 Air Conditioner / Heat Pump Operation
Air Conditioner / Heat Pump Operation
How does an Air Conditioner or Heat Pump Work?
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about how to diagnose and repair air conditioning and heat pump systems.
Here in simple language we explain how an air conditioner or heat pump works. We describe each of the major components, explain what it does, and thus what is its purpose in providing cooling, or for a heat pump, either cooling or heating in a building.
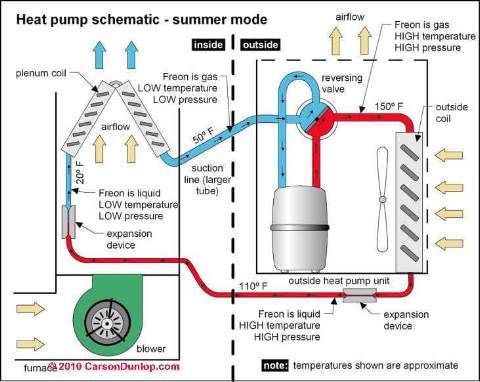
Page top image & air conditioning schematic drawing below were provided courtesy of Carson Dunlop Associates, a Toronto home inspection, education & report writing tool company [ carsondunlop.com ].
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
How an Air Conditioner or Heat Pump Works
Let's introduce the basic concepts of air conditioning: what are the major parts of an air conditioning or heat pump system, where is each of these components, and what does it do?
Just below is a simple explanation of how an air conditioning system works, with enough detail so that it isn't simply magic (the schematic of an air conditioner shown at page top is compliments of Carson Dunlop Associates - a Toronto home inspection, report writing system & education company).
If you prefer, a detailed list and photos of air conditioner components can be seen
at AIR CONDITIONER COMPONENT PARTS.
- An air conditioning or heat pump compressor:
An electric motor found in the compressor/condenser unit (usually outdoors) which compresses low pressure refrigerant gas into a high pressure, high temperature gas. Usually the compressor is in the outdoor portion of an air conditioning or heat pump system.
The air conditioner or heat pump compressor unit is basically a high pressure pump driven by an electric motor.
The air conditioning compressor is usually packaged in the outdoor compressor/condenser unit illustrated by our page top drawing. You won't see the actual motor - it is inside the compressor/condenser unit shown in the photo below.
See COMPRESSOR CONDENSER
and see REFRIGERANT GASES & PIPING.  A condenser or condensing unit:
A condenser or condensing unit:
typically a condensing coil inside which high temperature high pressure refrigerant gas flows, and over which a fan blows air to cool the refrigerant gas back to a liquid state (thus transferring heat from the refrigerant gas to the air being blown by the fan).
The condenser unit is basically a coil of finned tubing and a fan to blow air across the coil.
Usually the condenser unit is in the outdoor portion of an air conditioning system, often packaged along with the compressor motor discussed above.
See COMPRESSOR CONDENSER and see our page top sketch, too. The change of state of the refrigerant, from hot high pressure gas to a liquid releases heat (including heat collected inside the building) to the outdoors.- A refrigerant metering device:
which dispenses liquid refrigerant into an evaporator coil. The metering device may be simply a thin section of tubing (a capillary or "cap" tube) or it may be a bit more sophisticated thermostatic expansion valve (TEV) which includes a temperature sensing control that can open and shut the device against refrigerant flow.
See THERMOSTATIC EXPANSION VALVES
or see CAPILLARY TUBES. - An evaporator coil or cooling coil:
typically the cooling coil is a section of finned tubing (it looks a lot like a car radiator) into which liquid refrigerant is metered and permitted to evaporate from liquid to gas state inside the coil.
This state change of the refrigerant, from liquid to gas, absorbs heat, cooling the evaporator coil surface and thus cooling indoor air blown across the cooling coil. Usually the cooling coil is located inside the air handler.
See AIR HANDLER / BLOWER UNITS and articles
like DIRTY COOLING COIL / EVAPORATOR COIL.
Evaporative cooling systems, or swamp coolers are discussed separately
at EVAPORATIVE COOLING SYSTEMS.  An air handler blower unit:
An air handler blower unit:
which provides a fan to blow building air across or through the evaporator coil.
The air handler blower fan unit moves building air across the evaporator coil surface in order to condition building air by cooling it (and thus also by removing moisture from the cooled air).
See AIR HANDLER / BLOWER UNITS
and BLOWER FAN OPERATION & TESTING.- A duct system
which distributes conditioned air from the air handler in to the occupied space (supply ducts), and which takes air from the occupied space and returns it to the cooling system air handler.
See DUCT SYSTEM.  Heat Pump Systems:
Heat Pump Systems:
use the same components we have described just above, with the addition of
a REVERSING VALVE on HEAT PUMPS
that in essence permits the system to run "backwards" in cold weather.
Split system air conditioners and heat pumps (indoor unit shown in our photo) dispense with a duct system. The wall unit combines a heating or cooling coil and a blower fan to move conditioned air into the room.
In air conditioning mode, the heat pump is moving heat from inside the building to outdoors while in heating mode, the heat pump is moving heat from outdoor air (or water in some designs) to the building interior.
Because the ability of a heat pump to extract heat from outdoor air diminishes at low outdoor temperatures, heat pump systems in northern climates also include a backup or auxiliary heating system.
Details of how heat pumps work, are inspected, diagnosed, and repaired begin
at HEAT PUMPS
Our photo above shows the indoor half of a split system air conditioner or heat pump: the wall mounted unit blows cooled or heated air into the room (if it's a heat pump). Split system air conditioners or heat pumps don't use ductwork to distribute the conditioned air.- Air conditioner controls and features:
which include a room thermostat, electrical switches, fuses or circuit breakers, condensate handling system, and air filters.
See OPERATING CONTROLS
and AIR FILTERS for HVAC SYSTEMS.
Or see THERMOSTATS, HEATING / COOLING for the basics of how to turn the air conditioner on & set room temperature.
...
Reader Comments, Questions & Answers About The Article Above
Below you will find questions and answers previously posted on this page at its page bottom reader comment box.
Reader Q&A - also see RECOMMENDED ARTICLES & FAQs
Question: single phase 208-230V air handler blower motor failure
Drew said:
Have single phase 208-230V air handler blower motor failure. This 1/2 horse Nordyne part number M0023905R motor has a circuit board in the tail cap. There are two (2) 1000 uF caps on that circuit board. Everything on that board has been coated with some type potting compound, and the cap's board attachments are not accessible. I assume these caps are built-in start and run.
Question is: If I replace this motor with a similar H.P., voltage, and frame size (and it does not have built in start and run caps... how should I wire suitable caps to serve.
Thanks in advance for any help. - 2022/08/18
Moderator reply:
Your new motor should come with its own start and run capacitor. You ought to have to do nothing but hook up the motor.
If you find that's not the case, just give us a shout by posting a new comment on this page or better, at
MOTOR CAPACITOR WIRING GUIDE
https://inspectapedia.com/electric/Starting_Capacitor_Wiring.php
...
Continue reading at DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE A/C or HEAT PUMP or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- A/C or HEAT PUMP COMPONENTS
- AIR CONDITIONING & HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS - home
- AIR CONDITIONER / HEAT PUMP OPERATION - how does an air conditioner or heat pump actually work?
- AIR HANDLER / BLOWER UNITS - home
- COMPRESSOR / CONDENSER REPAIR - home
- CONTROLS & SWITCHES on A/C or HEAT PUMP - what and where are all of the controls?
- DIAGNOSTIC GUIDE A/C or HEAT PUMP - first steps to diagnose an air conditioner or heat pump
- MANUALS & PARTS GUIDES - HVAC - home
- SPLIT SYSTEM AC / HEAT PUMP REPAIRS - home
Suggested citation for this web page
AIR CONDITIONER OPERATION - HOW IT WORKS at InspectApedia.com or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to AIR CONDITIONING & HEAT PUMPS
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- [3] Thanks to Jon Bolton, an ASHI, FABI, and otherwise certified Florida home inspector who provided photos of failing Goodman gray flex duct in a hot attic.
- [30] Carson Dunlop, Associates, Toronto, have provided us with (and we recommend) Carson Dunlop Weldon & Associates' TECHNICAL GUIDE to manufacturer's model and serial number information for heating and cooling equipment ($69.00 U.S.).
- [32] FlowKinetics LLC, 528 Helena Street Bryan, Texas 77801 USA, Tel: (979) 680-0659, Email: inform@flowkinetics.com, Website: www.flowkinetics.com, "FKS 1DP-PBM Multi-Function Meter Pressure, Velocity & Flow User’s Manual", web search 07/16/2012, original source: http://www.flowkinetics.com/FKS_1DP_PBM_Manual.pdf [copy on file] and "FKT Series Flow Measurement And Pressure Acquisition System User's Manual" http://www.flowkinetics.com/FKTSeriesManual.pdf [copy on file]
- [33] Histoire de l'Académie royale des sciences avec les mémoires de mathématique et de physique tirés des registres de cette Académie: 363–376. Retrieved 2009-06-19.- Pitot Tubes, Henri Pitot (1732)
- [34] Wikipedia Web: https://www.wikipedia.org/ provided background information about some topics discussed at this website provided this citation is also found in the same article along with a " retrieved on" date. NOTE: because Wikipedia entries are fluid and can be amended in real time, we cite the retrieval date of Wikipedia citations and we do not assert that the information found there is necessarily authoritative.
"Pressure sensor", retrieved 7/16/2012 - In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.

