps the same aquifer, that could be the cause.
On 2020-06-07 by fmaclean@bellaliant.net
We have a 15 ft dug well. We went to bed and the water in the well was almost overflowing. We woke up the next morning and the cut off valve had kicked in because the water level was so low. It rained all night. There was no water being used. The pump never turned on. We had a plumber come in and he said there are no leaks in your lines.
Your pump is working fine. The well still didn't seem to want to recover. We turned off the breaker and the well recovered to full in two hours. We turned the breaker back on and turned the pump on and for the next two months no water issues.
Well always full to overflowing. Last night went to bed lots of water in well, no water used, this morning we have no water. Pump turned off because water level drained to cut off valve. What is going on? Why is our water disappearing? It is not coming in to the house.
On 2020-05-22 - by (mod) -
Vicki
It may be possible to make minor repairs to the surround for your well, but take great care not to enter, nor fall into the well, as obviously that would be fatal.
You should not work alone.
You should also make some diagnosis of why the existing masonry wall is failing, so that that underlying problem is corrected. Otherwise you're wasting your effort.
If you post some photos, one per comment, I may be able to offer more specific suggestions. Without knowing the present construction and materials it does not seem useful for me to propose specific repair items or methods. For example, I don't know if your well surround is made of stone or concrete or concrete block or something else.
On 2020-05-21 by Vicki M
MY dug well that has an above-ground protecting wall and a cover over the actual well opening is in my bard yard across a stream no equipment can get to it, the wall is splitting and cracking and falling on the ground can I repair this and how
On 2019-12-16 - by (mod) - Can a dug well freeze solid?
Rachel:
Can a dug well freeze solid? Sure.
Water in a hand dug well or even a bored well can freeze, depending on the climate, air temperature, and distance from the surface of the water to the ground surface. It's not common but can happen, especially in very cold weather and where the well water level is close to the ground surface/.
A water well whose water rises to above the winter frost-depth is more-likely to freeze if the well is not protected from frost. That's why people may build an insulated structure around and over the well.
To be accurate you will want to know the frost depth in the location where your fictional (or historical-fictional) well is located. That's the typical depth at which soil can freeze in winter weather. (Snow cover, leaf cover, etc. can reduce the chances of soil freezing but that's probably not relevant to your plot).
So if you want your dug well to freeze-over you need
1. characters in the story who don't know much about wells and freezing problems
2. a dug well that was not protected from cold weather by a structure built over and enclosing the well
3. the level of water in your dug is above the frost-depth for that location
Then in cold weather that dug well water may freeze. The ice on the dug well water will be of course at the surface; it might be just a skim coat that your character can break through by dropping a heavy bucket down into the well (on a rope of course) to fetch water.
But in prolonged very cold weather the surface water in the dug well could freeze to inches or even more. and in unusual cases might be so thick that people would have to look elsewhere for their water.
In New England the frost depth may be 3-4 feet while in northern Minnesota it might be 6-7 feet below the ground surface.
So if the top of your well water is just 2 feet below the ground surface in New England, or just four feet below ground surface in Two Harbors Minnesota, in very cold winter weather the well top may freeze solid.
I think the reason the well doesn't freeze more-often is that in most situations the resting level of water in wells is well below the frost line.
That's my answer, and I'm sticking to it ... until well freezes over.
But it's not just me. Here is what the U.S. Department of Agriculture says in one of their water well articles:
... protect all wells from freezing, mowing, livestock, etc., by enclosing the well within an insulated well house. ... https://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov/references/public/AL/642_Water_Well.pdf
On 2019-12-15 by Rachel
Hi! I am writing a novel and an old-fashioned well plays a bit of a part. Is it possible for well water to freeze over?
On 2019-11-25 - by (mod) -
Forgive me Sharon but it's not both a spring and a well; If the water source is a spring, perhaps feeding water into a springhouse from which water is pumped to cisterns serving each home, it is, in almost all locations in the world, impossible to guarantee that that water remains potable - free from bacteria or other contaminants, as it's exposed to surface waters and runoff;
So first you will want a regular water testing program and second you may need water quality treatment and disinfecting equipment.
Having to blow out algae clogs is, on the face of it, confirmation that you want to be concerned about water quality.
Re-lining a well ? I think we need to get a confident definition of what kind of water source this really is.
On 2019-11-24 by Sharon
We just purchased a home built in 1800 in New Hampshire. The water comes from a spring-fed well across the street. There are pipes from that well to both our house and to another house up the road. In other words, the one well across the street feeds all three houses.
Right next to the road by our house is a "well" or cistern that is filled by the well across the street. Apparently this system has worked in the past.
The neighbor said he has had to blow out the pipe leading to his house because algae was growing in it. Just now our cistern is empty, and no water is flowing into it at all.
The neighbor suggests we reline the well and then try to blow out the pipes to unplug them. I'm wondering if this will provide us with safe drinking water. And if so, what is the best way to reline the cistern. Thanks.
On 2019-03-11 - by (mod) -
Brian
Please see the information at HAND DUG WELL PROCEDURE
And let me know if you have any questions
On 2019-03-11 by Brian
have a 30 year old shallow well (15') with a 5' galvanized steel cribbing. Water depth in well is from 8" of water down to 3' of water. We came thru a very dry fall and the water table dropped about 3'. recharge of the well is about 2 gal per hour.
The well I believe could be another 5-6' deeper. this would put us well into the water table and would provide better capacity during dry periods where the water table has dropped. I believe it was only made 15' deep as that was as far as the back hoe could reach when they dug the well.
Q. What will be the best way to make the well deeper.
1) put in a sandpoint
2) dig the well deeper. If so do I need to extend the cribbing to the "new" well bottom. and if so what would / could I use?
thanks
On 2019-03-09 - by (mod) -
It may be possible to return a dug well to service but I can't estimate the cost because I have no idea of the conditions. You need a secure well-structure, a safe well cover, and of course you need water in your well.
On 2019-03-09 by mike schoonover
I have an abandoned dug water well that was dug many years ago. I wish to get it operative with possibly a hand pump. Can it be done and at what cost?
On 2015-07-25 by Mod - Ground Penetrating Radar used to determine depth to water below ground surface
David:
Local well drillers and hydrogeologists often know the common water table depth, though that can vary considerably from one property to another.
And though it can be a costly survey, ground penetrating radar has been used for determining the depth to water, as you can read in Johnson 1992. That survey combined use of ground penetrating radar and also measurement of water levels at local ponds in the area of study. That data permitted a map of the water table. But be sure to take a look at the abstract that we quote below.
- Beres Jr, Milan, and F. P. Haeni. "Application of ground‐penetrating‐radar Methods in Hydrogeologie Studies." Groundwater 29, no. 3 (1991): 375-386.
- Daniels, David J., ed. Ground Penetrating Radar. Vol. 1. Iet, 2004.
- Doolittle, J. A., B. Jenkinson, D. Hopkins, M. Ulmer, and W. Tuttle. "Hydropedological investigations with ground-penetrating radar (GPR): Estimating water-table depths and local ground-water flow pattern in areas of coarse-textured soils." Geoderma 131, no. 3-4 (2006): 317-329.
- Hengari, Gideon M., Carlton R. Hall, Tim J. Kozusko, and Charles R. Bostater. "Use of ground penetrating radar for determination of water table depth and subsurface soil characteristics at Kennedy Space Center." In Earth Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing/GIS Applications IV, vol. 8893, p. 889318. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2013.
- Johnson, David G., USE OF GROUND-PENETRATING RADAR FOR WATER-TABLE MAPPING, BREWSTER AND HARWICH, MASSACHUSETTS [PDF] (1992), USGS, U.S. Geological Survey, Water-Resources Investigation Report 90-4086, Prepared In Cooperation With The
Massachusetts Department Of Environmental Protection,
Division Of Water Pollution Control,
And The Towns Of Brewster And Harwich, Massachusetts, original source: https://pubs.usgs.gov/wri/1990/4086/report.pdf
Abstract: More than 125 miles of continuous ground-penetrating radar profiles of the sand and gravel aquifer on Cape Cod, Massachusetts, were made in the towns of Brewster and Harwich. Penetration of the radar signal ranged from less than 3 feet in areas containing clay near the surface, to more than 95 feet in clay-free sand and gravel.
About 60 percent of the radar profiles showed water-table images that were easily identified on the graphic record.
Depths to water were calculated from the radar records using an average signal velocity of 0.45 feet per nanosecond in the unsaturated zone.
Comparison of depths to water derived using ground-penetrating radar with the altitude of water levels measured in wells and ponds at 85 sites showed an average difference of about 7 percent (1.8 feet) with standard deviation of 6.4 percent (1.8 feet). Additionally, good agreement was achieved between water-table altitudes calculated using ground-penetrating radar and seismic-refraction methods with altitudes determined at selected observation wells.
Ground-penetrating radar was used in conjunction with water levels measured at ponds and wells to construct a water-table map with 2-foot contours in the 45-square mile area of Brewster and Harwich.
The radar proved unsuccessful in determining zones of contribution to pumping wells, but provided sufficient water-table information to delineate a ground-water mound at a septage disposal bed and steep water-table
gradients toward a stream near the Harwich landfill.
On 2015-07-25 by Solomon david
I want to know if there is any eqiument or (material) that can be use for testing dug well to know how deep or how many (feet) befor you get water.
...
Continue reading at HAND DUG WELL PROCEDURE - how to construct a hand dug well or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see HAND DUG WELL FAQs - questions & answers posted originally at this page.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- EPA GUIDE to WATER QUALITY for a discussion of dug well water sanitation and potability
- HAND DUG WELLS - home
- HAND DUG WELL PROCEDURE - home
- HAND DUG WELL WATER in PHUKET
- HAND PUMP for WELLS
- OLD WELL - RETURN TO SERVICE
- WATER PUMP LIFE EXPECTANCY
- WATER TESTS for CONTAMINANTS - home
- WELL ABANDONMENT PROCEDURE
- WELL CAPS & COVERS safety and sealing requirements
- WELL CHLORINATION & DISINFECTION - home
- WELLS CISTERNS & SPRINGS - home
- WELL CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION SOURCES
Suggested citation for this web page
HAND DUG WELLS at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to WATER SUPPLY, PUMPS TANKS WELLS & SPRINGS
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- Mark Cramer Inspection Services Mark Cramer, Tampa Florida, Mr. Cramer is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors and is a Florida home inspector and home inspection educator. Mr. Cramer serves on the ASHI Home Inspection Standards. Contact Mark Cramer at: 727-595-4211 mark@BestTampaInspector.com
- John Cranor [Website: /www.house-whisperer.com ] is an ASHI member and a home inspector (The House Whisperer) is located in Glen Allen, VA 23060. He is also a contributor to InspectApedia.com in several technical areas such as plumbing and appliances (dryer vents). Contact Mr. Cranor at 804-873-8534 or by Email: johncranor@verizon.net
- "Comparison of large and small diameter wells", Natural Resources Management & Environment Department, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, FAO Corporate Document Repository - Self-Help Wells - see http://www.fao.org/docrep/X5567E/x5567e04.htm
- Access Water Energy, PO Box 2061, Moorabbin, VIC 3189, Australia, Tel: 1300 797 758, email: sales@accesswater.com.au Moorabbin Office: Kingston Trade Centre, 100 Cochranes Rd, Moorabbin, VIC 3189
Australian supplier of: Greywater systems, Solar power to grid packages, Edwards solar systems, Vulcan compact solar systems, water & solar system pumps & controls, and a wide rage of above ground & under ground water storage tanks: concrete, steel, plastic, modular, and bladder storage tanks. wners - Typical Shallow Well One Line Jet Pump Installation, Grove Electric, G&G Electric & Plumbing, 1900 NE 78th St., Suite 101, Vancouver WA 98665 www.grovelectric.com - web search -7/15/2010 original source: http://www.groverelectric.com/howto/38_Typical%20Jet%20Pump%20Installation.pdf, [Copy on file as /water/Jet_Pump_Grove_Elect_Jet_Pumps.pdf ] -
- Our recommended books about building & mechanical systems design, inspection, problem diagnosis, and repair, and about indoor environment and IAQ testing, diagnosis, and cleanup are at the InspectAPedia Bookstore. Also see our Book Reviews - InspectAPedia.
- Crystal Clear Supply provides portable ceramic water filter purifiers and portable reverse osmosis water treatment equipment - see http://www.crystalclearsupply.com/category_s/7.htm
- Handbook of Disinfectants and Antiseptics, Joseph M. Ascenzi (Editor), CRC, 1995, ISBN-10: 0824795245 ISBN-13: 978-0824795245 "The evaluation of chemical germicides predates the golden age of microbiology..." -
This well-focused, up-to-date reference details the current medical uses of antiseptics and disinfectants -- particularly in the control of hospital-acquired infections -- presenting methods for evaluating products to obtain regulatory approval and examining chemical, physical, and microbiological properties as well as the toxicology of the most widely used commercial chemicals. - When Technology Fails, Matthew Stein, Chelsea Green Publisher, 2008,493 pages. ISBN-10: 1933392452 ISBN-13: 978-1933392455, "... how to find and sterilize water in the face of utility failure, as well as practical information for dealing with water-quality issues even when the public tap water is still flowing". Mr. Stein's website is www.whentechfails.com/
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.










