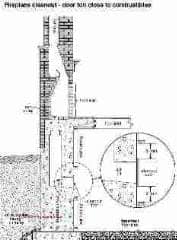
 Chimney Cleanout Door
Fire Clearance Distance
Chimney Cleanout Door
Fire Clearance Distance
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about chimney cleanout doors & fire safety
Fire clearance to combustibles for chimney cleanout opening doors:
What is the required distance between a chimney cleanout door and the nearest combustible material? Chimney Cleanouts are required but must be at a safe distance from combustibles.
This article describes fire clearances for chimney cleanout doors. We also explain some of the other hazards associated with chimney cleanout doors. These articles on chimneys and chimney safety provide detailed suggestions describing how to perform a thorough visual inspection of chimneys for safety and other defects. Chimney inspection methods and chimney repair methods are also discussed.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
Chimney Cleanout Doors Left Open or Close to Combustibles
 A missing chimney cleanout door or a cleanout door left open means that there is a fire safety
hazard (sparks or ashes falling out onto the basement floor) and also
that it is impossible to control the draft in the flue.
A missing chimney cleanout door or a cleanout door left open means that there is a fire safety
hazard (sparks or ashes falling out onto the basement floor) and also
that it is impossible to control the draft in the flue.
[Click to enlarge any image]
we have found heating boilers with draft problems and "repair attempts" like removing the boiler's barometric damper, when all the while the root problem of bad chimney draft was that the cleanout door was open or missing.
A missing chimney cleanout door is most serious because it is unsafe.
But a missing cleanout door or simply a cleanout door that is left ajar makes it very difficult for the chimney to develop adequate draft.
In turn this means that a fireplace or an oil or gas fired heating appliance may be both unsafe (carbon monoxide gas, fire hazards) and also in poor operating state.
For example on oil fired heating systems and some fireplace chimneys we've found a draft inducer installed on a chimney to cope with inadequate draft when the root problem was a basement cleanout door that had fallen off.
On gas fired appliances, inadequate draft from a missing chimney door could lead to dangerous or even fatal carbon monoxide poisoning in a building.
See CARBON MONOXIDE
Chimney Cleanout Codes IFGC 2015
501.15.3 Cleanout.
Masonry chimney flues shall be provided with a cleanout opening having a minimum height of 6 inches (152 mm).
The upper edge of the opening shall be located not less than 6 inches (152 mm) below the lowest chimney inlet opening.
The cleanout shall be provided with a tight-fitting, noncombustible cover.
- 2015 CHAPTER 5, CHIMNEYS AND VENTS, SECTION 501 (IFGC), [PDF] (2015) Seattle building code, Retrieved 2017/07/22, original source: http://www.seattle.gov/dpd/cs/groups/pan/@pan/documents/web_informational/p2622099.pdf
...
Reader Comments, Questions & Answers About The Article Above
Below you will find questions and answers previously posted on this page at its page bottom reader comment box.
Reader Q&A - also see RECOMMENDED ARTICLES & FAQs
Question:
(Dec 16, 2014) Jim said:
By typical code, how far do combustibles have to be from the chimney cleanout door? I'd like an answer in inches and feet. My chimney, which I've not used yet, needs both a ash dump door and a ash dump cleanout door. The masonry openings for both are in great shape, and are the proper sizes to utilize standard doors.
When I bought the house, believe it or not, the ash dump cleanout port (NOTE: no door) was covered with insulation and drywall. Very hazardous. I know.
I'd like to refinish the basement walls, again, with drywall and insulation, with proper clearance from the cleanout door. (Horizontal and vertical clearance requirements would be nice.) I don't intend to use the ash pit myself; I plan to clean the fireplace after every use.
This is the first house I've ever been in with an ash pit, so, personally, I am reluctant to use it. Seems like a real potential for messes and hazards
(Dec 16, 2014) Jim said:
Nevermind.....the answer is in the drawing itself at CHIMNEY CLEANOUT CLEARANCE to COMBUSTIBLES. I'll be sure to allow more than the 6" minimum distance from the door opening. That seems to be a little close for my concerns. I'll probably not have any wall/framing below the door, at a minimum.
Thanks.
Reply:
Thanks Jim. I agree that 6" is a minimum standard.
And watch out: inspect ash pit construction with care; sometimes we find problems with combustibles left in the structure where they don't belong, or shared flues whose draft can be a problem.
...
Continue reading at CHIMNEY CLEANING PROCEDURE or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- CHIMNEY CLEANOUT CLEARANCE to COMBUSTIBLES
- CHIMNEY CLEANING FRAUD
- CHIMNEY CLEANING PROCEDURE
- CHIMNEY HEIGHT & CLEARANCE CODE
- CHIMNEY INSPECTION DIAGNOSIS REPAIR - home
- DIRECT VENTS / SIDE WALL VENTS
- FIRE CLEARANCES, FLUE VENT CONNECTORS
- FIRE CLEARANCES, METAL CHIMNEYS
- MASONRY CHIMNEY GUIDE - home
- METAL CHIMNEYS & FLUES
Suggested citation for this web page
CHIMNEY CLEANOUT CLEARANCE to COMBUSTIBLES at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to CHIMNEYS & FLUES
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- NFPA #211-3.1 1988 - Specific to chimneys, fireplaces, vents and solid fuel burning appliances.
- NFPA # 54-7.1 1992 - Specific to venting of equipment with fan-assisted combustion systems.
- GAMA - Gas Appliance Manufacturers' Association has prepared venting tables for Category I draft hood equipped central furnaces as well as fan-assisted combustion system central furnaces.
- National Fuel Gas Code, an American National Standard, 4th ed. 1988 (newer edition is available) Secretariats, American Gas Association (AGA), 1515 Wilson Blvd., Arlington VA22209, and National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), Batterymarch Park, Quincy MA 02269. ANSI Z223.1-1988 - NFPA 54-1988. WARNING: be sure to check clearances and other safety guidelines in the latest edition of these standards.
- Fire Inspector Guidebook, A Correlation of Fire Safety Requirements Contained in the 1987 BOCA National Codes, (newer edition available), Building Officials and Code Administrators International, Inc. (BOCA), Country Club HIlls, IL 60478 312-799-2300 4th ed. Note: this document is reissued every four years. Be sure to obtain the latest edition.
- Uniform Mechanical Code - UMC 1991, Sec 913 (a.) Masonry Chimneys, refers to Chapters 23, 29, and 37 of the Building Code.
- New York 1984 Uniform Fire Prevention and Building Code, Article 10, Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning Requirements
- New York 1979 Uniform Fire Prevention & Building Code, The "requirement" for 8" of solid masonry OR for use of a flue liner was listed in the One and Two Family Dwelling Code for New York, in 1979, in Chapter 9, Chimneys and Fireplaces, New York 1979 Building and Fire Prevention Code:
- "Top Ten Chimney (and related) Problems Encountered by One Chimney Sweep," Hudson Valley ASHI education seminar, 3 January 2000, contributed by Bob Hansen, ASHI
- Chimney Inspection Checklist, Carson Dunlop, Associates, Toronto, Ontario
- "Rooftop View Turns to Darkness," Martine Costello, Josh Kovner, New Haven Register, 12 May 1992 p. 11: Catherine Murphy was sunning on a building roof when a chimney collapsed; she fell into and was trapped inside the chimney until rescued by emergency workers.
- "Chimneys and Vents," Mark J. Reinmiller, P.E., ASHI Technical Journal, Vol. 1 No. 2 July 1991 p. 34-38.
- "Chimney Inspection Procedures & Codes," Donald V. Cohen was to be published in the first volume of the 1994 ASHI Technical Journal by D. Friedman, then editor/publisher of that publication. The production of the ASHI Technical Journal and future editions was cancelled by ASHI President Patrick Porzio. Some of the content of Mr. Cohen's original submission has been included in this more complete chimney inspection article: CHIMNEY INSPECTION DIAGNOSIS REPAIR . Copies of earlier editions of the ASHI Technical Journal are available from ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
- Natural Gas Weekly Update: http://tonto.eia.doe.gov/oog/info/ngw/ngupdate.asp Official Energy Statistics from the U.S. Government
- US Energy Administration: Electrical Energy Costs http://www.eia.doe.gov/fuelelectric.html
- Our recommended books about building & mechanical systems design, inspection, problem diagnosis, and repair, and about indoor environment and IAQ testing, diagnosis, and cleanup are at the InspectAPedia Bookstore. Also see our Book Reviews - InspectAPedia.
- Ceramic Roofware, Hans Van Lemmen, Shire Library, 2008, ISBN-13: 978-0747805694 - Brick chimneys, chimney-pots and roof and ridge tiles have been a feature of the roofs of a wide range of buildings since the late Middle Ages. In the first instance this ceramic roofware was functional - to make the roof weatherproof and to provide an outlet for smoke - but it could also be very decorative. The practical and ornamental aspects of ceramic roofware can still be seen throughout Britain, particularly on buildings of the Victorian and Edwardian periods. Not only do these often have ornate chimneys and roof tiles but they may also feature ornamental sculptures or highly decorative gable ends. This book charts the history of ceramic roofware from the Middle Ages to the present day, highlighting both practical and decorative applications, and giving information about manufacturers and on the styles and techniques of production and decoration. Hans van Lemmen is an established author on the history of tiles and has lectured on the subject in Britain and elsewhere. He is founder member and presently publications editor of the British Tiles and Architectural Ceramics Society.
- Chimney Inspection Checklist, Carson Dunlop, Associates, Toronto, Ontario
- Chimney & Stack Inspection Guidelines, American Society of Civil Engineers, 2003 - These guidelines address the inspection of chimneys and stacks. Each guideline assists owners in determining what level of inspection is appropriate to a particular chimney and provides common criteria so that all parties involved have a clear understanding of the scope of the inspection and the end product required. Each chimney or stack is a unique structure, subject to both aggressive operating and natural environments, and degradation over time. Such degradation may be managed via a prudent inspection program followed by maintenance work on any equipment or structure determined to be in need of attention. Sample inspection report specifications, sample field inspection data forms, and an example of a developed plan of a concrete chimney are included in the guidelines. This book provides a valuable guidance tool for chimney and stack inspections and also offers a set of references for these particular inspections.
- Fireplaces, a Practical Design Guide, Jane Gitlin
- Fireplaces, Friend or Foe, Robert D. Mayo
- NFPA 211 - Standards for Chimneys & Fireplaces, NFPA 211: Standard for Chimneys, Fireplaces, Vents, and Solid Fuel-Burning Appliances, 2006 Edition (older editions and standards are found at the same bookstore)
- Principles of Home Inspection: Chimneys & Wood Heating, in (Principles of Home Inspection), Carson Dunlop, Associates, Toronto, Ontario
- U.S. vs. Canadian Unlined Masonry Chimney Flue Requirements & Case Study
- NFPA 211 - 3-1.10 - Relining guide for chimneys
- NFPA 211 - 3-2 - Construction of Masonry Chimneys
- NFPA 211 - 3-3 - Termination Height for chimneys
- NFPA 211 - 3-4 - Clearance from Combustible Material
- NFPA 54 - 7-1 - Venting of Equipment into chimneys
- Brick Institute of America - Flashing Chimneys
Brick Institute of America - Proper Chimney Crowns
Brick Institute of America - Moisture Resistance of Brick - American Gas Association - New Vent Sizing Tables
- Chimney Safety Institute of America - Chimney Fires: Causes, Effects, Evaluation
- National Chimney Sweep Guild - Yellow Pages of Suppliers
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.

