Choose a Room Air Conditioner Size
Choose a Room Air Conditioner Size
Air Conditioner BTU Requirements Chart:
by number of rooms or size of rooms to be cooled
Does ceiling height matter?
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about how to determine the necessary cooling capacity in BTUs for a room or building area cooled by a window air conditioner or a portable air conditioning unit
Air conditioner BTU requirements: this article provides an air conditioner BTU chart that shows how to choose a room air conditioner for window or through-wall mounting.
We provide room air conditioner or window air conditioner BTU sizing & choice charts.
We also show how to actually calculate how much BTU cooling capacity you need based on building area or square feet, and we warn about dehumidification problems if you buy an air conditioner that is too big for the space you are cooling.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
- Daniel Friedman, Publisher/Editor/Author - See WHO ARE WE?
BTU Cooling Capacity Range for Types of Room Air Conditioners
Use the ROOM AIR CONDITIONER SIZE CHART given just below to choose your air conditioner or heat pump size (expressed in BTUs) but for a more accurate capacity estimate, continue by increasing or decreasing that BTU number according to the factors we give at CALCULATE the BTU COOLING REQUIREMENT
You'll see that when choosing a window, through-wall or portable A/C unit you want to consider both room size and the number of rooms to be cooled in the building.
In contrast, when planning a central air conditioning system that uses ductwork to deliver conditioned air to each room, the total number of square feet in the whole cooled space is the starting point. In that case the "large areas" in the table below.
Article Contents
- ROOM AIR CONDITIONER SIZE CHART - Start by checking this Air Conditioner BTU Size Table
- ADJUST A/C SIZE for CEILING HEIGHT, HOT or HUMID CLIMATES
- CALCULATE the BTU COOLING REQUIREMENT - Calculate BTU requirements by modifying the table value for these factdors
- COOLING CAPACITY in SqFT per TON of A/C - Convert Tons of Cooling Capacity to BTUh, Express Cooling Capacity Requirement per Square Foot or Meter
- OVERSIZED A/C = DEHUMIDIFICATION PROBLEMS - Consider additional load if humid environments
- OTHER PORTABLE A/C TYPES - other types of air conditioners have different capacity ranges
- CAPACITY RANGE of A/C TYPES - Central, Multi-Room, Portable, Window Units
- DATA TAG DECODING for COOLING CAPACITY in BTUs
...
Room Air Conditioner Sizing and Choosing Chart
The table below gives recommended air conditioning BTU's necessary to cool a single room. The data in the table assumes that the ceiling over the room is insulated and that the room is not over or is not itself a special heat-producing area such as a kitchen or boiler room.
Table 1: Base BTUs - Recommended Air Conditioner BTUs |
||||||||||
| Number of Rooms Cooled |
Room Area MINimum sq.ft. |
Room Area MAXimum sq.ft. |
BTUs Needed |
|||||||
| One Room | . | 100 | 4,000 - 6,000 | |||||||
| 100 | 180 | 6,000 - 7,500 | ||||||||
| 180 | 270 | 7,500 - 9,000 | ||||||||
| 270 | 400 | 9,000 - 10,500 | ||||||||
| Several Rooms | . | 400 | 10,500 - 12,000 | |||||||
| 400 | 500 | 12,000 - 13,500 | ||||||||
| 500 | 700 | 13,500 - 15,000 | ||||||||
| 700 | 800 | 15,000 - 16,500 | ||||||||
| Large Areas | . | 900 | 16,500 - 18,000 | |||||||
| 900 | 1000 | 18,000 - 19,500 | ||||||||
| 1,000 | 1,100 | 19,500 - 21,000 | ||||||||
| 1,000 | 1,100 | 19,500 - 21,000 | ||||||||
| 1,100 | 1,200 | 12,000 - 22,500 | ||||||||
| 1,200 | 1,500 | 22,500 - 24,000 | ||||||||
| 1,500 | 1,700 | 24,000 - 25,500 | ||||||||
| 1,700 | 1,900 | 25,500 - 27,000 | ||||||||
| 1,900 | 2,200 | 27,000 - 28,500 | ||||||||
| 2,200 | 2,600 | 54k - 60k BTUh | ||||||||
| 2,600 | 3,800 | 72k - 84k BTUh | ||||||||
| 3,800 | 5,000 | 90k - 95k BTUh | ||||||||
...
Adjust A/C BTU Requirement for Ceiling Height or Hot or Humid Climates
Adjusting BTU Requirement for Atypical Ceiling Heights
BTU capacity tables for air conditioner selection typically assume typical 8 foot ceiling heights in residential spaces.
If your ceilings are significantly higher, say 14 feet or more, you may want to use the next larger room area size when selecting the BTUh capacity needed for your air conditioner, particularly if your building is located in a hot climate with higher heating loads.
For other building height variations the BTU adjustment depends on how much more than 8 feet in height is the ceiling, and more technically, the total room size and shape. An HVAC engineer would consider how air moves in the space.
For example a 20 x 20 x 8 ft. going to 9 ft. room that is increased in ceiling height by just one foot might have much less impact on the cooling ability of a given BTUh capacity air conditioner than a 10 x 10 x 8 ft. going to 10 x 10 x 16 ft. space.
A subjective opinion is that starting with an 8 foot ceiling we'd add 5% BTUH capacity per foot of ceiling height increase per foot over 9 ft.
Some experts find that small changes in ceiling height on cooling capacity are negligable.
- Novoselac, A. and Srebric, J., 2002. A critical review on the performance and design of combined cooled ceiling and displacement ventilation systems. Energy and buildings, 34(5), pp.497-509.
Abstract:
This paper reviews the studies and design of cooled ceiling and displacement ventilation (CC/DV) systems in buildings. If properly designed, the combined CC/DV systems can provide better indoor air quality and thermal comfort level compared to the widely used variable air volume (VAV) mixing systems.
The cooling load removed by DV is a key design parameter. A low DV load has a positive effect on thermal comfort due to a small vertical temperature gradient, yet also has a negative effect on indoor air quality due to the increased mixing of room air. The impact of the room height on the temperature and contaminant concentration profiles is negligible in the occupied zone.
The CC/DV systems are more effective in removing active contaminants (as indicated by CO2) than passive contaminants (e.g. VOCs). The condensation risk on the chilled ceiling panel is high because of the high humidity ratio in the region close to the panel. To prevent condensation on the panel, it is important to properly control the system for transient regimes, such as startup and shutdown periods, and to minimize infiltration of humid outdoor air.
Whether a CC/DV system may or may not reduce energy consumption depends on the supply air temperature, outdoor airflow rate, and cooling load.
Therefore, it is necessary to develop design guidelines for CC/DV systems for US buildings because the climate, building layout, and cooling load can be different from those studied elsewhere.
- Mumma, Stanley A. "Chilled ceilings in parallel with dedicated outdoor air systems: Addressing the concerns of condensation, capacity, and cost." ASHRAE Transactions 108 (2002): 220.
Adjust BTU Requirement for Variations in Building Heat Gain Rate
In locations of high heat gain or high solar gain such as a significant exposure to direct sunlight or many sun-facing windows, or for buildings with little insulation, you may need to select a higher-capacity air conditioner than given by the table.
- 2021 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) General Requirements - Climate Zones
- Mitsubishi Air Conditioning Sizing Chart [PDF] gives cooling capacity cross referenced with air conditioner model and capacity vs floor area in square meters - local copy saved as MHIAA-Split-System-Room-Sizing-Chart-March-2024.pdf
For example, for cooling loads in the Caribbean you also need to consider the high humidity in the area.
Standard cooling capacity is about 20 BTUs per square foot of floor space, but for hot humid climates like the Caribbean you'd want to increase the cooling capacity by 10%, or more; so 22-25 BTUs per square foot would be desirable.
Keep in mind that in addition to climate, BTU sizing requirements need ot consider other factors that we list above on this page at BTU CHART for AIR CONDITIONERS / HEAT PUMPS
...
How To Calculate the BTUs needed to cool a given space: follow this procedure:
- Calculate the total square feet to be cooled: Measure the size of the room (or rooms) to be cooled, to obtain total square feet.
Multiply room length by width for each room and if there are multiple rooms, add the room areas together to get a single number. - Read the Base BTUs needed from Table 1 below
- Add additional BTUs for these factors:
- + 4,000 BTUs for each room below a ceiling or roof which is not insulated
- + 4,000 BTUs for a home or residential kitchen included in the cooled area
- + 1,500 BTUs for each window which receives significant daily sunshine
- + 1,500 BTUs for a room over a kitchen or boiler room IF the kitchen or boiler room is actively producing heat during the cooling period
- + 600 BTUs per person over two, if more than two occupants will be occupying the room during the cooling period
- + 10% for hot humid climates such as buildings in the Caribbean
- + 10% for buildings that are not well insulated
- +10% if your building receives a lot of direct sun or has more than typical amount of South facing glass windows and sliding doors
- Ceiling height may affect the BTU requirements but probably only where ceiling heights are particularly tall such as more than 14 ft. or about 4.2 meters. Then for a portable or window or through-wall A/C unit you'll want the next larger air conditioner unit size offered by the manufacturer.
- Floor level in the building may affect the BTU requirements, particularly in high rise buildings where elevator shafts and stairways, combined with vent openings on upper floors cause heat to rise in the building.
- Additional help with this data: https://www.acdirect.com/blog/what-size-air-conditioner-do-i-need/ a vendor of air conditioning equipment
- Subtract BTUs from the total required if these factors are present:
- - 1,000 BTUs if the room is on the shaded side of the building
- Calculate the final total BTUh needed from the above steps by adding and subracting the factcors listed from the
base BTUs in Table 1 - ROOM AIR CONDITIONER SIZE CHART
This should place you in the right range of cooling capacity needed. Review the warning below about buying an oversized air conditioner. - Climate Zone Impact on Cooling BTU Requirements - adjust your BTU requirement for the climate zone where your building is located
Climate Zone Adjustments to Air Conditioner Size
Climate Zone ZONE 1 ZONE 2 ZONE 3 ZONE 4 ZONE 5 A/C Capacity Room Size in Square Feet 1.5 Tons - 18,000 BTUh - 5.2 kwh 600 - 900 sq.ft. 600 - 950 sq.ft. 600 - 1000 sq.ft. 700 - 1050 sq.ft. 700 - 1100 sq.ft. 2 Tons - 24,000 BTUh - 7 kwh 900 - 1200 - 1250 - 1300 - 1350 - 1400 2.5 Tons - 30,000 BTUh - 8.8 kwh 1200 - 1500 - 1550 - 1600 - 1600 - 1650 3 Tons - 36,000 BTUh - 10.6 kwh 1500 - 1800 - 1850 - 1900 - 2000 - 2100 3.5 Tons - 43,000 BTUh - 12.6 kwh 1800 - 2100 - 2150 - 2200 - 2250 - 2300 4 Tons - 48,000 BTUh - 14 kwh 2100 - 2400 - 2500 - 2600 - 2700 - 2700 5 Tons - 60,000 BTUh - 17.6 kwh 2400 - 3000 sq.ft. - 3100 sq.ft. - 3200 sq.ft. - 3300 sq.ft. - 3300 sq.ft. Notes to the table above
For each zone that is cooler than Zone 1 (the warmest climate), the same A/C cooling unit (in tons capacity) can cool about 50 square feet more for the smaller A/C units and 100 squre feet for larger units of 4 tons or more.
Zone 5 is the coolest climate; Climate zone maps are given by the links below.
U.S. Climate Zones Map - U.S. Department of Energy
Climate Zones for Buildings - US Department of Energy
1 Ton of BTUh capacity (in BTUs per hour) = 12,000 BTUs/hour = 2.5 kW (Kilowatts) per hour or kwh 18000"kilowatt hours".
...
How Much Cooling Capacity do we need Per Square Foot of Building Area?
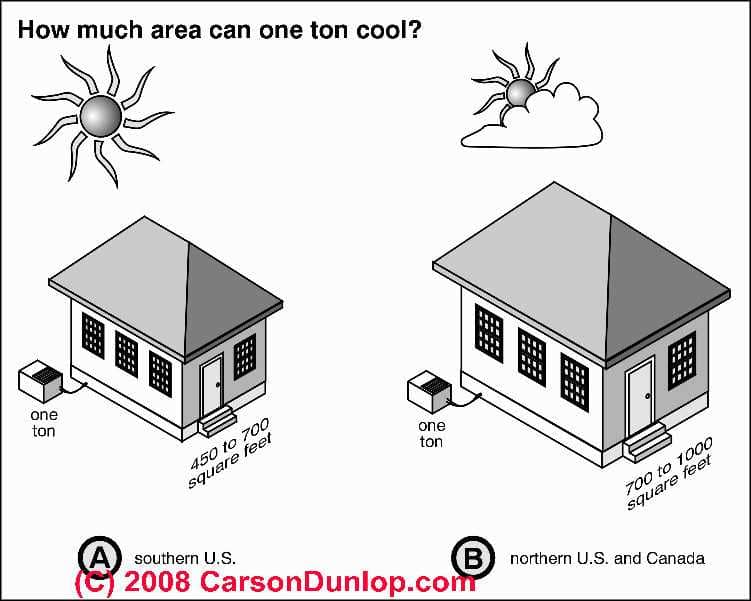 How Much Space can One Ton of Cooling Capacity Serve?
How Much Space can One Ton of Cooling Capacity Serve?
Maybe 450 sq.ft. to 1000 sq.ft. of a typical home can be cooled per ton of cooling capacity: that is, one ton (or 12,000 btuh) of air conditioning can cool about 500 sq.ft. of space. Sketch courtesy of Carson Dunlop Associates, a Toronto home inspection, education & report writing tool company [ carsondunlop.com ].
But the real answer is, it depends. Some of the factors that affect the ability of an air conditioner to cool a space need to be considered besides just the number of square feet. These include at least the following questions about air conditioning load and cooling requirements:
- What are the sun and heat characteristics of the geographic area where the building is located (southern U.S. vs. northern U.S. or Canada, for example)? That is, what is the climate zone where the building is located?
See our climate zone vs cooling zone table above. - How much direct sunlight is falling on the building?
- Is it bright hot sun or only partly sunny?
- What are the exterior colors of surfaces on which sunlight is falling?
- How well the building is insulated?
- How drafty is the building?
- How many occupants are in the building?
- What other heat sources (or cooling sources) are in the building?
- How high are the interior ceilings?
- How does air circulate within the occupied spaces?
- What defects in the air conditioning system need to be overcome, such as duct system errors or damage, dirty filters, blocked cooling coils, etc. ?
...
Watch out: Don't Buy an Oversized or "Too Big" Air Conditioner

Watch out: Do not buy an air conditioner which is oversized (too many BTUh) for the area you need to cool. You may think that bigger is better, but not in the case of air conditioning.
To make a room comfortable the air conditioner needs to both cool the room air AND dehumidify the room air.
If the air conditioner is too large for the space to be cooled, the temperature will drop quickly and the A/C unit will shut off before the air has become adequately dry. The room will be either too cold or too humid for comfort. Sketch courtesy of Carson Dunlop Associates, a Toronto home inspection, education & report writing tool company [ carsondunlop.com ].
More detail about how to diagnose and cure an air conditioner that is not dehumidifying can be found
A/C Size Mistakes: units too big or too small
- Over-sized air conditioner problems are found at DEHUMIDIFICATION PROBLEMS
- We also introduce the oversized air conditioner problem at LOST COOLING CAPACITY.
- at ADDING A/C: RETROFIT SIZING we discuss home cooling system sizing mis-match on retrofit jobs.
- Also see WINDOW / WALL AIR CONDITIONERS.
...
Other types of portable or individual area air conditioners

- Heating & Cooling units -
capable of both cooling or heating a room using electricity. Basically these units are small heat pumps that are mounted in a building window or wall. Heating/Cooling units will give two different BTUh figures, one for cooling and one for heating.
These figures will differ, for example, producing 18,000 BTUh in cooling mode but only 12,000 BTUh in heating mode. The difference between heating and cooling, and the amount of heat actually available will depend also on the outdoor temperatures when in heating mode (as with any heat pump system, the unit cannot provide heat below certain temperatures.)" - Slider or Casement Window units -
narrow tall cooling systems which are designed to fit into the narrow space provided by casement or slider windows. - Through-wall air conditioners -
air conditioning units which are designed to be installed into a metal sleeve which is then itself installed in an opening cut into the building wall, leaving windows unobstructed, or perhaps for use in a room without a suitable window in which an air conditioner could be placed. BTU output is typically a bit more than the smallest window air conditioners but otherwise is similar in range. - Portable room air conditioners -
units on wheels which are plugged into an outlet but can be moved room-to-room and do not require a window for their exhaust.
These cooling units are of modest cooling ability, typically around 10,000 BTUh though some producers such as Sunpentown offer units up to 14,000 BTUh.
See PORTABLE ROOM AIR CONDITIONERS for details about portable room air conditioners.
See PORTABLE AIR CONDITIONER BTU CHART for sizing or choosing a portable air conditioner based on room size
...
BTU Capacity Range by Type of Air Conditioner Unit or System
- Single Room Air Conditioner Capacity -
Portable, window, or through-wall air conditioners like the ones shown in oui photo are typically described by their manufacturer as suited for t rooms up to 20' x 20' or 400 sq.ft. in area.
BTUs in this product range are typically from 6,000 BTUh to 10,000 BTUh. - Portable room air conditioners -
7,500 to 14,000 BTUH, portable, using one or in some cases two flexible ducts to move heat from the room, through cooling coil and the compressor, to outdoors
- Multiple Room Air Conditioner Capacity -
typically for a total area of up to 800 sq.ft. BTUs in this product range are typically from 10,000 BTUh to 16,000 BTUh. - Large Capacity Air Conditioner Capacity -
typically for multiple rooms or very large rooms up to a total area from 900 sq. ft. to 2,000 sq.ft. BTUs in this product range are typically from 16,000 to 28,000 BTUh. - Central Air Conditioning -
typically to cool an entire floor or multiple floors in a home.
...
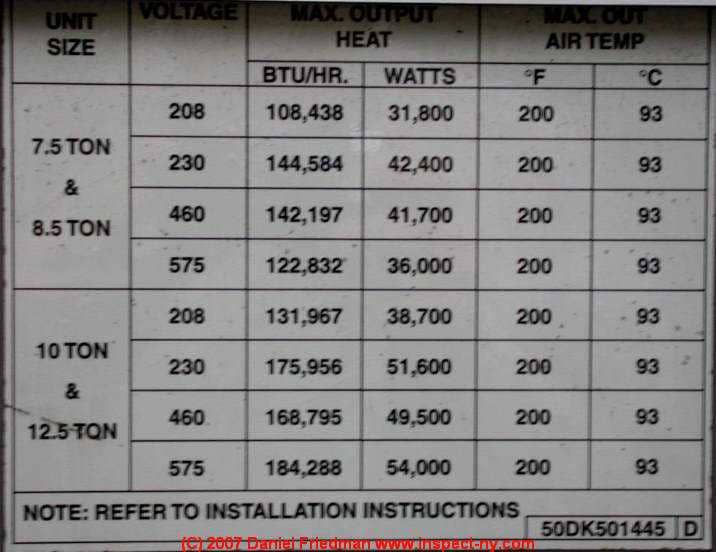
How to Determine BTUs or Tons of Cooling Capacity of an Air Conditioner from its Data Tags
- See RATED COOLING CAPACITY for an explanation of how to determine the cooling capacity of an air conditioner that is already installed at a building or go directly to these links within that article:
FROM MODEL # - how to determine the BTU capacity or Tons of cooling capacity of an air conditioner from model number - FROM EQUIPMENT RLA # - how to determine the BTU capacity or Tons of cooling capacity of an air conditioner from the RLA number
- COOLING RULES OF THUMB - how to guesstimate how many tons or BTUs of cooling a building needs
you can decode data tags on air conditioners to read the BTUH ratings -
see DATA TAGS on AIR CONDITIONERS where explain how to read the data tag: the unit model number usually also indicates the A/C unit size or capacity in BTUh
And in that article we give links to two detailed A/C size decoding documents that should have what you need.
Remember that we want the air conditioner's model number, not the unit's serial number.
You'll find Carrier contact information and manuals that explain how their model numbers are encoded
at CARRIER AIR CONDITIONERS, BOILERS FURNACES
The capacity in BTUs is often obvious in the model number but it's worth keeping in mind that because there is no international standard for the format of air conditioner or heat pump model number coding, the actual BTU number, where, and how it's encoded in the model number, will vary among manufacturers.
On newer air conditioners, the unit's data tag often states the BTUs explicitly in its own field on the data tag. Below is an example from Whirlpool air conditioner data tag decoding guide in the article we cited just above. See that Nominal Capacity field in positions 7 and 8 of the air conditioner's model number.
and below is a capacity chart from a commercial air conditioner's data tags
...
...
Continue reading at BTU SIZING for AIR CONDITIONERS FAQS or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- A/C TYPES, ENERGY SOURCES
- BTU CHART for AIR CONDITIONERS / HEAT PUMPS
- BTU CHART for HEATING FURNACES
- DEHUMIDIFICATION PROBLEMS if your A/C or heat pump system is over-sized it may not dehumidfy adequately.
- PORTABLE AIR CONDITIONER BTU CHART
- WINDOW / WALL AIR CONDITIONERS
Suggested citation for this web page
BTU CHART for AIR CONDITIONERS / HEAT PUMPS at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to AIR CONDITIONING & HEAT PUMPS
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
IF above you see "Comment Form is loading comments..." then COMMENT BOX - countable.ca / bawkbox.com IS NOT WORKING.
In any case you are welcome to send an email directly to us at InspectApedia.com at editor@inspectApedia.com
We'll reply to you directly. Please help us help you by noting, in your email, the URL of the InspectApedia page where you wanted to comment.
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- Thanks to various industry and air conditioner sales publications and consumer pamphlets including Sears Kenmore(R) air conditioning sales
- Sunpentown International (SPT), 21415 Baker Parkway, City of Industry, CA 91789, 800-330-0388 / 909-468-5288, produces portable room air conditioners. Web search 12/31/2010. FAQ for portable room air conditioners: http://www.sunpentown.com/learnmore.html
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.