Climate Zones & BTU Requirements
Climate Zones & BTU Requirements
Heating & Cooling BTUs by U.S. Climate Zone
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about this article topic.
Climate Zones of North America:
Find here: Climate Zone map for the U.S. giving heating and cooling zones and the definition of climate zones.
We include rules of thumb for estimating the necessary BTUs per square foot for cooling or heating a building in each climate zone.
We also include maximum cooling and mazimum heating requirements based on 30-year temperature averages provided by the U.S. government.
This article series defines Heat Loss, R-value, U-value, & K-Value measures of heating loss rate or insulation effectiveness and provides basic building insulation and heat loss guidelines including how to measure or calculate heat loss in a building.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
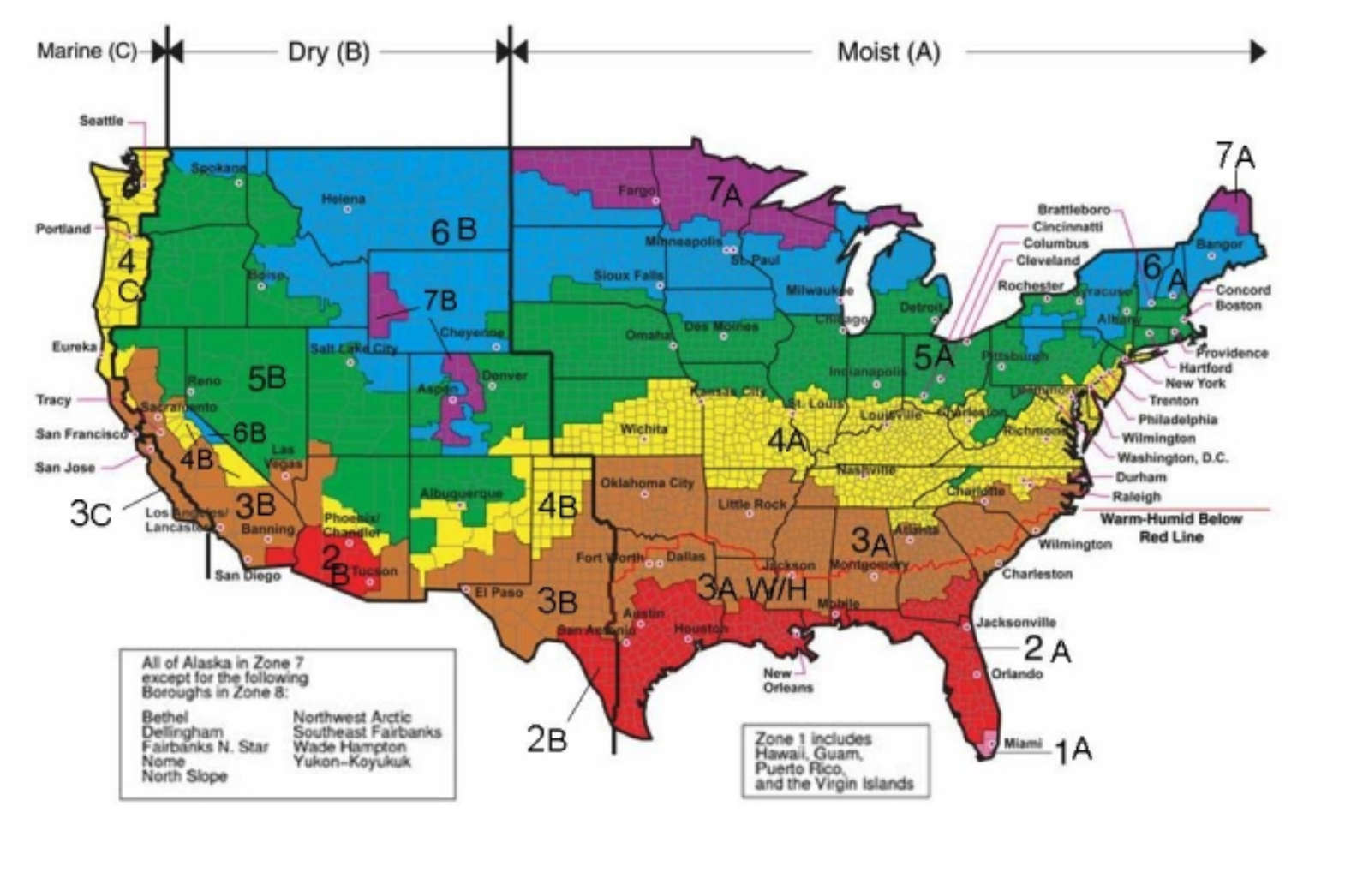
U.S. Climate Zones, Heating, Cooling BTUh Requirements
U.S. Heating Climate zones and Cooling Climate Zones are mapped using the same seven areas shown below, as of the IECC climate zone map provided by the U.S. Department of Energy.
The following map and heating and A/C cooling requirements for the various temperature and climate zones in the United States are adapted from the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE).
Cooling BTUh or A/C size requirements by climate zone are given below at COOLING CLIMATE ZONE BTU REQUIREMENTS.
Heating BTUh or boiler/furnace size requirements by climate zone are given below at HEATING CLIMATE ZONE BTU REQUIREMENTS.
Source: IECC Climate Zone Map, U.S. Department of Energy (US DOE), retrieved 2018/06/21, original source: https://basc.pnnl.gov/images/iecc-climate-zone-map.
Typical Heating BTUh Requirements Per Square Foot
This table of required heating BTUs per square foot is based on the IECC climate zone map shown above.
- Climate Zone 1 - 30-35 BTUs / sq. ft.
- Climate Zone 2 - 35-40 BTUs / sq. ft.
- Climate Zone 3 - 40-45 BTUs / sq. ft.
- Climate Zone 4 - 45-50 BTUs / sq. ft.
- Climate Zone 5 - 50-60 BTUs / sq. ft. (some sources cite 50-55 BTUs / sq.ft.)
- Climate Zone 6 - citation needed; popular heating zone maps for the U.S. do not follow the current DOE climate zone definitions that we accept here.
- Climate Zone 7 - ditto.
Also see GAS BTUH, CUBIC FEET & ENERGY
Required Heating BTUs per Square Foot for each Climate Zone
Below: the table gives Required Heating BTUs per Square Foot for each Climate Zone using the simplified climate zone map above.
Simplified HeatingBTU Requirements |
|
| Heating Zone | Heating BTUs / Sq. Ft. |
| Zone 1 | 30-35 |
| Zone 2 | 35-40 |
| Zone 3 | 40-45 |
| Zone 4 | 45-50 |
| Zone 5 | 50-60 |
Notes to the table above
- Current Source for U.S. Climate Zones Map - U.S. DOE [Website] - retrieved anew 2024/12/22, updated by the DOE thorugh 21 November 2023
- EIA, U.S. Energy Atlas Climate Zones - DOE Building America Program [Website] - retrieved 2024/12/22
Excerpt: This map layer depicts the climate zone designations used by the U.S. Department of Energy Building America Program by county boundaries (generalized).
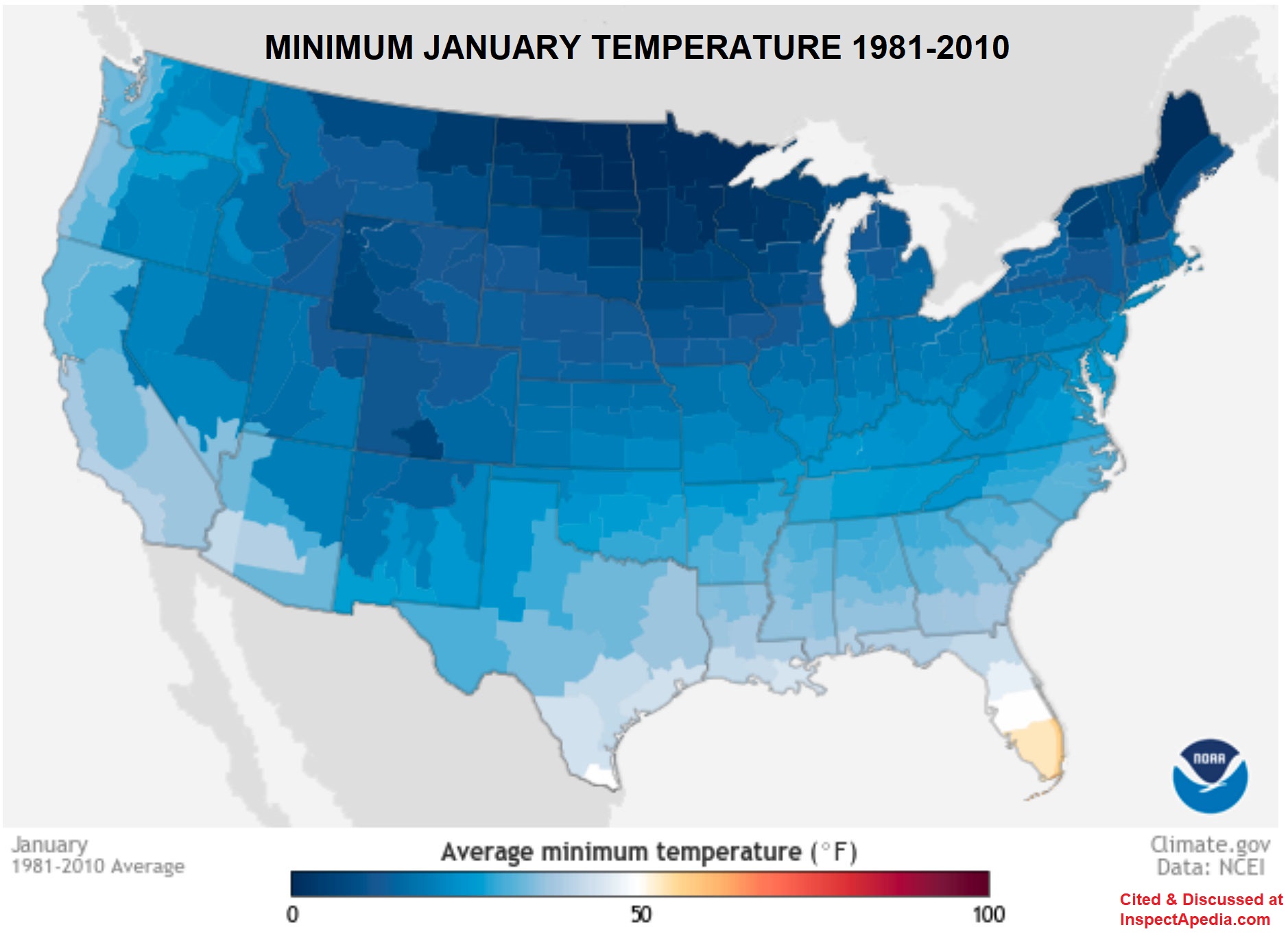
U.S. 30-Year Average January Temperatures = peak heating need
Below: The 30-year average minimum temperatures reached in January across the U.S. between 1981 and 2010 - source: U.S. climate.gov retrieved 2021/06/08
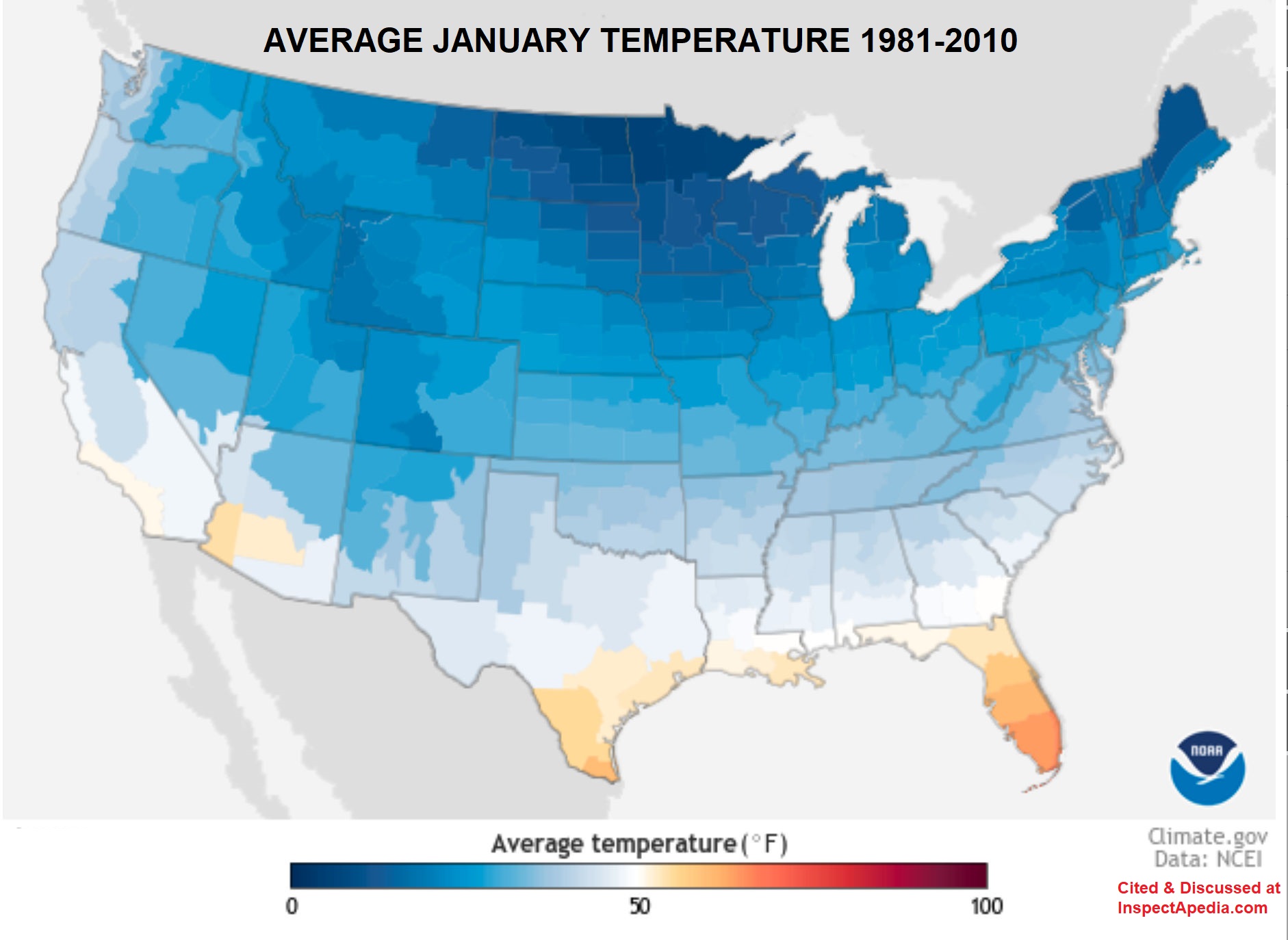
Below: The 30-year average temperature for the month of January across the U.S. between 1981 and 2010 - source: U.S. climate.gov retrieved 2021/06/08
Typical Cooling BTUh Requirements per Square Foot
This table of required cooling BTUs per square foot is based on a similar cooling zone map but that includes 8 cooling zones, described in the table.
Air Conditioner Heat Pump Tons Needed by Cooling Zone - ballpark3 |
|||
| Climate Zone1 | Square Feet | Required Cooling BTUs or A/C Tons | Example Climate Zone Areas |
Zone 1 Hottest |
1 | 50-60 BTUh | Tons x 12,000 = BTUh Tip of Florida See IECC RESIDENTIAL PRESCRIPTIVE REQUIREMENTS below |
| 600-900 sq.ft. | 1.5 Tons / 18,000 BTUh | ||
| 900-1200 | 2 | ||
| 1200 - 1500 | 2.5 | ||
| 1500 - 1800 | 3 | ||
| Zone 2 | 1 | 45-50 BTUh | Most of Florida, Southern Texas, South Georgia |
| 600-950 | 1.5 | ||
| 950-1250 | 2 | ||
| 1250 - 1550 | 2.5 | ||
| 1550 - 2000 | 3.7 - 4.7 | ||
| 2000 - 2600 | 4.7 - 6 | ||
| 2600 - 3500 | 6 to 8 | ||
Zone 3 Moderate |
1 | 40-45 BTUh | Central Texas, Central Georgia, South Carolina, Central GeorgiaCentral Texas, Central Georgia, South Carolina, Central Georgia, most of California |
| 600 - 1000 | 1.5 | ||
| 1000 - 1300 | 2 | ||
| 1300 - 1600 | 2.5 | ||
| 1600 - 1900 | 3 | ||
| 1900-2500 | 3 Note 5 | ||
| Zone 4 | 1 | 35-40 BTUh | North Texas Panhandle, Washington State, Southern Michigan, Southern New York, Virginia, North Georgia |
| 700 - 1050 | 1.5 | ||
| 1050 - 1350 | 2 | ||
| 1350 - 1600 | 2.5 | ||
| 1600 - 2000 | 3 | ||
Zone 5 Cool |
1 | 30-35 BTUh | Most of Washington State, Southern Michigan, Western New York, most of Pennsylvania, Northern California & Coastal, Boston area |
| 700 - 1100 | 1.5 | ||
| 1100 - 1400 | 2 | ||
| 1400 - 1650 | 2.5 | ||
| 1650 - 2100 | 3 | ||
| 2100 - 2500 | 3.2 - 3.7 | ||
| 2500 - 3000 | 3.7 - 4 | ||
| 3000 - 3500 | 3.7 - 5.1 | ||
Zone 6 Cooler |
1 | Northeast Washington State, Northern Michigan peninsula, Central New York North, Southern Wisconsin | |
| citation needed | 2 | ||
| 2.5 | |||
| 3 | |||
Zone 7 Cold |
1.5 | Southern Minnesota, Most of Maine, Most of Northern Michigan, Northern Wisconsin | |
| citation needed | 2 | ||
| 2.5 | |||
| 3 | |||
Zone 8 Coldest |
1.5 | Northern Minnesota, Northern Maine, Most of Northern Michigan, Northern Wisconsin | |
| citation needed | 2 | ||
| 2.5 | |||
Notes to the table above
- IECC RESIDENTIAL PRESCRIPTIVE REQUIREMENTS, 2009 IECC International Energy Conservation Code defines eight climate zones in the U.S. and provides an interactive heating or cooling zone map, retrieved 2018/06/21, original source: https://energycode.pnl.gov/EnergyCodeReqs/
- U.S. Department of Energy, CLIMATE ZONES [PDF] retrieved 2018/06/21, original source: https://www.energy.gov/eere/buildings/climate-zones
- Watch out: Some HVACR equipment installers warn that just using a BTUh multiplier x square feet is not a very accurate way to estimate the heating or cooling load for your building.
That's because the heat gain or loss will be very different in different rooms or areas of the building such as those facing the sun, those with more windows, etc. - If you are looking for heating BTUh requirements
see HEATING CLIMATE ZONE BTU REQUIREMENTSAlso see DEGREE DAY HEATING DEGREE DAYS or COOLING DEGREE DAYS
- U.S. Energy Star Program Air Conditioner Sizing recommendations, retrieved 2019/09/27 original source: https://www.energystar.gov/index.cfm?c=roomac.pr_properly_sized.
Watch out: this source does not relate cooling requirements to cooling zones in the U.S. - Note that for "cold" climate zones 7 and 8 in the table above typical government energy sources don't give complete cooling load BTU requirement data.
The US DOE link above provides additional building specifications for each heating zone such as recommended insulation levels.
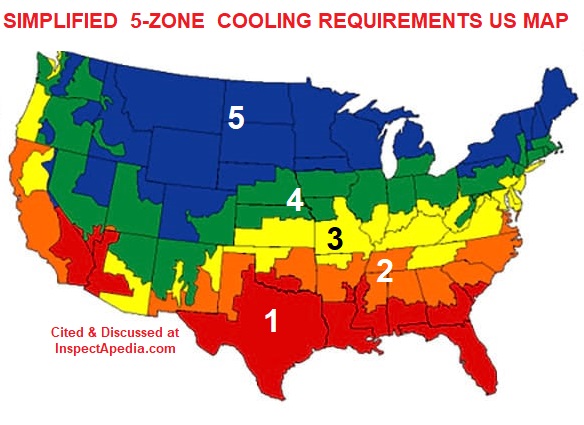
Alternative Cooling BTU Requirements Zone Map
Below is a simplified 5 Climate Zone Map for the U.S.
Below: the table gives Required Cooing or Air Conditioning BTUs per Square Foot for each Climate Zone using the simplified climate zone map above. An updated version of the U.S. climate zone map from the US EIA is shown after the table given below.
| Simplified Cooling BTU Requirements per 1000 Square Feet of Area |
Cooling Capacity |
| Zone | BTUs / Sq. Ft. |
| Zone 1 | 50-60 BTUh |
| Zone 2 | 45-50 BTUh |
| Zone 3 | 40-45 BTUh |
| Zone 4 | 35-40 BTUh |
| Zone 5 | 30-35 BTUh |
| General Rule of Thumb for room A/C units | 20 BTUs |
Notes to the table above
- 1 ton cooling capacity = 12,000 BTUs
- Zone 5 also includes Alaska
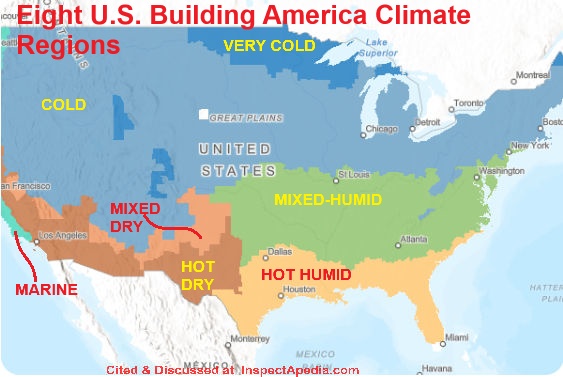
- CURRENT CLIMATE ZONES MAP - U.S. EIA [Website] - retrieved 2024/12/23 and shown below with annotations added by the InspectApedia editors.
Website excerpt:
This data for this layer [and the map below] is taken from
Building America Best Practices Series, Volume 7.3 - GUIDE to DETERMINIG CLIMATE REGIONS by COUNTY PDF] (2015) - local copy saved as Climate_region_guide_7.3.pdf
This document includes detailed climate zone information for every county in the U.S.
Website excerpt:
The eight U.S. Building America climate regions described here [shown on the map above] are based on the climate designations used by the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) and the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE).
The IECC climate zone map was developed by DOE researchers at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory with input from Building America team members, in particular Joseph Lstiburek of Building Science Corporation.
The IECC map was developed to provide a simplified, consistent approach to defining climate for implementation of various codes; it was based on widely accepted classifications of world climates that have been applied in a variety of different disciplines.
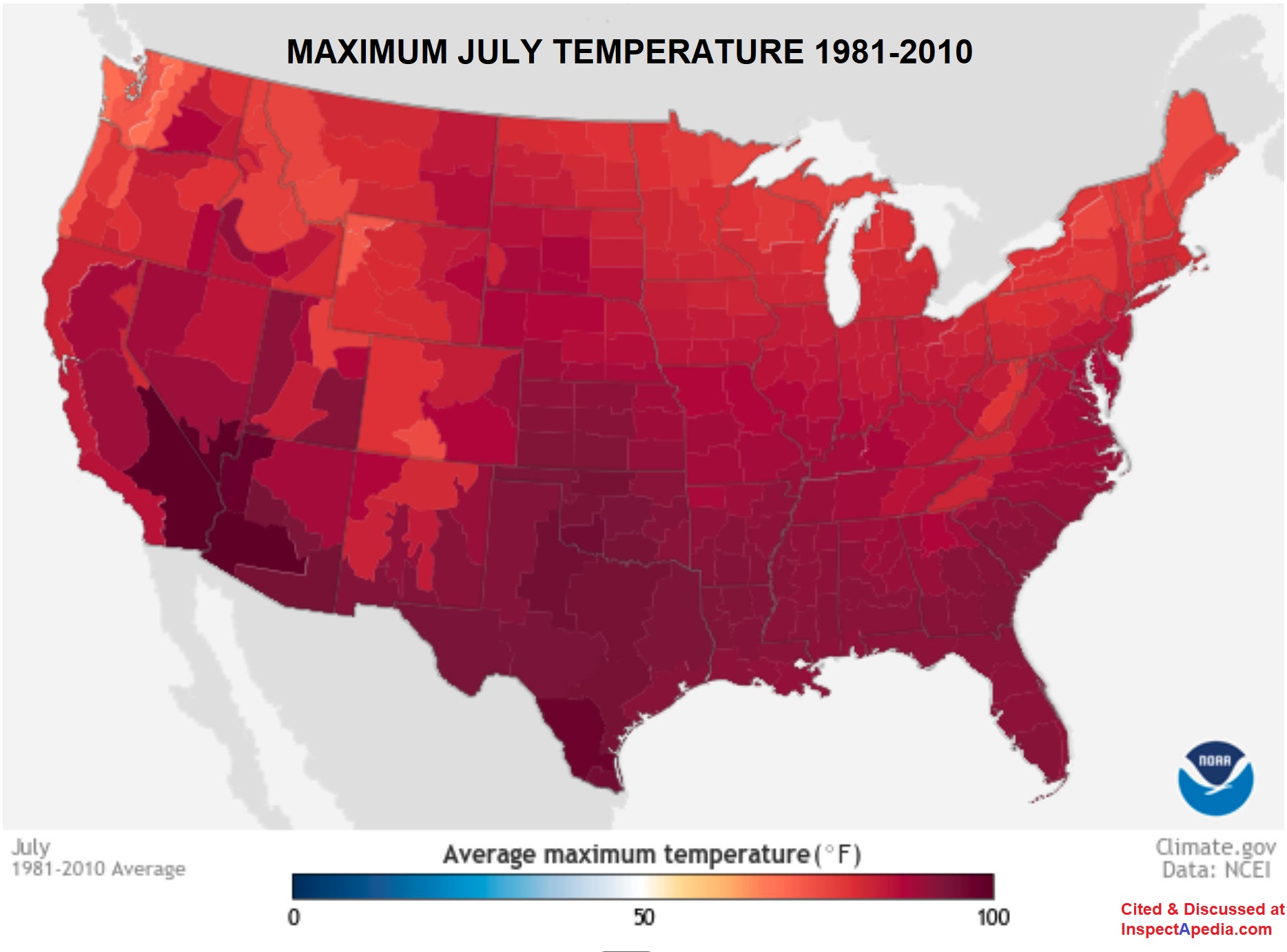
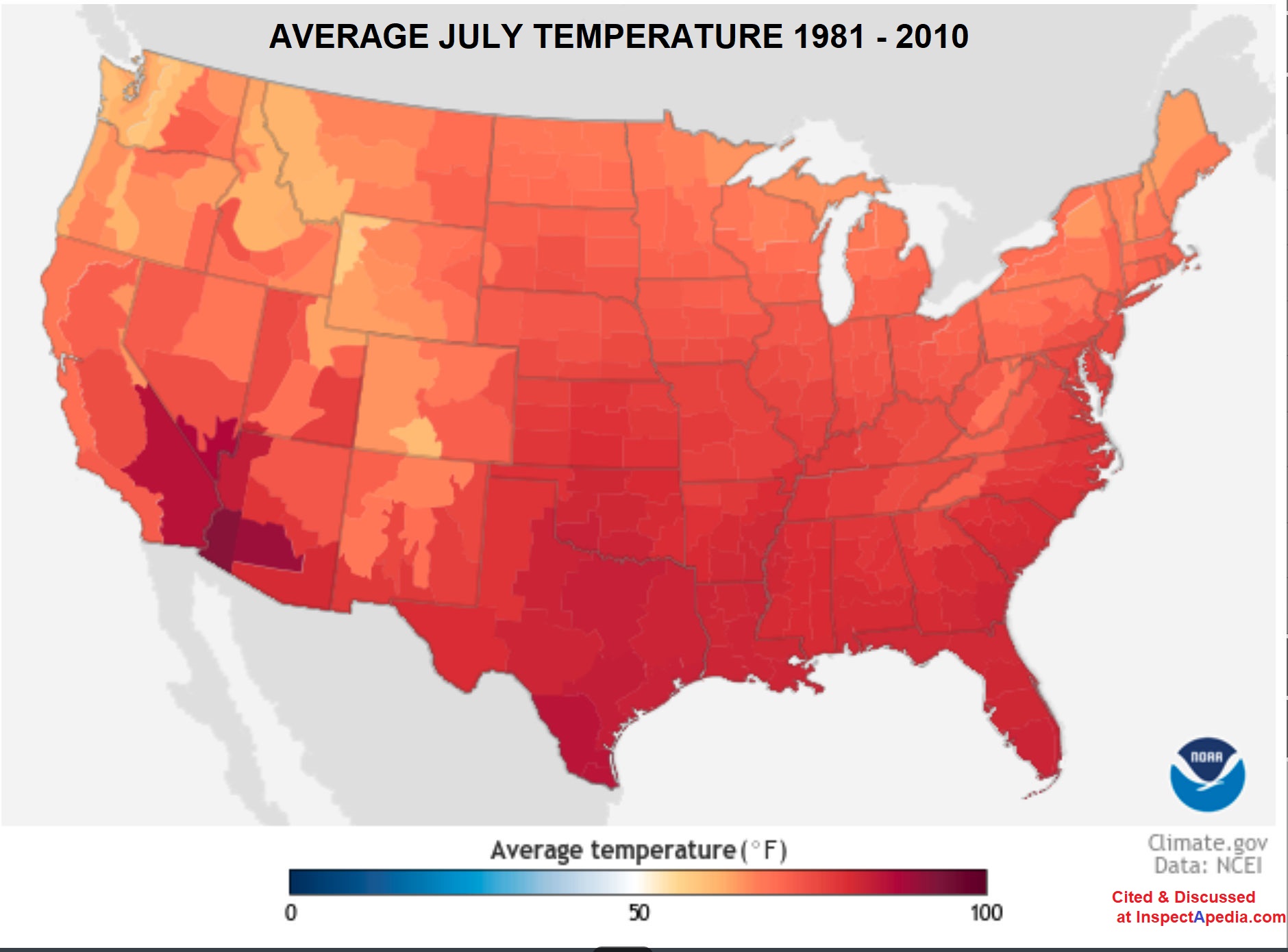
U.S. 30-Year Average July Temperatures = peak cooling need
Below: The 30-year average maximum temperatures reached in July across the U.S. between 1981 and 2010 - source: U.S. climate.gov retrieved 2021/06/08
Below: The 30-year average temperature for the month of July across the U.S. between 1981 and 2010 - source: U.S. climate.gov retrieved 2021/06/08
What is the Relationship of Cooling Capacity and Dehumidification?
Tons of ice does not, however, explain an important factor in the comfort produced by air conditioning systems, reduction of indoor humidity - that is, removing water from indoor air. Cool air holds less water (in the form of water molecules or gaseous form of H2O) than warm air.
Think of the warmer air as having more space between the gas molecules for the water molecules to remain suspended.
When we cool the air, we in effect are squeezing the water molecules out of the air. When an air conditioner blows warm humid building air across an evaporator coil in the air handler unit, it is not only cooling the air, it is removing water from that air.
Both of these effects, cooler air and drier air, increase the comfort for building occupants.
One ton of cooling capacity equals 12,000 BTU's/hour of cooling capacity.
Also see
DEW POINT CALCULATION for WALLS
How do we measure cooling or heating efficiency: the relationship between BTUs and cooling or heating operating cost?
Note that the BTU rating of an air conditioner itself does not tell you how economically those tons of cooling capacity are being produced.
For the answer to that question see SEER RATINGS & OTHER DEFINITIONS for air conditioners and heat pumps.
...
Reader Comments, Questions & Answers About The Article Above
Below you will find questions and answers previously posted on this page at its page bottom reader comment box.
Reader Q&A - also see RECOMMENDED ARTICLES & FAQs
How many BTU's are needed for Hennepin County Minnesota?
How many BTU's are needed for Hennepin County Minnesota? - On 2021-06-08 by Anonymous -
Replyu by (mod) - Heating BTU's needed for Hennepin County Minnesota
@Anonymous,
Hennepin County in our state (Minnesota) is considered in climate zone 7 or northern Hennepin possibly zone 8 - as given in the climate zone TABLE above. Or zones 6 & 7 using the older climate zone MAP.
Short answer: you need between 1.5 thousand and 3 thousand BTUs.
Detailed Answer:
But from your question alone nobody can tell you how many BTUs you need to heat or cool your home.
To make a useful and credible estimate of the heating or cooling BTU requirements for your building you really need building specifics:
- its air-leakiness
- the R-value of insulation in the building's walls and ceilings
and to some extent also
- the shape of the building: a 2000 square foot building that is all on one level will have different heating and cooling requirements than one that is stacked up in four 500 sqft floors.
I'm embarrassed to say that our heating/cooling BTUs per Square Foot heating and cooling zone TABLE (shown above on this page) is fuzzy for zones 6 and 7 which include Minnesota - where we state
"popular heating zone maps for the U.S. do not follow the current DOE climate zone definitions that we accept here" for Minnesota and other parts of the northern U.S.
Using the IECC map (also on the page above) you're in zone 6 or northern MN zone 7
Or using the older IECC map that
So when we put this article together using the best data we could find, we're left with: for southern MN (zone 6)
Continuing:
Using a typical HEATING zone BTU calculator, for zone 6 you need about 55,000 BTUs per 1000 square feet of home area
Using a typical COOLING zone BTU calculator, for zone 6 you need about 22,000 BTUs per 1000 square foot of home area
Thank you for a helpful question
How many BTUS are recommended for Wallowa County Oregon
How many BTUS are recommended for Wallowa County Oregon. Depending on the map I view it seems to fall into different zones. Zone 5 shows up a lot however. Im using Radiant floor heat in a 5 inch concrete slab.
Thanks very much On 2020-10-10
by Tom
Reply by (mod) - Heating BTUS recommended for Wallowa County Oregon
Tom
To determine how many BTUs you need for your home in Oregon choose heating zone 4 (or 5 if you prefer)
and then
take note of the number of square feet of your home; without square feet there is no reasonable estimate of BTUs that would make sense.
Watch out: Consider that homes vary widely in heat loss rate. In a poorly-sealed building, air leaks alone can overwhelm even very high-R insulated walls and ceilings.That's why we must take all of these heating and cooling BTU requirements with a grain of salt (or a cube ice).
Consider also that with a radiant floor heating system in a 5-inch concrete slab, the success of that heating system depends enormously on just how the radiant heat system was installed.
If the tubing is too deep in the slab (not in the top 2") or if the slab was not properly and completely insulated from the ground, then the radiant heating system may not ever work successfully.
See RADIANT HEAT MISTAKES
What are the BTU requirements for larger houses?
Your tonnage estimate chart only covers small houses. What about houses 2000 to 4000 sq ft - On 2019-09-26
by Anonymous -
Reply by (mod) - BTU requirements for large houses
Thanks for asking Anon;
I have added some data for larger square-foot homes in the tables above.
You can also use the "BTUS per Square Foot" figure to calculate cooling or heating loads.
To make sense of these requirements it's important to note
- the heating or cooling zone in which the building is located
- the building's air leakage rate
- the building's sun exposure
- the building's insulation and its ventilation rate
and there are some more subtle factors that count such as
- ceiling height
- number of building occupants
- presence of equipment that adds to cooling loads in a building
- use of other energy savings features such as low-E glass in windows and doors
...
Continue reading at DEFINITION of HEATING, COOLING & INSULATION TERMS or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- DEGREE DAY HEATING DEGREE DAYS or COOLING DEGREE DAYS
- DEW POINT TABLE - CONDENSATION POINT GUIDE
- ENERGY SAVINGS PRIORITIES
- SEER RATINGS & OTHER DEFINITIONS for air conditioners and heat pumps.
Suggested citation for this web page
CLIMATE ZONES for the U.S. at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to DEFINITIONS
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Questions & answers or comments about the definitions of heating & cooling terms.
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- Thanks to reader Peter J. Collins for discussing and helping clarify definitions of R U and K - August 2010
- "Solar Heat Gain & Windows, the facts about", NFRC, National Fenestration Rating Council, January 2005, NFRC website: www.nfrc.org retrieved 12/4/2010, original source: http://www.nfrc.org/documents/SolarHeatGain.pdf.
- ASHRAE resources on building insulation, dew point and wall condensation - see the ASHRAE Fundamentals Handbook, available in many libraries.
- 2005 ASHRAE Handbook : Fundamentals: Inch-Pound Edition (2005 ASHRAE HANDBOOK : Fundamentals : I-P Edition) (Hardcover), Thomas H. Kuehn (Contributor), R. J. Couvillion (Contributor), John W. Coleman (Contributor), Narasipur Suryanarayana (Contributor), Zahid Ayub (Contributor), Robert Parsons (Author), ISBN-10: 1931862702 or ISBN-13: 978-1931862707
- 2004 ASHRAE Handbook : Heating, Ventilating, and Air-Conditioning: Systems and Equipment : Inch-Pound Edition (2004 ASHRAE Handbook : HVAC Systems and Equipment : I-P Edition) (Hardcover) by American Society of Heating, ISBN-10: 1931862478 or ISBN-13: 978-1931862479
- 1996 Ashrae Handbook Heating, Ventilating, and Air-Conditioning Systems and Equipment: Inch-Pound Edition (Hardcover), ISBN-10: 1883413346 or ISBN-13: 978-1883413347 ,
- Principles of Heating, Ventilating, And Air Conditioning: A textbook with Design Data Based on 2005 AShrae Handbook - Fundamentals (Hardcover), Harry J., Jr. Sauer (Author), Ronald H. Howell, ISBN-10: 1931862923 or ISBN-13: 978-1931862929
- 1993 ASHRAE Handbook Fundamentals (Hardcover), ISBN-10: 0910110964 or ISBN-13: 978-091011096
- Principles of Heating, Ventilating, And Air Conditioning: A textbook with Design Data Based on 2005 ASHRAE Handbook - Fundamentals, Harry J., Jr. Sauer, Ronald H. Howell, William J. Coad.
- Super-Insulated Retrofit Book: A Homeowner's Guide to Energy-Efficient Renovation, Robert Argue
- The super-insulated retrofit book: A homeowner's guide to energy-efficient renovation (Sun builders series), Brian Marshall
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.