 Radon Measurement Guide for Homeowners & Home Inspectors
Radon Measurement Guide for Homeowners & Home Inspectors
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about methods for measuring the hazard level of radon gas in buildings
Best ways to measure radon:
This article explains procedures for measuring the indoor exposure to radon gas in air or water, and we describe the proper steps to remove radon and improve indoor air quality in homes.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
Guide to Measuring Radon - Sources of Home Test Kits for Radon & Radon Action Level Definition
 This article includes excerpts or adaptations from Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction (Steve Bliss, J Wiley & Sons) , by Steven Bliss, courtesy of Wiley & Sons.
This article includes excerpts or adaptations from Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction (Steve Bliss, J Wiley & Sons) , by Steven Bliss, courtesy of Wiley & Sons.
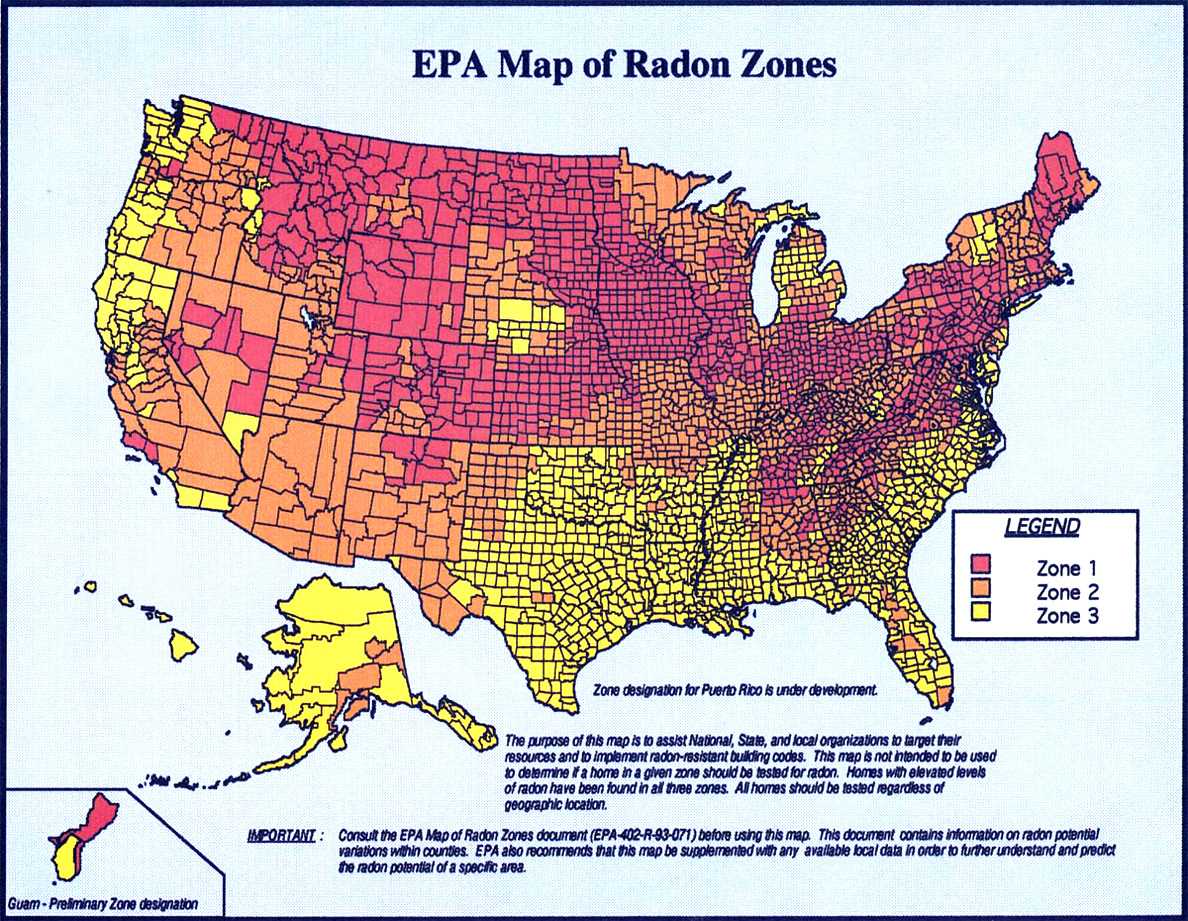
While some regions of the country have more homes with elevated radon levels, high indoor levels can occur anywhere.
[Click to enlarge any image]
For that reason, the EPA recommends that all homes be tested. Although soil testing is possible prior to building, there is currently no reliable way to predict what household levels will be until a home is completed.
Testing indoor levels is straightforward, using inexpensive test kits available from hardware stores or by mail order.
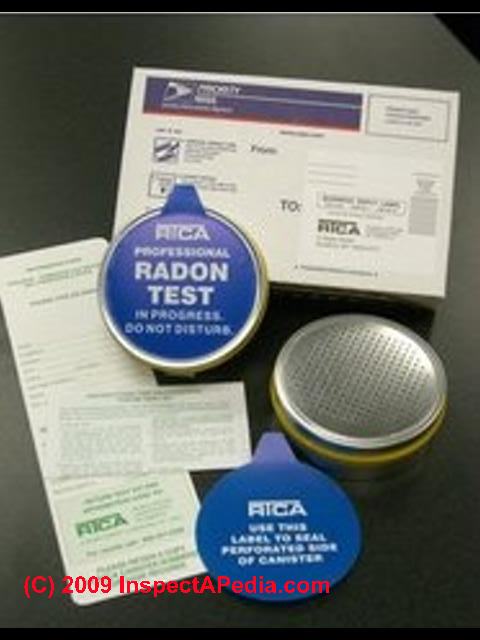
Select a radon test kit that is nationally or state-certified. Our photo (page top) shows an economical radon test kit available from RTCA - the Radon Testing Corporation of America. Home test kits for radon typically cost $20. for one test canister.
The “action level” established by the EPA for remediation in homes is 4 pCi/L, although it recommends that people consider taking action at 2 pCi/L or above—since no exposure level is without risk. The average indoor level in the U.S. is 1.3 pCi/L, while outdoor levels average 0.4 pCi/L.
Really, what is the health hazard from breathing air in which radon gas is detected at 4 picocuries per liter?
As we explain in more detail at RADON IMPACT ON HOME SALES, the original EPA radon gas testing recommendation was for further long term testing if a short term test for radon showed 4 pCi/L of radon in indoor air.
The level of radon gas in air, if present at all, can vary significantly over time due to a variety of building conditions such as indoor convective air current changes, building temperature variation, and variations in building ventilation. Because real estate sales transactions often do not welcome a year long radon remedy escrow fund impeding the sale of a property, 4 picocuries became an "action level for radon."
Readers should note this additional explanation of the hazard level of breathing air contaminated at a level of 4 picocuries of radon:
If you breathe air contaminated with radon gas at an average level of 4 picocuries per liter of air for eighteen hours a day for seventy years, then IFyou contract lung cancer after that time, you can assert that the lung cancer could have been caused by the radon gas exposure.
In other words, for 4 pCi/L radon gas exposure for any time period less than 18 hours a day for 70 years, the occurrence of lung cancer in an individual cannot be distinguished from random occurrences in the population and so cannot be asserted to be due to the radon gas exposure - Ed. .
Radon Testing Methods & Procedures
 Radon tests should be conducted away
from drafts, high heat, and high humidity in a
regularly used room on the lowest level in the home
that is used as living space, or in radon-testing lingo: test the lowest habitable space.
Radon tests should be conducted away
from drafts, high heat, and high humidity in a
regularly used room on the lowest level in the home
that is used as living space, or in radon-testing lingo: test the lowest habitable space.
So if your home has a full-height ceiling basement that is presently un-finished but that could be made into living space, it's reasonable to perform the test there.
Short-term radon tests last for 2 to 90 days, and long-term tests run for up to a year.
Place the radon test canister 2-3 feet above the floor on a chair, box, or table, in a house that has been closed for at least 24 hours before starting the test and that will be kept closed for the duration of the test period.
Place the radon test canister close to the center of the room, not by a window, door, or masonry such as a brick fireplace that can cause abnormal readings (some bricks contain and emit radon).
Do not place the radon test kit in a dead-air space, and do not place the canister where the building's HVAC system will blow on or across it.
Because radon levels vary daily and seasonally, longer test periods are better indicators of the average level. However, if two short-term tests yield an average result greater than 4 pCi/L, the EPA recommends taking steps to lower the level to 2 pCi/L or lower.
Since 1985, millions of homes have been tested for radon, and an estimated 800,000 homes have been mitigated.
-- adapted with permission from Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction.
...
Continue reading at RADON REMOVAL INDOORS, HOW-TO or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Related Articles
Suggested citation for this web page
RADON MEASUREMENT GUIDE at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to BUILDING INDOOR AIR QUALITY IAQ
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Questions & answers or comments about methods for measuring the hazard level of radon gas in buildings
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- RTCA, the Radon Testing Corporation of America, is in Elmsford, NY - 800-457-2366
- US EPA Radon level maps for the United States (747 K PDF file) - US EPA data on radon risk by geographic area - original source http://www.epa.gov/radon/zonemap.html
- Granite Countertops and Radiation Hazards, U.S. EPA (PDF), retrieved 12/15/2010, original source: http://www.epa.gov/rpdweb00/tenorm/granite-countertops.html
- RTCA, the Radon Testing Corporation of America, is in Elmsford, NY - 800-457-2366
- "Radon Basics", Q&A article, Solar Age, April 1984, includes advice for radon-resistant construction for an underground house built of concrete
- "Radon Basics-PDF", Q&A article, Solar Age, April 1984, includes advice for radon-resistant construction for an underground house built of concrete
- Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction, by Steven Bliss. John Wiley & Sons, 2006. ISBN-10: 0471648361, ISBN-13: 978-0471648369, Hardcover: 320 pages, available from Amazon.com and also Wiley.com. See our book review of this publication..
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.

