 Intermittent Sand Filter Septic Systems Design
& Model Regulations
Intermittent Sand Filter Septic Systems Design
& Model Regulations
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about intermittent sand filter wastewater disposal systems: design specifications, installation, testing, maintenance, building codes
Intermittent sand bed and sand filter septic system designs, specifications, model regulations.
This article uses the New York State wastewater treatment standard for individual household septic systems to provide an example of state regulated design and installation of intermittent sand filter septic systems.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
Regulations for the Design of Alternative Septic Systems: Intermittent Sand Filter Septic Systems Design Criteria
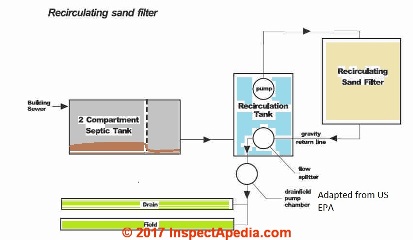
 This document gives New York State's model sand bed septic design specifications.
This document gives New York State's model sand bed septic design specifications.
Original source: Title: Appendix 75-A.9 - Alternative Septic Systems [Regulation and System Design Criteria for Raised Septic Systems, Septic Mound Systems, Intermittent Sand Filter Bed Systems, Evaporation-Transpiration Septic Systems, Evaporation-Transpiration Absorption Septic Systems, and Other Alternative Septic Systems] Effective Date: 12/01/1990
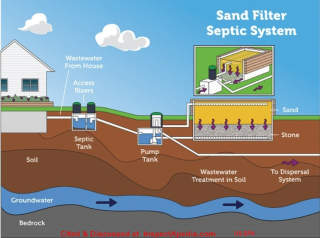
For details about sand bed septic systems like that shown in this EPA illustration, design, installation, inspection, maintenance, or repair, are given in more detail
Also see MEDIA FILTER SEPTIC SYSTEMS - home
(1) Sand Bed Septic Systems - General
In a sand filter septic system, the septic tank or aerobic unit effluent is intermittently spread across the surface of a bed of sand through a network of distribution lines. Collector pipes beneath the filter collect treated effluent after it has passed through the sand.
(2) Site Requirements for Sand Filter Bed Septic Systems
(i) All horizontal separation distances shown in Table 2 must be met and the minimum required vertical separation to groundwater must be met from the bottom of the collector pipes.
(ii) An environmental assessment determines that the development of the site with a sand filter is consistent with the overall development of the area and will cause no adverse environmental impacts.
(3) Design Criteria for Sand Filter Bed Septic Systems
(i) Septic tanks installed before a sand filter shall have dual compartments or two tanks in series. The use of a gas baffle on the outlet is strongly recommended.
(ii) The direct discharge of sand filter effluent to the ground surface or to a body of water shall not be approved by the Department of Health or a local health department acting as its agent.
(iii) Distributor lines shall be placed at three foot center lines as level as possible.
(iv) Collector pipes shall be centered between distribution lines at a slope of 1/16 to 1/8 inch per foot.
(v) Effluent shall be distributed to the sand filter by means of pressure distribution or siphon dosing. Pressure distribution lines shall be a minimum of 1.5 inches and a maximum of three inches in diameter. If siphon dosing is allowed, the distributor pipe(s) shall have a diameter of three to four inches.
(vi) The distribution system shall be designed to dose the filter at least three times daily based upon the design flow rates with each dose.
(vii) The sand media shall have an effective grain size of 0.25 to 1.0 mm. If nitrification is not required by the local health department, the effective grain size shall be in the range of 0.5 to 1.00 mm. All sand shall pass a 1/4 inch sieve.
(viii) The uniformity coefficient of the sand shall not exceed 4.0.
(ix) The maximum allowed daily sand loading rate shall be 1.15 gal/day/sq. ft.
(x) Effluent from the collector pipes shall be discharged to an absorption bed located below the original ground level or a mound that is built up above the original ground surface.
The size of the bed/mound shall be based upon the estimated quantity of effluent reaching the collector pipe and an application rate of 1.2 gal/day/sq. ft. regardless of the underlying soil percolation.
The fill material for the bed/mound shall consist of medium sand with a percolation rate, tested at the borrow pit, not faster than five minutes per inch. All minimum vertical and horizontal separation distances shall be maintained as described in Section 75-A.4.
(4) Construction of Sand Bed Septic Systems
(i) After excavation, the collector pipe shall be placed in 3/4 inches to 1 1/2 inches size aggregate.
(ii) There shall be a minimum of four inches of this aggregate beneath the entire system above the collectors.
(iii) A three inch layer of crushed stone or clean gravel with a size of 1/8 inches to 1/4 inches is carefully placed on top of the aggregate.
(iv) A minimum of 24 inches of the approved sand is placed above the crushed stone or gravel.
(v) The distributor pipes are placed in a layer of aggregate that provides a minimum of four inches across the entire surface of the filter and at least two inches above and below the distributor pipes.
(vi) A permeable geotextile, two inches of hay or straw, or untreated building paper is placed over the entire bed area to prevent the infiltration of fines into the filter.
(vii) The entire surface of the filter shall be covered with six to 12 inches of topsoil, mounded to enhance the runoff of rainwater from the system and seeded to grass.
(viii) The bed/mound following the filter shall be covered with 12 inches of topsoil and seeded to grass.
More About Intermittent Sand Filter Bed Septic Systems is at Continue Reading just below.
Examples of Sand Bed Septic Design Regulations
New York - Appendix 75-A.9 - Alternative Septic Systems [Regulation and System Design Criteria for Raised Septic Systems, Septic Mound Systems, Intermittent Sand Filter Bed Systems, Evaporation-Transpiration Septic Systems, Evaporation-Transpiration Absorption Septic Systems, and Other Alternative Septic Systems] Effective Date: 12/01/1990
Ohio - SAND MOUND SEPTIC DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS [PDF] retrieved 2017/10/20, original source: http://www.odh.ohio.gov/
Ohio - SEPTIC SEPARATION from SEASONAL HIGH WATER LEVEL [PDF] Drainage to manage the level of seasonal water in soils
Also see Bicki, T. J., and R. B. Brown. "ON-SITE SEWAGE DISPOSAL: THE IMPORTANCE OF THE WET SEASON WATER TABLE." [PDF] Journal of Environmental Health 52, no. 5 (1990): 277-279.
...
Continue reading at SAND BED SEPTIC SYSTEMS used as a Component of Alternative Septic Systems for Difficult Sites. This document includes the NYS Appendix 75-A section on sand filter beds as well as sand filter bed design comments and advice from other experts, or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Sandy Soil Septic System Articles
- AEROBIC SEPTIC SYSTEMS, ATUs - home
- SEPTIC CONSULTANTS, DESIGNERS, ENGINEERS
- BAT MEDIA SEPTIC PLANTS
- BED the SEWER LINE in SAND
- MEDIA FILTER SEPTIC SYSTEMS - home
- SAND BED SEPTIC SYSTEMS
- SAND SEPTIC MEDIA FILTERS
- SAND FILTER SEPTIC DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS
- SANDY SOIL SEPTIC DESIGNS
- SEPTIC MEDIA FILTER CAPACITY & MAINTENANCE
- SEPTIC MEDIA FILTER SOURCE LIST
- SEPTIC MEDIA FILTER SYSTEM OPERATION
- SEPTIC SYSTEM DESIGN ALTERNATIVES - home
- SEPTIC SYSTEM DESIGN BASICS - home
- ALTERNATIVE DESIGN SEPTIC SYSTEM SUPPLIERS
- TYPES OF SEPTIC SYSTEMS - master list
Suggested citation for this web page
SAND FILTER SEPTIC DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to SEPTIC SYSTEMS
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Questions & answers or comments about intermittent sand filter wastewater disposal systems: design specifications, installation, testing, maintenance, building codes.
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- New York State Department of Health, APPENDIX 75-A WASTEWATER TREATMENT STANDARDS - INDIVIDUAL HOUSEHOLD SYSTEMS , [PDF] New York State Department of Health, 3 February 2010, retrieved 3/1/2010, original source: https://www.health.ny.gov/regulations/nycrr/title_10/part_75/appendix_75-a.htm
- US EPA ONSITE WASTEWATER TREATMENT SYSTEMS MANUAL [online copy, free] Top Reference: US EPA's Design Manual for Onsite Wastewater Treatment and Disposal, 1980, available from the US EPA, the US GPO Superintendent of Documents (Pueblo CO), and from the National Small Flows Clearinghouse. Original source http://www.epa.gov/ORD/NRMRL/Pubs/625R00008/625R00008.htm Onsite wastewater treatment and disposal systems, Richard J Otis, published by the US EPA. Although it's more than 20 years old, this book remains a useful reference for septic system designers. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water Program Operations; Office of Research and Development, Municipal Environmental Research Laboratory; (1980)
- Advanced Onsite Wastewater Systems Technologies, Anish R. Jantrania, Mark A. Gross. Anish Jantrania, Ph.D., P.E., M.B.A., is a Consulting Engineer, in Mechanicsville VA, 804-550-0389 (2006), Advanced Onsite Wastewater Systems Technologies. Outstanding technical reference especially on alternative septic system design alternatives. Written for designers and engineers, this book is not at all easy going for homeowners but is a text we recommend for professionals--DF.
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.

