 Well Life
Well Life
Life Expectancy of Water Wells
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about the typical life of water wells - how long will the well last?
Life expectancy of a water well: how long can a water well of different types (dug, driven, drilled) be expected to deliver a usable quantity of water?
This article describes factors affecting the Life Expectancy of Drinking Water Wells & Water Tanks.
When will the well run out of water? Can we increase the well yield or water quantity without having to drill a new well? How long should a well last? What factors affect the life expectancy and continuous water yield of different types of wells?
What are the different life expectancies and water yields of different types of wells: driven point, hand dug, drilled, artesian walls, etc.? What is the expected life of well parts: well casing, foot valve, different types of water piping materials?
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
What is the Typical Life Expectancy of Water Wells
 Watch out: Before assuming that a water problem is due to the
water pump or the water well itself,
see WATER PUMP REPAIR GUIDE a specific case which offers an example of diagnosis of loss of water pressure, loss of water, and analyzes the actual repair cost.
Watch out: Before assuming that a water problem is due to the
water pump or the water well itself,
see WATER PUMP REPAIR GUIDE a specific case which offers an example of diagnosis of loss of water pressure, loss of water, and analyzes the actual repair cost.
If you know that your well is performing poorly with a poor flow rate or poor well recovery rate,
see WELL YIELD IMPROVEMENT, and
to protect the well pump from damage due to low well water or other hazards
see WATER PUMP PROTECTION SWITCH
or
see WELL PIPING TAIL PIECE .
[Click to enlarge any image]
How Long Should a Water Well Last?
The life expectancy of drinking water or irrigation wells is quite variable and depends on a number of factors which we describe here. We welcome suggestions or reports of personal experience with the life of wells, pumps, and water tanks.
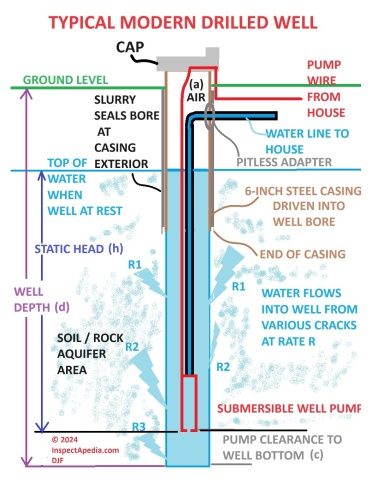
Sketch courtesy of Carson Dunlop Associates, a Toronto home inspection, education & report writing tool company [ carsondunlop.com ].
Here are some factors that affect the life of a well - by which we mean the continued ability of a well to yield water to its users.
First let's make clear that we're talking about the well itself, the hole in the ground and its ability to give an adequate quantity and flow rate of drinking water, not the equipment used to get water out of the ground, such as the water piping, water pump, pump controls, water tank or valves.
The issue of water potability - can it be used for drinking - is separate from the ability of the well to deliver water at all, but beware: a well with a good flow rate and good potability can change in both of those factors.
See WATER TESTING for a discussion of contaminants that occur in drinking water, how to test for them and how to remove them.
- General Geographic Location of the Well: In what part of the country was the well drilled and what are local ground water conditions. At the rim of the Grand Canyon in Arizona a successful water well may need to be drilled to 900' to obtain a successful water delivery rate.
- Local geography and groundwater conditions - exactly where was the well drilled and what are local water table conditions.
For example, a 45' deep well drilled near Lake Superior in Minnesota and tapping a low mineral content aquifer may last for generations while a similarly deep well on a hilltop in the Hudson Valley of New York state, drilled in a new development where many wells are suddenly tapping an existing aquifer may suddenly fail after only one year (see more on this cause below). - Seasonal Fluctuations in Local Water Table in some areas, such as a drop in the level of groundwater during the dry season or during droughts,
can result in a reduced well recovery rate or complete loss of well water.
Open the well casing to locate and record distance from ground level to the top of the water.
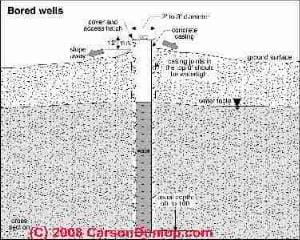
Compare this level at different seasons (after the well has been at rest and had a chance to recover). - Type of well: dug well, driven point well, or modern 6" steel casing-lined drilled well.
- Hand Dug Wells: some dug wells dug in the 1800's still deliver water but no longer can deliver water of acceptable potability as surface runoff
contaminates these.
Hand dug wells are discussed in more detail
at HAND DUG WELLS . - A modern drilled well may deliver water for generations if it taps a good aquifer with low mineral content;
The same modern drilled well, deep or shallow, may fail suddenly when someone nearby drills a new well that taps and draws down
the same local aquifer; or nearby road blasting can cause new rock fissures to open up sending silt or other contaminants into a
previously well functioning well.
Modern drilled wells, of various types, are discussed in detail
at DRILLED WELLS STEEL CASING . - Driven point wells often have rapid reduction in water flow rate, depending on the type of soil into which the driven point was inserted.
Even in areas of sandy soils where these shallow wells are frequently used, water quality is questionable as surface contaminants easily enter the water supply, and water quantity is unreliable in areas where the water passage holes in the driven point become easily clogged with debris.
Driven point wells are illustrated and discussed further
at DRIVEN POINT WELLS . - Springs as a water supply can last for generations but as with hand dug and driven point wells, are increasingly exposed to
pollution from surface runoff and high level ground water.
In Mexico's San Miguel de Allende, the mountain spring which caused the village to be sited in its present location in the 1500's still produces water sufficient to operate fountains and a public laundry in the year 2007.
See WATER QUALITY & QUANTITY San Miguel de Allende Mexico
However most of the city's water is produced today by nine modern drilled wells and water for agriculture is provided from a reservoir, la Presa.
Springs as a water supply are discussed in detail
at SPRINGS as WATER SUPPLY . - Seasonal fluctuations in ground water level and long term changes in the aquifer
- Mineral level and type of minerals in water supply, or amount of sediment in the water supply are important features in the life expectancy of a water well.
In areas of hard water, minerals in the water tend to clog the rock fissures through which water flows into the well - harder water
clogs the fissures faster, reducing well output.
Note that a process called "hydrofracking" (or similar terms) uses frozen CO2 or other measures to "re-open" clogged rock fissures to increase well yield.
The nice thing about these processes is that their practitioners usually offer that if they cannot increase the well yield there is no charge. (In the 1930's and earlier, people used dynamite to re-open clogged low-yield wells - a more dangerous process as well as one which risked collapsing the entire well.)
Details of the diagnosis and cure of clogged water supply piping can be found
at WATER PIPE CLOG DIAGNOSIS .
In sum, there is no simple short reliable answer to how long a water well will continue to give good quality and acceptable quantity of water, but our experience is that driven point wells have minimum flow and shortest life in many areas as the well point clogs, and driven point or drilled wells into bedrock in areas of very high mineral content water may begin to show clogging and reduced water flow in as little as a decade.
Ask about local water conditions: Ask your neighbors, local water testing laboratories, local well drillers, and plumbers what they've experienced with well drilling success in your immediate neighborhood.
At what depths is an adequate water flow rate usually found? What contaminants have been found in wells in the area for which you should
be particularly alert?
How are local wells affected by seasonal or longer term changes in the water table?
Other well piping components that are not part of the well pump itself, but that affect pump life, such as
- WELL PIPING CHECK VALVES ,
- WELL PIPING FOOT VALVES
- WATER PUMP PROTECTION SWITCH , or a
- WELL PIPING TAIL PIECE may also need to be installed, repaired, or replaced if the well is a low-flow or poor performing one.
Life expectancy of Well Casings, Well Piping, Foot Valves, Water Pump Wiring, Well Plumbing Connections
- Well casings: modern drilled wells for residential use typically include a 6" diameter steel casing which is inserted into the drilled well
and down into bedrock. The casing is sealed around its exterior to keep (often unsanitary) surface runoff or surface contaminants out of the
well interior.
Mechanical damage can cause a crack in the well casing; this happened to a well at our laboratory when nearby roadwork included rock blasting. It might be possible to repair a cracked well casing but often the crack leads to contaminated water and the need to drill a new well. - Air leaks: Well piping or equipment can develop an air or water leak and stop delivering water or reduce water delivery at any time.
- Galvanized water pipes often last 20-40 years before becoming leaky, but when used to conduct water which corrosive leaks
develop earlier, and when used to conduct water which is high in mineral content, such piping may clog quickly.
Hot water piping tends to clog faster than cold water piping where water mineral content is high, and clogs often occur at hottest sections of piping such as close to a water heater or inside of a tankless coil used to produce domestic hot water. - Plastic water piping such as the commonly used black ABS well piping used to bring water up out of a well and
to the building it serves is very resistant to mineral clogging, corrosion, and leaks, except for poorly-made connections between
the piping and various plastic elbows or unions, or from failures due to mechanical damage:
we've seen loss of water supply traced to a plastic water pipe which was damaged during backfill, for example.
Some types of plastic water piping used in-homes may be damaged by a high chlorine content in the water, particularly PBS or polybutylene piping which was previously the subject of some class action litigation. Modern PBS connectors have been redesigned to avoid this concern. - Copper water piping is not usually used inside of a well nor between a well and the building but is commonly used for in-home water piping. The corrosivity and mineral content can affect the life of copper piping as can the quality and thickness of the copper itself.
- A well's "foot valve" or "pichanca" in Latin America, is used at the end of piping inserted into a shallow or deep well which is pumped by an above-ground
one line or two line jet pump. The foot valve eventually fails, leaking water out of the rising pipe back into the well
and thus losing prime on the pump - possibly leading to loss of water supply.
This is not a problem with the well itself but could be mistaken for a well failure.
The repair is to pull up the piping out of the well and check and replace the foot valve. If your pump is losing prime and you have this type of equipment remember to check the foot valve as well as checking for leaks in the piping in the well itself. - Water pump wiring especially for submersible pumps, and the pumps themselves are vulnerable to damage from lightning strikes.
It's possible that the combination of electrical wiring and the steel well casing are attractive to lightning, particularly when the
well casing extends above ground level (as is common practice with modern drilled wells).
Electrical surge and lightning protection systems are available for installation (usually at the electrical panel) to reduce the risk of well wiring or pump damage from lightning.
...
Continue reading at WELL YIELD IMPROVEMENT or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX .
Or see WATER WELL LIFE FAQs - questions and answers about the life of a water well or its components posted originally at this page.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- WATER TANK LIFE EXPECTANCY
- WELL FLOW RATE - how much water can the well deliver
- WELL LIFE EXPECTANCY
- WELL PUMP TYPES & LIFE EXPECTANCY for a related discussion of how long well pumps, well controls, and related water supply system components can be expected to last.
- WELL YIELD IMPROVEMENT
- WELL YIELD, SAFE LIMITS
- WELL WATER PRESSURE DIAGNOSIS
Suggested citation for this web page
WELL LIFE EXPECTANCY at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to WATER SUPPLY, PUMPS TANKS WELLS & SPRINGS
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.

