 Water Pump Duty Cycle & Head Capacities
Water Pump Duty Cycle & Head Capacities
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about things that impact the life of a well pump or water pump
Well pump duty cycle:
Definition of duty cycle for a well pump or similar electric motor. This article defines & explains the duty cycle of water pumps. We describe the relationship between pump motor duty cycle and pump life.
Well pump definitions, types, & water pump life: this article series describes the different types of water pumps or well pumps, and we list the factors affecting the life expectancy of water pumps and we include a list of steps to take to maximize the life of a well or water pump and its motor.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
Well Pump Duty Cycle: Percent of Pump-On Time
 Definition: the duty cycle of any electric motor describes how hard the motor is expected to work, expressed as how often and for how long the motor runs as a percentage of total time that the motor is installed and available.
Definition: the duty cycle of any electric motor describes how hard the motor is expected to work, expressed as how often and for how long the motor runs as a percentage of total time that the motor is installed and available.
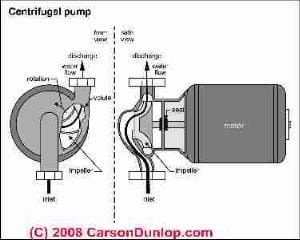
Page top photo of a typical centrifugal water pump is provided courtesy of Carson Dunlop Associates, a Toronto home inspection, education & report writing tool company [ carsondunlop.com ].
Our photo at left shows a Meyers 2-line jet pump
[Click to enlarge any image]
A typical water pump duty cycle is probably less than 10% - that is, in a 24 hour period the water pump is expected to be "on" less than 20% of the time, or less than 2.4 hours. If the actual motor installation and use exceed its rated duty cycle you can expect the pump life to be reduced accordingly.
Watch out: conditions such as a water leak or water left on at a building can cause a water pump to run continuously. Most water pump motors can handle this condition provided that there is actually water in the system.
But if the pump runs "dry" it is likely to be damaged. If the water pump is running and no water is being provided, or if water is turned off in the building but the pump never shuts off, you should turn off electrical power to the system.
See WATER PUMP WONT STOP RUNNING
In typical use the frequency of start and stop of an electric motor driving a well pump varies as water usage rates in the building vary, depending further on the settings of the pressure control switch, the condition of the water pressure tank and its air charge, and the use of short cycling or other protection devices.
What are the minimum and maximum water pump on cycle times?
A water pump's minimum "on" cycle will occur when the pressure tank water content volume and pressure are just above the pressure control switch cut-in pressure, when water is run just long enough to turn on the pump, then water use stops. This minimum on cycle time extends just long enough to refill the pressure tank to the cut-off pressure. The actual time required depends on the delivery rate capacity of the well and water piping and the pump's horsepower and pumping capacity in gallons per minute.
A water pump's maximum "on" cycle is quite long, even hours, and in some cases such as pumps used for irrigation systems, the pump may be on for several days at a time.
Even in simple residential installations a pump may be on for long periods. For example when an occupant is watering a lawn or filling a swimming pool, if the water flow rate exceeds the well and pump's output capacity then the water supply system and pump will run continuously until the water is turned off. At that point the pump will continue to run until the pressure tank has reached the cut-off pressure.
According to the Peerless Pump Company, pump duty cycles depend on several variables from which we paraphrase with adaptations for clarity:
Duty cycle: Duty cycles vary widely depending on pump size, [water pressure] tank size, [pressure] control switching and other factors. The well pump motor may have recommended limits set by the manufacturer for allowable starts per day or per hour.
Submersible well pumps generally allow relatively rapid cycling without overheating because of their low inertia and rapid acceleration. However, every water pumping system should be designed to minimize cycling as much as is practical.
If water pump on-off cycling is excessive, stop-start stress and wear in the motor, pump, coupling, pipe and controls may have more influence than total pumping time has on system life. [1] - Peerless Pump Company Technical Bulletin No. 32
 Watch out: well pump duty cycle data may be hard to spot. Reading a typical pump catalog we may not even find explicit duty cycle specifications except for special applications such as transfer pumps.
Watch out: well pump duty cycle data may be hard to spot. Reading a typical pump catalog we may not even find explicit duty cycle specifications except for special applications such as transfer pumps.
Instead you will have to read between the lines. A water pump designed for agriculture, irrigation, lawn sprinkling, and some contracting uses is surely intended to handle long pump-on times while a typical residential water supply pump may not have that intended use.
Where pump motor duty cycle data is not provided, you should select the pump based on the manufacturer's description of its intended application.
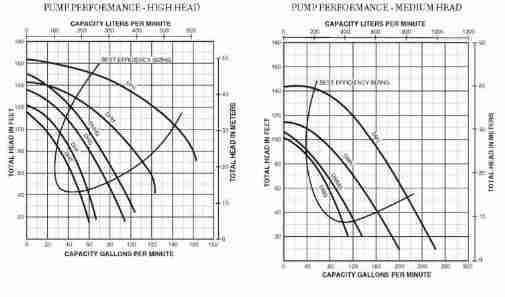
Pump capacity descriptions also distinguish between high-head installations and medium-head installations where "head" is the height and length-resistance of water piping through which the pump has to lift or move water.
Shown above are the high head and medium head pump capacity charts for Myers D-series pumps. - Pump Catalog, www.bobdeansupply.com Fort Myers Branch, Fort Myers Fl, 800-282-8378, email: sales@bobdeansupply.com
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) definitions of electric motor duty cycles
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has defined eight duty cycle designations that they think describe an electrical motors' operating conditions, designated S1-S8.
Key differences among duty cycles for electric motors are whether the motor runs continuously or only itermittently, how long and how often the motor runs, whether the motor is on long enough to reach its maximum operating temperature and whether the motor is off long enough to cool down to ambient temperature.
In our OPINION, none of the IEC's eight definitions exactly match the duty cycle of an electric motor used to operate a well pump or water pump, niether for submerged water pumps nor for above-ground jet pumps.
The closest IEC electric duty cycle definition to the application of water pumps is
Duty Cycle Type S4: Intermittent periodic duty with starting. defined as: Sequential, identical start, run and rest cycles with constant load. Temperature equilibrium is not reached, but starting current affects temperature rise.
impact of water pump head height & multiple water tanks on water pump life
Reader Question:
A pump is pumping water from underground storage tank to an overhead tank (Tank A) at a height of 50 feet (the delivery pipe first goes horizontal at pump level for 40 feet and then rises to height of 50 feet).
Water level above the foot valve of pump varies from 5feet to 1/2 feet. At the pump level if we tap a connection on the delivery pipe (around 20 feet away from pump outlet) and give the water to a different tank at 10 feet (Tank B), the water reaches both the tanks (A & B). But will this do any damage to the pump (its winding etc). - I.S. 9/19/2013
Reply:
 I am not certain I have a full understanding of your situation, nor what kind of pump we are discussing; and an onsite expert often will see other factors that are important.
I am not certain I have a full understanding of your situation, nor what kind of pump we are discussing; and an onsite expert often will see other factors that are important.
But based on just your email, it sounds as if you are in effect just adding more water storage volume - not something that harms a pump motor. You will probably need appropriate check valves and controls to prevent the higher tank from back-filling the lower one.
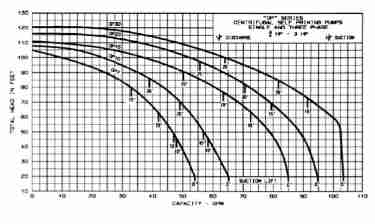
Keep in mind that the higher the pumping head the lower will be the pump's water delivery capacity. The actual impact of head on pump capacity depends on the water pump type, horsepower, piping details and probably other features.
Our pump capacity versus head height graph shown at left is adapted from datas for Myers Quick Prime 3/4 to 3 hp centrifugal water pumps.
Myers also provides a 5 hp centrifugal water pump for heavy duty applications - a model that probably exceeds most residential application needs.
[Click to enlarge any image seen at InspectAPedia]. - Pump Catalog, www.bobdeansupply.com Fort Myers Branch, Fort Myers Fl, 800-282-8378, email: sales@bobdeansupply.com
Reader comment:
Thanks Daniel. Yes I have check valve in place that prevents the lower tank from overflowing. My only concern that the pump should not get damaged because of this setting.
Reply:
As long as the water pump is able to always reach the cut-off pressure set in its control switch, and is protected from short cycling, you should be ok. If you want to check further technically you'd look at the pump's operating temperature when it has been on for a long pump cycle, comparing that to the rated operating temperature on its data tag.
If you see abnormally high temperatures I'd also check the line voltage level and the actual current draw in amperage when the pump is running. Abnormally low voltage is hard on some electric motors. High amps draw is usually an indication of trouble in the equipment itself and would call for further investigation.
You haven't said what type of pump is installed, but you might want to take a look at the different pump types listed at the end of this article as well as at these links on pump life:
...
Continue reading at WATER PUMP LIFE MAXIMIZATION or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
Suggested citation for this web page
WATER PUMP DUTY CYCLE at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to WATER SUPPLY, PUMPS TANKS WELLS
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Questions & answers or comments about things that impact the life of a well pump or water pump.
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- [1] Peerless Pump Company, "ECHNICAL INFORMATION Bulletin NUMBER THIRTY-TWO SUBMERSIBLE MOTORS. RELIABLE PERFORMANCE DEPENDS ON RELIABLE INSTALLATION " Peerless Pump Company, 2005 Dr. M.L. King Jr. Street, P.O. Box 7026, Indianapolis, IN 46207-7026, USA Telephone: (317) 925-9661 Fax: (317) 924-7338 www.peerlesspump.com, retrieved 9/20/2013 original source: http://www.peerlessxnet.com/documents/tibs/ TIB-32_Submersible-Motors-Reliable-Performance-Installation.pdf
- Air in Drinking Water, Environmental Fact Sheet, New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services, 29 Hazen Drive, Concord NH 03301 - web search 07/14/2010 original source: http://des.nh.gov/organization/commissioner/pip/factsheets
/dwgb/documents/dwgb-3-18.pdf - Mark Cramer Inspection Services Mark Cramer, Tampa Florida, Mr. Cramer is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors and is a Florida home inspector and home inspection educator. Mr. Cramer serves on the ASHI Home Inspection Standards. Contact Mark Cramer at: 727-595-4211 mark@BestTampaInspector.com
- John Cranor [Website: /www.house-whisperer.com ] is an ASHI member and a home inspector (The House Whisperer) is located in Glen Allen, VA 23060. He is also a contributor to InspectApedia.com in several technical areas such as plumbing and appliances (dryer vents). Contact Mr. Cranor at 804-873-8534 or by Email: johncranor@verizon.net
- Kinetic water rams are described and demonstrated at waterram.com/faq.php
- Penn State, Water Fact Sheet #3, USING LOW-YIELD WELLS [PDF], Penn State College of Agricultural Sciences, Cooperative Extension, School of Forest Resources, web search 07/24/2010, original source: http://pubs.cas.psu.edu/FreePubs/pdfs/XH0002.pdf
- Grove Electric, Typical Shallow Well One Line Jet Pump Installation [PDF], Grove Electric, G&G Electric & Plumbing, 1900 NE 78th St., Suite 101, Vancouver WA 98665 www.grovelectric.com - web search -7/15/2010 original source: http://www.groverelectric.com/howto/38_Typical%20Jet%20Pump%20Installation.pdf
- Grove Electric, Typical Deep Well Two Line Jet Pump Installation [PDF], Grove Electric, G&G Electric & Plumbing, 1900 NE 78th St., Suite 101, Vancouver WA 98665 www.grovelectric.com - web search -7/15/2010 original source: http://www.groverelectric.com/howto/38_Typical%20Jet%20Pump%20Installation.pdf
- Water Ace Jet Pump Installation Manual, instructions from Water Ace Pump Co., web search 08/28/2010, original source: http://www.waterace.com/pdf/R510%20R520%20and%20R100%20Jet%20Pumps%20Manual.pdf
Consumer hotline: 800-942-3343 - instructions for the installation and maintenance of
Water Ace shallow well pump Model R510 1/2 HP
Water Ace deep well pump Model R100 convertible 1HP and
Water Ace deep well jet pump Model R250 convertible 1/2 hp.
Water Supply & Drain Piping, Wells, Pumps, Water Supply Equipment
- Access Water Energy, PO Box 2061, Moorabbin, VIC 3189, Australia, Tel: 1300 797 758, email: sales@accesswater.com.au Website: http://www.accesswater.com.au/
Moorabbin Office: Kingston Trade Centre, 100 Cochranes Rd, Moorabbin, VIC 3189
Australian supplier of: Greywater systems, Solar power to grid packages, Edwards solar systems, Vulcan compact solar systems, water & solar system pumps & controls, and a wide rage of above ground & under ground water storage tanks: concrete, steel, plastic, modular, and bladder storage tanks. - Grove Electric, Typical Shallow Well One Line Jet Pump Installation [PDF], Grove Electric, G&G Electric & Plumbing, 1900 NE 78th St., Suite 101, Vancouver WA 98665 www.grovelectric.com - web search -7/15/2010 original source: http://www.groverelectric.com/howto/38_Typical%20Jet%20Pump%20Installation.pdf
- Grove Electric, Typical Deep Well Two Line Jet Pump Installation [PDF], Grove Electric, G&G Electric & Plumbing, 1900 NE 78th St., Suite 101, Vancouver WA 98665 www.grovelectric.com - web search -7/15/2010 original source: http://www.groverelectric.com/howto/38_Typical%20Jet%20Pump%20Installation.pdf
- Our recommended books about building & mechanical systems design, inspection, problem diagnosis, and repair, and about indoor environment and IAQ testing, diagnosis, and cleanup are at the InspectAPedia Bookstore. Also see our Book Reviews - InspectAPedia.
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.

