 R-22 Refrigerant Pressure Chart
R-22 Refrigerant Pressure Chart
R-22 pressures, temperatures ,quantities, boiling points
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about refrigerant pressure readings in air conditioners, heat pumps, & other refrigeration equipment
R-22 refrigerant charge quantity for air conditioners & heat pumps:
We discuss how to diagnose refrigerant pressure problems; how to determine the proper refrigerant charge quantity.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
R-22 Refrigerant Data
CFCs, ChloroFluoroCarbons - first generation refrigerants like R22 (1950s & later) were widely used in refrigerators and air conditioners.
R22 was phased out in 2010 and is no longer widely available. R 404A and later R407c may replace R22 in some applications.
Below this table of example refrigerant operating pressures for R-22, we provide links to complete refrigerant pressure/temperature charts as PDF files that you can download free.
R-22 Refrigerant Temperature vs Pressure Data© 2022 InspectApedia.com |
||||||
| Ambient Temperature | R22 Vapor Pressure at Sea Level | R-22 Low Side Pressure2 | R-22 High Side Pressure3 | |||
| °F 1 | °C | psig | kpa | Bar | ||
| -50° | -45.6° | 6.1 | 42 | 0.4 | ||
| -10° | -23.3° | 16.5 | 113.7 | 1.1 | ||
| 0° | -17.8° | 24 | 165.4 | 1.7 | ||
| 30° | -1.1° | 54.7 | 377 | 3.8 | 50 psig5 | |
| 32° | 0° | 57.5 | 396.4 | 4 | ||
| 40° | 4.4° | 68.3 | 470.9 | 4.7 | ||
| 50° | 10° | 83.8 | 577.8 | 5.8 | ||
| 60° | 15.5° | 101.4 | 699.1 | 7 | ||
| 65° | 18.3° | 111.3 | 767.4 | 7.7 | 25-35 | 135-155 psig |
| 70° | 21.1° | 121.5 | 837.7 | 8.4 | 35-40 | 140-165 |
| 75° | 23.9° | 132 | 910.1 | 9.1 | 40-45 | 150-175 |
| 80° | 26.7° | 143.5 | 989.4 | 9.9 | 40-50 | 175-220 |
| 85° | 29.4° | 170 | 1172 | 10.2 | 60 | 250 |
| 90° | 32.2° | 176.5 | 1217 | 12.2 | 64 psig | 250+ psig |
| 95° | 35° | 181.9 | 1254 | 12.5 | 68 psig | 250+ psig |
| 100° | 37.85° | 196.2 | 1353 | 13.5 | ||
| 110° | 43.3° | 226.4 | 1561 | 15.6 | ||
| 120° | 48.9° | 260.9 | 1799 | 17.9 | 260 psig | |
| 125° | 51.7° | 279 | 1924 | 19.2 | ||
| 150° | 65.6° | 381.7 | 2632 | 26.3 | ||
Notes to the table above
- psig = psi gauge pressure
- kpa = kilopascals
- Bar = atmospheres where 1 Bar = 14.5 psig or normal pressure at sea level.
Other Properties for R22 Refrigerant
- R22 temperature/pressure relationship: see the table above
- R22 alternative names: CHClF2 Chlorodifluoromethane, Difluoromonochloromethane, generic term: hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HCFC)
- R22 boiling point: -40.8 degree Celsius at atmospheric pressure (sea level or 1 ATM)
- R22 density: 3.66 g/cm3, in gas form - this is a colorless gas
- R22 molar mass: 86.47 g/mol
- R22 gas cylinder identification: light green
- R2 status: no longer in active use, replaced with R458A
- R22 and other common refrigerants is an odorless, colorless gas that will be liquid at sufficiently low temperature and/or high pressure
- This chart is using outdoor ambient temperature
- Typical low pressure or suction side, may vary by equipment and metering controls - these are "gauge pressure readings" or "psig"
- Typical high side pressure, may vary by equipment
- These psig readings for R-22 are what you'd expect the pressure of the gas to be in an enclosed container at the temperature given and at steady state.
Both older R-22 and R-134 operate at lower pressures than R-410A.
R22 Refrigerant Pressure Rules of Thumb
Typical Off, Low, High side R22 Pressures & Temperatures
On a properly-charged and working air conditioning system using R-22 refrigerant
Low pressure refrigerant switches on Carrier HVACR typically open at 50 psi and close at 100 psi. - Prah, Frank, CMS, "Refrigerant 410A", [PDF] Refrigeration Service Engineers Society, 1666 Rand Road, Des Plaines IL 60016 USA, Tel: 847-297-6464, retrieved 2016/08/29, original source: https://www.rses.org/assets/r410a/R-410A.PDF
- R-22 Low-Side pressure when compressor is OFF = R22, at 70 deg F, R22 vapor pressure at sea level will be 121.5 psi. or 176.5 psi at 90°F ambient temperature, system OFF,
Note that when a refrigeration system has been off long enough to reach its normal, idle state, both high-side and low-side refrigerant pressures will be equal and will depend on the surrounding ambient temperature. - R-22 Low-Side Turn-On Pressure = 50 psig (R22 at 30 deg F) is a typical pressure at which the HVACR compressor/condenser will turn-on
100 psig (R 22 at 85 deg F) is a typical pressure at which the HVACR compressor will turn off [Questionable, further research in process - Ed.] - R-22 Low-Side Operating Pressure =
The low-side pressure of an A/C system at 70 deg ambient temperature will be 35-40 psi
- R-22 Low-Side Typical Operating Pressure-Range = 58 - 85 psig
Varies by indoor wet bulb temperature and outdoor ambient temperature, where higher heat loads increase the vapor line pressure.
Other sources give the low side pressure range = 60 - 80 psig. - Refrigerant Low-Side Suction Line Temperature: 35-40 °F below the building's return air temperature measured at the air handler.
Example: temperature at the return air entry to the air handler = 80°F.
Calculate the evaporation temperature = suction line temperature range: (80°F - 35°F = 45°F) - (80°F - 40°F = 40°F)
so at 80°F return air temperature, the suction line temperature would be between 40°F and 45°F - R-22 High-Side vapor pressure at sea level, = (rule of thumb) 2 x ambient temperature (F) + 50 psi
OPINION: this rule of thumb gives pressures a bit higher than shown in our R-22 pressure and temperature table above.
Example: at 75°F
Table pressure: R-22 High-Side operating refrigerant pressure = 150-175 psig
With the equipment OFF and stabilized, from the R22 refrigerant pressure tables, given in this article, the R22 pressure will be a bit lower, at 132.2 psi.
Calculated pressure: R-22 High-Side pressure = (75 x 2) + 50 = 200 psig - this is "high" so you should take this as an upper limit. - R-22 High-Side Typical Operating Pressure Range:
The high-side pressure of an A/C system at 70 deg ambient temperature will be 135-155 psi. - R-22 Superheat & Sub-Cooling Temperature Range= 8 - 18°F
Measure the suction line temperature neaer its entry to the compressor/condenser unit. (Superheat = Suction-line temp. - Evaporation temp. )
R-22 Refrigerant Pressure / Temperature Chart & Table Downloads
- R22 PRESSURE-TEMPERATURE CHART [PDF] iGas, 8105 Anderson Road, Tampa, FL 33634 USA, a supplier of refrigerant gases, Web: igasusa.com Tel: 813-443-0757 gives pressure and temperatures in both F & C for R22 from -49°F (-5.4 psig) up to 150°F (381.7 psig)
Note: these are Saturation Pressure-Temperature Data for R22 (psig)*
* Saturation pressure for a refrigerant is the temperature at which the refrigerant gas or vapor and the liquid refrigerant are in equilibrium. That means that at its saturation pressure, the refrigerant will exist in both liquid and vapor forms at the same time. - REFRIGERANT PRESSURE / TEMPERATURE CHARTS for R-22, R-410A, R-134A, R-404A REFRIGERANTS [PDF]
Advantage Engineering, Inc. 525 East Stop 18 Road Greenwood, IN 46142USA, Tel: 317-887-0729 Web site: www.AdvantageEngineering.com Email: sales@AdvantageEngineering.com
- REFRIGERANT TEMPERATURE / PRESSURE CHARTS for R-407, R-22, R410a, R-407c, R-134a, R404a, [PDF], Op. Cit.,
- REFRIGERANT PRESSURE / TEMPERATURE CHARTS for R-11, R-113, R-123, R-12, R-13, R-134A, R-114, R-14 or Freon-14, Tetrafluoromethane,R-22, R-23, R-410A, R-409A, R-416A, R-500, R-503, R-507, R-503 [PDF]
Airgas Refrigerants, Inc., Headquarter Office 2530 Sever Road, Suite 300 Lawrenceville, GA 30043 Tel: 1-800-473-3766, Website: www.airgasrefrigerants.com Email: ARF-Contact.us@airgas.com
Typical HVAC R-22 Refrigerant Pressures
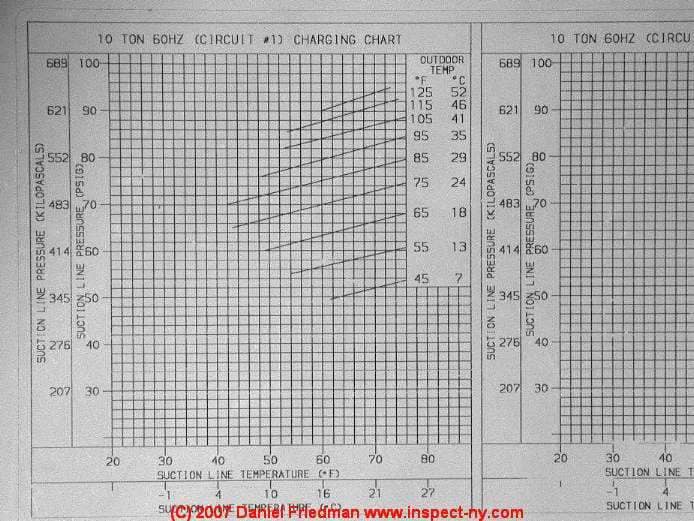
Typical residential air conditioning refrigerant pressures vary depending on the model, compressor motor size and design, and the refrigerant used.
The design pressures may be provided on labels attached to the equipment but the actual air conditioner operating pressure will vary in part as a function of the incoming air temperatures.
"Charging Charts" (such as the commercial unit charging chart shown here) are provided in service manuals to determine the target suction vacuum (negative) pressure and output pressure for a given compressor motor.
Use of the charging chart for the specific compressor is the correct way to service it. The following example pressures are based on "rules of thumb" that get you in the right "ballpark" if no charging chart is at hand.
Example of actual air conditioner compressor high side output pressure:
Using R-22 refrigerant and assuming an outside air temperature of 85 °F called for 120 °F inside the compressor (add 35 °F to incoming air temperature) and an output high-side compressor pressure of about 260 psi.
Example of actual air conditioner low side input or suction line pressure during operation:
Low-side pressure during normal operation of the same compressor model and refrigerant and the same outdoor air temperature of 85 °F called for 45 °F temperature entering the compressor (subtract 40 °F from incoming air temperature) which on the service chart indicates that the incoming or suction line pressure would be about 75 psi.
Example of a more theoretical air conditioner or heat pump pressure and temperature at the compressor and at the cap tube or thermostatic expansion valve:
During normal operation: at an outdoor temperature of 72 °F, liquid refrigerant (R12 for example) leaving the outdoor condensing coil and entering the cap tube or TEV might be at 100 psi and 95 °F.
These numbers vary by changes in ambient temperature, compressor model, and refrigerant gas used.
On the low side of the TEV or cap tube (in the cooling coil in the air handler) where the liquid refrigerant is changing state to a gas, it may be cooled down to 10 °F. and by the time the refrigerant leaves the cooling coil (evaporator coil) and gets back to the compressor motor it will be all vapor and may be at just 15 psi. [R12 refrigerant changes from liquid to vapor at 14.6 psi at 10 °F.]
Air Conditioner or Heat Pump Refrigerant Equalization Pressure - System-OFF refrigerant pressures
When you measure heat pump or cooling system pressures makes as much difference as where you measure it. When an air conditioning or heat pump system has turned off and been off for some time (30 minutes or more) pressures equalize throughout the system between the high and low sides.
At that point the refrigerant pressure in both the high side and low side of the air conditioner or heat pump system will be in accordance with the ambient air temperature and the properties of the particular refrigerant gas present.
The static or equalized system refrigerant pressure will be defined by the refrigerant gas type (which defines its boiling point and pressure at various temperatures).
For example with that cute old R12 refrigerant, as long as there is just about any refrigerant in the system - enough so that there is some liquid refrigerant, i.e. it's not all just gas) then in equalized condition at 70 psi ambient temperature the refrigerant pressure will be 70 psi.
With a temperature correction chart you can read the static or equalized refrigerant pressure for any refrigerant gas and the actual ambient temperature.
Reminder: this refrigerant gas behavior means that if you use pressure test gauges to measure the refrigerant pressure in the static or equalized air conditioning or heat pump system, the gauges only tell you the refrigerant pressure, not the quantity of refrigerant that is present in the system.
See GAUGE, REFRIGERATION PRESSURE TEST
Correcting R-22 Refrigerant Pressure & Leaks
R-22 Refrigerant Pressure & Leak Correction
If you already know your refrigerant pressures are wrong or that you have a refrigerant leak, please
...
Reader Comments, Questions & Answers About The Article Above
Below you will find questions and answers previously posted on this page at its page bottom reader comment box.
Reader Q&A - also see RECOMMENDED ARTICLES & FAQs
What is the correct pressure for R22 at typical ambient temperature?
I belive there is a mistake when says 30PSI at low side when system is off: When system is OFF, both high and low sides reach an equilibrium pressure, which is much more than the operating pressure. Typically will be around 125 to 140 PSI.
Once the compressor starts, the diferential starts arising: high side will be even higher, low side will be lower, 65 to 855 PSI depending on system temperature and design of evaporator.
Sorry I meant 65 to 85 PSI for pressure of operation, at low side, of course. These values only for R22. R410 is much higher. - On 2024-01-26 by Raul
Reply by InspectApedia Publisher (mod) - when an air conditioning or heat pump system is not running, the high and low side pressures will be the same.
@Raul,
Thank you so much for these helpful comments,.You're absolutely right that when an air conditioning or heat pump system is not running, the high and low side pressures will be the same.
That refrigerant pressure will always be lower than the high side pressure when the system is running and higher than the low side pressure when the system is running.
What the pressure will be depends on the ambient temperature and the particular refrigerant.
Thank you again for the comment, we will review the article above to see what we need to correct or clarify.I have reviewed and corrected the R22 ambient pressures the article above and have given some example R22 pressures at various ambient temperatures.
You're quite right: now readers can take a look at the refrigerant pressure charts given as PDFs in the article above.
For example, R22, at 70 deg F, R22 will be at a pressure of 121.5 psi.For R22 refrigerant to be at 30 psi the ambient temperature would be between 5° and 10° F or -15° to -12° C.
Question: Suction line 73 psi, High Pressure Liquid Line 233 psi. - Equalize to 115psi When System is Off
The pressures on our home AC system (R22) seem fine when operating: suction line 73psi, liquid line 233 psi.
When the system is off, the pressure equalizes to 115psi.
On the manifold I used, the suction gauge indicates anything over 110 psi as in the "danger" zone.
In short, would 115psi on the suction line only be a problem when the system is operating but not when it's off? Thanks! - Pete 6/27/12
Reply:
Pete, Yes I think you're quite right.
When most A/C systems are off for some time, especially older residential designs, pressure equalizes throughout the system and will ultimately be the standard pressure for that refrigerant gas at the ambient temperature, with a little adjustment for altitude above sea level.
Refrigeration gas pressure/temperature charts (from various manufacturers) summarize these properties. For example R22, at 65 degF will stabilize at about 111 psi if memory serves.
How quickly will using the wrong referigerant damage an air conditioning or heat pump system?
Does anybody know how long it takes for air conditioner to go bad if someone put a pound of the wrong refrigerant in an R22 unit?
Photo: water bubble in my ceiling that I think is coming from our damaged attic heat pump.
- On 2023-07-27 by Freedom -
Reply by InspectApedia Publisher (mod) -
@Freedom,
Yes,
From the instant that the HVAC system is turned back ON after charging it with the "wrong" refrigerant, the system is not working properly.
That is not to say that we can predict just what damage might be caused to the equipment.Your photo appears to show a leak bubble in a painted ceiling. If that's what we're looking-at, I'd be looking for a water leak above that area, such as an air conditioner or heat pump condensate leak.
Diagnose weak cooling and ice on the discharge line of my air conditioner
I am having AC of LG make , 12 years old.
I facing a problem of low cooling, The standing oressure is 150 psig and running pressure is 30 psig
Also ice formation occurs at discharge line ,
What could be reason. Low refrigerant or some other? - On 2022-05-22 by Swapnil patil -
Reply by InspectApedia-911 (mod) - causes of ice forming on the refrigerant discharge line
@Swapnil patil,
It's possible that there is a refrigerant leak and that your refrigerant charge is low. That can certainly cause icing.
There are of course other causes such as blocked air flow, dirty air filter, dirty fan, crimped ductwork, or a failure to run defrost cycles.Put another way, high temperature or high pressure on the air conditioner low side is a sign of a problem.
That is, as pressure on the high side goes way up, low side pressure will increase as well, and we may exceed the operating temperature of the system.
The Low side temperature must be low enough to get transfer of heat from the indoor air into the evaporator coil.
The High Side temperature must be high enough to get transfer of heat into the outdoor air.
...
Continue reading at REFRIGERANT PRESSURE READINGS & CHARTS - home, or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- AIR CONDITIONING & HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS - home
- COMPRESSOR CONDENSER - how and why high side and low side pressures in the cooling system enable an air conditioner to move heat from indoors to outdoors.
- DEFINITION of HEATING, COOLING & INSULATION TERMS - home
- DEFINITION of LATENT HEAT
- DEFINITION of SEER RATINGS
- DEFINITION of SENSIBLE HEAT
- DEFINITION of SUBCOOLING
- DEFINITION of SPECIFIC HEAT
- DEFINITION of SUPERHEAT
- OPERATING TEMPERATURES HVAC for a discussion of the typical temperatures at which various types of cooling systems operate.
- PRESSURE CONTROLS & SAFETY SWITCHES
- REFRIGERANT GASES & PIPING - home
- REFRIGERANT LEAK REPAIR
- REFRIGERANT PRESSURE READINGS & CHARTS - home
- SEER RATINGS & OTHER DEFINITIONS - additional definitions of the high side and low side of an air conditioning system.
- SPLIT SYSTEM AC / HEAT PUMP REPAIRS
- THERMOSTATIC EXPANSION VALVE TEV INSTALL, DIAGNOSE, REPAIR - abnormally low or abnormally high suction side pressure
Suggested citation for this web page
R22 REFRIGERANT PRESSURE / TEMPERATURE CHARTS at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to AIR CONDITIONING & HEAT PUMPS
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.


