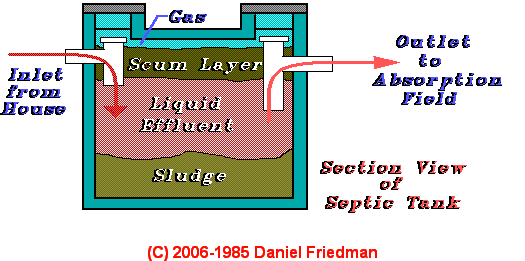
 Septic Wastewater Biocompatibility
Septic Wastewater Biocompatibility
Which onsite septic system effluent components of wastewater are helpful or harmful to soils or nearby waterways?
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about the effects of wastewater ingredients on soil and water in the environment
Effects of septic or sewage wastewater on soils:
This article includes a table describing the effects of common wastewater constituents on arid soil, tropical and temperate soil, and on both ocean water and fresh water bodies.
These effects of eleven principal septic tank efflent constituents on soil and water bodies vary widely from beneficial to very harmful and highly undesirable.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
Effects of Septic Effluent Components on Soil & Water in the Environment
The chart below, discussion, and nearly forty research reference citations address the effects on soil or land and water environments of the discharge of nitrogen, organic compounds, water discharged in onsite wastewater disposal systems such as common septic tanks, drainfields, seepage pits, drywells, and soakaway beds disposing of both graywater and blackwater or sewage effluent.
| Biocompatibility Chart of the Effects of Septic / Wastewater Ingredients on Soil & Water | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater Constituent | Effects on Soils | Effects on Water | Comments & References | ||
| Arid Land Soils | Wet, Temperate & Tropical Soils | Ocean Water | Fresh Water | ||
| Boron in wastewater |
Highly toxic to plants at typical wastewater concentrations | No effect | Undesirable | ||
| Chlorine (& bleach) in wastewater |
Undesirable in all soil types1 | No effect | Little effect | ||
| Industrial Toxins in wastewater |
Disastrous - extremely undesirable | Highly undesirable2 | Disastrous |
CHEMICAL CONTAMINANTS in WATER CHEMICALS to KEEP OUT OF SEPTICS ENDOCRINE DISRUPTORS at BUILDING Endocrine disrupting chemicals in indoor and outdoor air [PDF] CHEMICALS & CLEANERS into the SEPTIC TANK? |
|
| Nitrogen (N) in wastewater |
Very beneficial as Nitrogen is generally the limiting nutrient affecting plant growth | Beneficial Watch out: may leach into ground water if added or present at excessive levels |
Probably OK 3
|
Highly undesirable. Nitrogen is the second most important growth lmiting nutrient of algae in fresh water. |
|
| Organic Compounds in wastewater |
Beneficial food for soil microorganisms. May impact septic tank condition4 |
Must be removed by oxidation in pre-treatment of wastewater to prevent oxygen depletion in water. Fast biodegradation times are essential. |
|||
| Pathogens (microorganisms) in wastewater |
Harmlessly biodegrade under proper conditions. 5 | ||||
| pH Acidity or Alkilinity of wastewater |
pH Lowering is desirable | pH Raising is desirable | No effect | Little effect |
pH in Drinking-water - InspectAPedia.com [PDF from the WHO] |
| Phosphorous (P) in wastewater |
Beneficial. Leaching into groundwater or surface water unlikely due to low mobility in soil |
Extremely beneficial. Phosphorous is a limiting nutrient to plant growth | Probably OK6 | Extremely undesirable. Phosphorous is algae's most growth-limiting nutrient. | DISHWASHERS vs SEPTICS |
| Potassium (K) in wastewater |
Beneficial at washwater concentrations (laundry & dish washing) | Probably OK, effects are unlikely to be measurable | |||
| Sodium (Na) in wastewater |
Highly undesirable. Toxic buildup is likely. Septic drainfield risk7 |
Undesirable but partly flushed by rain from all but clay soils Septic drainfield risk7 |
No consequence | No consequence | SALT / SOFT WATER IMPACT on SEPTIC, PLUMBING, HEATERS |
| Sulfur in wastewater |
Beneficial | No consequence | |||
| Water8 | Highly benficial8 | Possibly beneficial8 | No Effect | Little Effect | |
Notes to the table above
1. Chlorine / bleach impacts:
at sufficient concentrations chlorine may kill off or reduce the level of septic tank bacteria that are needed for effective wastewater processing. At normal home usage levels we do not expect to see an effect. Some septic systems require disinfection of wastewater before it is discharged to the environment.
2. Industrial toxins in ocean water:
Even though diluted, may bio-concentrate in various life forms, moving up food chain to humans
3. Organic compounds:
at a particulate level such as food waste, organic material in wastewater may add to septic tank volume and require more frequent pumping to avoid disposal field clogging where private septic systems are involved. Grease discharged into septic systems and sewers can cause clogging and failures.
4. Nitrogen impact on water:
Nitrogen is potentially harmful in ocean water by encouraging growth of algae, but dilution in ocean envrionment probably means there is no measurable effect
5. Pathogenic microorganism discharge in wastewater impact on wastewater, septic tanks, soils:
"harmlessly biodegrade" in soils is probably accurate in general but may not be in septic tanks and wastewater treatments connected to health care facilities. A corrolary problem is the high concentration of antibiotics in wastewater produced by health care facilities, nursing homes etc., - at levels that can damage or destroy essential bacteria in septic tanks and in the soils receiving wastewater.
6. Phosporous impact on ocean water:
Phosphorous is potentially harmful in ocean water by encouraging growth of algae, but dilution in ocean envrionment probably means there is no measurable effect
7. Salt impact on soils & waterways:
Burks & Minnis (1994) and others have researched the impact of salt on septic system failure.
8. Water impact on soils:
although water volume discharge may be beneficial in general, water discharge in a volume sufficient to flood a septic disposal field is highly undesirable as results include septic system failure, sewage backups even into the building, and the discharge of un-treated wastewater into the environment.
Original source: Adapted from "Table 6: Biocompatibility Chart", p. 38 of unidentified document - citation needed. Also see the research citations found atReferences or Citations
...
Continue reading at SEWAGE PATHOGENS in SEPTIC SLUDGE or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
Suggested citation for this web page
WASTEWATER BIOCOMPATIBILITY at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to SEPTIC SYSTEMS
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- New York State Department of Health, APPENDIX 75-A WASTEWATER TREATMENT STANDARDS - INDIVIDUAL HOUSEHOLD SYSTEMS , [PDF] New York State Department of Health, 3 February 2010, retrieved 3/1/2010, original source: https://www.health.ny.gov/regulations/nycrr/title_10/part_75/appendix_75-a.htm
- "Biocompatibility Chart", "The chart below summarizes the biocompability of common wastewater constituents with the four most common disposal environments. Table 6: Biocompatibility chart[ - adapted and expanded by InspectApedia.com editor, with additional citations below [source unknown, under further research, apparently page 28 of a document, presentation or textbook]
- All, E. P. A. "Establishing treatment system performance requirements."
- Amahmid, O., Asmama, S., & Bouhoum, K. (1999). The effect of waste water reuse in irrigation on the contamination level of food crops by Giardia cysts and Ascaris eggs. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 49(1-2), 19-26.
- Bahe, Anita, Billie Comstock, Thomas Konsler, Sarah K. Liehr, Sharon C. Long, Krich Ratanaphruks, Chet A. Rock, and P. E. Kevin Sherman. "FACTORS AFFECTING THE PERFORMANCE OF PRIMARY TREATMENT IN DECENTRALIZED WASTEWATER SYSTEMS." [PDF]
- Balaji, Sundaramoorthy, Kadiyala Gopi, and Bhaskaran Muthuvelan. "Algal Research." (2013).
- Barak, J.D., Whitehand, L.C., & Charkowski, A.O. (2002). Differences in attachment of Salmonella enterica serovars and Escherichia coli O157:H7 to alfalfa sprouts. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(10), 4758-4763.
- Beuchat, L.R. (1996). Pathogenic microorganisms associated with fresh produce. Journal of Food Protection, 59(2), 204-216.
- Breuer, T., Benkel, D.H., Shapiro, R.L., Hall, W.N., Winnett, M.M., Linn, M.J., Timothy, J.N., Barrett, J., Dietrich, S., Downes, F.P., Toney, D.M., Pearson, J.L., Rolka, H., Slutsker. L., & Griffin, P.M. (2001). A multi-state outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections linked to alfalfa sprouts grown from contaminated seeds. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 7(6), 977-982.
- Brix, H. "Wastewater treatment in constructed wetlands: system design, removal processes, and treatment performance." Constructed wetlands for water quality improvement (1993): 9-22.
- Castro-Rosas, J., & Escartin, E.F. (2000). Survival and growth of Vibrio cholerae O1, Salmonella typhi, and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in alfalfa sprouts. Journal of Food Science, 65(1), 162-165.
- Chen, Xueming, Guohua Chen, and Po Lock Yue. "Separation of pollutants from restaurant wastewater by electrocoagulation." Separation and purification technology 19, no. 1 (2000): 65-76.
- Charkowski, A.O., Barak, J.D., Sarreal, C.Z., & Mandrell, R.E. (2002). Growth and colonization patterns of Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli O157:H7 on alfalfa sprouts and the effects of sprouting temperature, i inoculum /in·oc·u·lum/ (-ok´u-lum) pl. inoc´ula material used in inoculation.
- Chua, H., P. H. F. Yu, and L. Y. Ho. "Coupling of waste water treatment with storage polymer production." Applied biochemistry and biotechnology 63, no. 1 (1997): 627-635.
- Coelho, Alessandra D., Carmen Sans, Ana Agüera, Maria José Gómez, Santiago Esplugas, and Márcia Dezotti. "Effects of ozone pre-treatment on diclofenac: Intermediates, biodegradability and toxicity assessment." Science of the Total Environment 407, no. 11 (2009): 3572-3578.
- Jones, M. I., L. Y. Wang, A. Abeynaike, and Darrell A. Patterson. "Utilisation of waste material for environmental applications: calcination of mussel shells for waste water treatment." Advances in Applied Ceramics 110, no. 5 (2011): 280-286.
- LaPara, Timothy M., Cindy H. Nakatsu, Lisa M. Pantea, and James E. Alleman. "Stability of the bacterial communities supported by a seven-stage biological process treating pharmaceutical wastewater as revealed by PCR-DGGE." Water Research 36, no. 3 (2002): 638-646.
- Lee, Sang Yup, and Jong-il Choi. "Production and degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates in waste environment." Waste Management 19, no. 2 (1999): 133-139.
- Levine, Audrey D., George Tchobanoglous, and Takashi Asano. "Characterization of the size distribution of contaminants in wastewater: treatment and reuse implications." Journal (Water Pollution Control Federation) (1985): 805-816.
- Martinez-Huitle, Carlos A., and Sergio Ferro. "Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: direct and indirect processes." Chemical Society Reviews 35, no. 12 (2006): 1324-1340.
- Malato, Sixto, Manuel I. Maldonado, Isabel Oller, and Ana Zapata. "Removal of Pesticides from Water and Wastewater by Solar-Driven Photocatalysis." In Emerging Compounds Removal from Wastewater, pp. 59-76. Springer Netherlands, 2012.
- Oller, I., S. Malato, J. A. Sánchez-Pérez, M. I. Maldonado, and R. Gassó. "Detoxification of wastewater containing five common pesticides by solar AOPs–biological coupled system." Catalysis Today 129, no. 1 (2007): 69-78.
- Oller, I., S. Malato, and J. A. Sánchez-Pérez. "Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—a review." Science of the total environment 409, no. 20 (2011): 4141-4166.
- Qadir, Manzoor, Dennis Wichelns, Liqa Raschid-Sally, P. G. McCornick, Pay Drechsel, Akissa Bahri, and P. S. Minhas. "The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries." Agricultural Water Management 97, no. 4 (2010): 561-568.
- Riordan, M. James. Septic system checkup: the Rhode Island handbook for inspection. Department of Environmental Management, 2000.
- Shon, H. K., S. Vigneswaran, and S. A. Snyder. "Effluent organic matter (EfOM) in wastewater: constituents, effects, and treatment." Critical reviews in environmental science and technology 36, no. 4 (2006): 327-374.
- Siegrist, Robert L. "Soil clogging during subsurface wastewater infiltration as affected by effluent composition and loading rate." Journal of Environmental Quality 16, no. 2 (1987): 181-187.
- SONG, Min, Fu-li GAO, and Yun-long YANG. "Study on the MBBR (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) and Its Application [J]." Sci-Tech Information Development & Economy 2 (2007): 093.
- Tchobanoglous, George, and Franklin L. Burton. "Wastewater engineering." MANAGEMENT 7 (2003): 1-4. [PDF retrieved 1/14/2014]
- Van Cuyk, S., R. Siegrist, A. Logan, S. Masson, E. Fischer, and L. Figueroa. "Hydraulic and purification behaviors and their interactions during wastewater treatment in soil infiltration systems." Water Research 35, no. 4 (2001): 953-964.
- Yonar, Taner, Kadir Kestioglu, and Nuri Azbar. "Treatability studies on domestic wastewater using UV/H< sub> 2</sub> O< sub> 2</sub> process." Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 67, no. 3 (2006): 223-228.
- Yongsiri, Chaturong, Jes Vollertsen, and Thorkild Hvitved-Jacobsen. "Influence of wastewater constituents on hydrogen sulfide emission in sewer networks." Journal of Environmental Engineering 131, no. 12 (2005): 1676-1683.
- "Bacterial Pathogens Recovered from Vegetables Irrigated by Wastewater in Morocco", Y. Karamoko, K. Ibenyassine, M. M. Ennaji, B. Anajjar, R. Ait Mhand, M. Chouibani, Journal of Environmental Health, June 2007.
Abstract:
The authors obtained 50 vegetable samples from various regions in Morocco and examined them to determine the micro biological quality of these products. Aerobic count, coliform, enterococci, and Staphylococcus areus were evaluated. This analysis revealed high levels of enterococci, fecal coliforms, and total coliforms. No coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureas was detected in any of the samples analyzed. Biochemical identification of Enterobacteriaceae showed the presence of Citrobacter freundii (28 percent), Enterobacter cloacae (27 percent), Escherichia coli (16 percent), Enterobacter sakazakii (12 percent), Klebsiella pneamoniae (17 percent), Serratia liquefaciens (11 percent), and Salmonella arizonae (0.7 percent). The results clearly demonstrate that vegetables irrigated with untreated wastewater have a high level of microbiological contamination. Consequently, these vegetables may be a threat for the Moroccan consumer and may be considered a serious risk to Moroccan public health. ABSTRACT FROM AUTHOR Copyright of Journal of Environmental Health is the property of National Environmental Health Association and its content may not be copied or emailed to multiple sites or posted to a listserv without the copyright holder's express written permission. However, users may print, download, or email articles for individual use. This abstract may be abridged. No warranty is given about the accuracy of the copy. Users should refer to the original published version of the material for the full abstract.
Contact Us to request a copy of this article stored as BacterialPathogens.pdf if you have difficulty obtaining a copy of this full article for private use. - Beuchat, L.R. (1996). Pathogenic microorganisms associated with fresh produce. Journal of Food Protection, 59(2), 204-216.
- Breuer, T, Benkel, D.H., Shapiro, R.L., Hall. W.N., Winnett. M.M., Linn, M.J., Timothy, J.N., Barrett. J., Dietrich, S., Downes, EP, Toney, D-M., Pearson, J.L., Rolka. H., Slutsker. L, & Griffin, PM. (2001). A multi-state outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections linked to alfalfa sprouts grown from contaminated seeds, Emerging Infectious Diseases, 7(6), 977-982.
- Evans, M.R., Ribiero, CD., & Salmon, R.L. (2003). Hazards of healthy Living: Boiled water and salad vegetables as risk Factors For Campylobacter infection. Emerging Infectious Disease, 9(10), 1219-1225.
- Frost, J.A., McEvoy, M.B., Bentley, C.A., Andersson, Y., & Rowe, B. (1995). An outbreak of Shigella sonnei infection associated with consumption of iceberg. Emerging Infectious Disease, 1(1), 26-28.
- Guo, X., Chen, j . , Brackett, R.E., & Beuchat. LR. (2001). Survival of Saimonellae on and in tomato plants From the time of inoculation at flowering and early stages of fruit development through fruit ripening. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(10), 4760-4764
- Guo, X., Chen, J., Brackett, R.E., & Beuchat, L.R. (2002). Survival of Salmonellae on tomatoes stored at high relative humidity, in soil, and on tomatoes in contact with soil. Journal of Food Protection, 65(2), 274-279.
- Guo, X., Iersel, M.W.V., Chen, J., Brackett, R.E., & Beuchat, L.R. (2002). Evidence of association of salmonellae with tomato plants grown hydroponically in inoculated nutrient solution. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(7), 3639-3643.
- Itoh, Y., Sugita-Konishi, Y., Kasuga, E, Iwaki, M., Hara-Kudo, Y., Saito, N., Noguchi, Y, Konuma, H., & Kumagai, S. (1998) Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli enterohemorrhagic Escherichia EHEC Any of the E coli serotypes–eg O29, O39, O145 that produces shiga-like toxins, causing bloody inflammatory diarrhea, evoking a HUS. See Escherichia coli O157:H7, Hemolytic uremic syndrome. O157:H7 present in radish sprouts. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64(4), 1532-1535.
- Madden, J.M. (1992). Microbial pathogens in fresh produce—The regulatory perspective. Journal of Food Protection, 55, 821-823.
- McMahon, M.A.S., & Wilson, I.G. (2001). The occurrence of enteric pathogens and Aeromonas species in organic vegetables. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 70(1-2),155-162.
- Puohiniemi, R., Heiskanen, T., & Siitonen, A. (1997). Molecular epidemiology of two international sprout-borne Salmonella outbreaks. Journal of Clinical Microbiology . 35(10), 2487-2491.
- Shearer, A.E., Strapp, CM., & Joerger, R.D. (2001). Evaluation of polymerase chain reaction-based system for detection of Salmonella enteritidis, Escherichia coli O157:H7, Listeria spp., and Listeria monocytogenes on Fresh Fruit and vegetables. Journal of Food Protection, 64(6), 788-795.
- "Septic Tank/Drainfield System Fact Sheet", Utah Department of Environmental Quality, Division of Drinking Water, Source Protection Program - (801) 536-4200 Division of Water Quality - (801) 538-6146 Sonja Wallace, Pollution Prevention Coordinator - (801) 536-4477 Environmental Hotline - 1-800-458-0145 - Original source: http://www.drinkingwater.utah.gov/documents/spec_services/pollution_prevention_septic_tanks.pdf
- New York State Wastewater Treatment Standards - Individual Household Systems, Appendix 75-A (1990), Public Health Law 201(1)(1).
- Takeuchi, K., Hassan, A.N., & Frank, J.F. (2001). Penetration of Escherichia coli O157:H7 into lettuce as influenced by modified atmosphere and temperature. Journal of Food Protection, 64(11), 1820-1823.
- New York State Alternative Septic System Design Regulations, Wastewater Treatment Standards - Individual Household Systems, Appendix 75-A, of Public Health Law 201(1)(1) 1990.
- Advanced Onsite Wastewater Systems Technologies, Anish R. Jantrania, Mark A. Gross, CRC Taylor & Francis, 2006 ISBN 0-8493-3029-7
- Anish Jantrania, Ph.D., P.E., M.B.A., Consulting Engineer, Mechanicsville VA, 804-550-0389
- The Septic System Owners's Manual, Lloyd Kahn, Blair Allen, Julie Jones, Shelter Publications, 2000. ISBN 0-936070-20-X
- Onsite wastewater treatment systems, Bennette D. Burks & Mary Margaret Minnis. Textbook and reference manual on all aspects of onsite treatment. This is one of the best books we've reviewed on the subject, with an excellent balance of clear simple explanation and solid engineering. Topics: Soil & Site Selection, Hydraulics, System Selection & Design, Wastewater Biology, History & Mythology of Onsite Wastewater Treatment. $49.95, Hogarth House, Ltd., 800-993-2665 x327 or order by telephone 800 -993-2665 x327 (Univ. Wisc. Bookstore)
- Wanielista, Marty, Matt Goolsby, Manoj Chopra, Ni-Bin Chang, and Mike Hardin. "POST CERTIFICATE OF OCCUPANCY ANALYSIS." (2011). [PDF retrieved 1/11/2014]
- Wright, C., Kominos, S.D., & Yee, R.B. (1976). Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa recovered from vegetable salads. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 31(3), 453-454.
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.

