 Guide to Types of Light Bulbs & Lamps
Guide to Types of Light Bulbs & Lamps
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about the properties of different types of light bulbs or lamps for indoor lighting use
A guide to light bulbs ("lamps"):
Here we provide a guide to the different types of light bulbs (lamps) used in indoor light fixtures. We describe the indoor use of halogen lights, and low-voltage lights.
We provide a guide for using fluorescent lights and compact fluorescent bulbs indoors and we include a table comparing fluorescent bulb light levels to incandescent light bulbs.
And we discuss issues surrounding the color temperature of fluorescent lighting. This article series details guidelines for selecting and installing interior lighting to meet the requirements for different building areas.
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
Guide to Lamp Types & Types of Bulbs for Indoor Lighting
 Here we provide a guide to the different types of light bulbs (lamps) used in indoor light fixtures. This article series details guidelines for selecting and installing interior lighting to meet the requirements for different building areas.
Here we provide a guide to the different types of light bulbs (lamps) used in indoor light fixtures. This article series details guidelines for selecting and installing interior lighting to meet the requirements for different building areas.
This article includes excerpts or adaptations from Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction (Steve Bliss, J Wiley & Sons) , by Steven Bliss, courtesy of Wiley & Sons.
[Click to enlarge any image]
Our page top photo illustrates dramatic use of lighting at the Metropolitan Opera building in New York City.
Article Contents
- BULB & LAMP TYPES GUIDE
- TABLE Comparing Bulb Light Outputs
- BAYONET BASE BULB TYPES
- HALOGEN LIGHTS INDOOR USES
- INCANDESCENT BULB GUIDE
- LED BULB & LIGHTING TYPES
- LOW-VOLTAGE LIGHTING GUIDE INDOOR for Building Interiors
- FLUORESCENT LIGHTING GUIDE INDOORS for Indoors and Guide to Using Compact Fluorescent Lights
- FLUORESCENT LIGHTS COMPACT INDOOR
- FLUORESCENT LIGHT BULB CODES & TYPES
- FLUORESCENT LIGHT REPAIRS
- FLUORESCENT vs INCANDESCENT BULBS
- LAMPS (BULBS) ANTIQUE CONNECTOR TYPES
For residential lighting, the main choices are incandescent, halogen, low-voltage, tubular fluorescent, and compact fluorescent.
Which lamp to choose for a given application will depend upon the amount of light needed (lumens), color of light desired, type of fixture (luminaire), and whether the application calls for a directed beam or a diffused light source.
Table Comparing Fluorescent bulb Light Output to Standard Incandescent Light Bulb Output
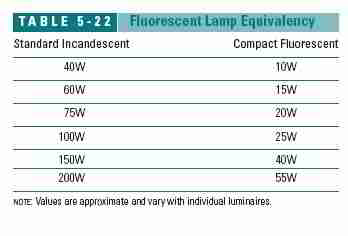
Also, some lamps are more energy-efficient, providing more lumens for the same amount of electricity consumed.
Fluorescent's are the most efficient, using up to 70% less energy than an equivalent incandescent bulb (see Table 5-22).
Incandescent Light Bulbs
Incandescent light bulbs include the familiar non directional “A” lamps, as well as a variety of directional flood and spot lamps designated by an “R” or “BR.”
Incandescent's have a low color temperature of around 2700 K, which produces a warm light with lots of red and yellow tones that make skin, natural wood, and other warm colors look good.
To some extent, things look good to us under incandescent light because it is what we are most accustomed to.
Incandescent lamps are inexpensive and are easy to dim, but they are also the least efficient type of bulb and the shortest lived.
Our photo illustrates an antique ceiling light fixture using incandescent bulbs in a home in Wappingers Falls, NY. Originally the fixture included small glass shades around each bulb - yet to be restored by the editor - DF.
A second, simple incandescent bulb is shown at left, in an outdoor light fixture where we found its bulb base loose and ready to short out.
And this bulb, a 75-watt unit was over-watted for the fixture whose sticker warned that 60-watts was its limit. Installing a bulb of higher watt-rating than the fixture permits is a fire hazard.
Halogen Lights for Use Indoors
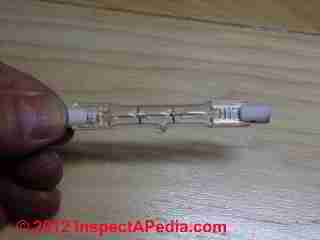 Halogen bulbs, also known as tungsten-halogen, is actually a
kind of incandescent with more blue and less red light
(3000 K), giving it a whiter appearance than standard incandescent
lamps.
Halogen bulbs, also known as tungsten-halogen, is actually a
kind of incandescent with more blue and less red light
(3000 K), giving it a whiter appearance than standard incandescent
lamps.
Halogen lamps provide good color rendition and good light for reading and fine detail work. When dimmed, however, halogen light becomes more yellow, like standard incandescent lighting. Also, dimming can cause a halogen lamp to darken due to tungsten evaporation. Turning the lamp to full illumination for about 10 minutes will restore its full power.
Halogen lamps tend to be smaller, produce 10 to 15% more lumens per watt than standard incandescent's., and last about twice as long.
They come in a wide range of beam spreads and wattages. However, since halogen lights burn very hot, they must be shielded from contact with other materials or they can create a fire hazard.
The halogen bulb shown at left is used in work lights and security lights. Work lights using this bulb and in use indoors must be kept a safe distance from combustibles.
Also, the bulbs should not be touched without wearing a glove (since the oil from your skin can create a weak spot on the bulb), and should be cleaned with alcohol.
Halogen PAR (parabolic aluminized reflector) lamps are enclosed in a protective glass casing, which allows them to be handled like ordinary bulbs. (See the 12-V bulbs illustrated below).
Low-Voltage lamps are tungsten-halogen, incandescent, or the newer xenon lamps, operating at 12 volts DC. Their small size makes them ideal for under cabinet lighting, and their very precise beam control makes them well-suited to accent lighting of artwork. Many low-voltage fixtures allow the lamps to rotate within the housing to precisely aim the beam.
Low-voltage Lighting Guide for Building Interiors
 Low voltage lights use a step-down transformer to
convert 120V line voltage to 12 volts DC.
Low voltage lights use a step-down transformer to
convert 120V line voltage to 12 volts DC.
Most newer fixtures use solid-state electronics, which are more energy efficient and longer lasting than the older magnetic type.
Transformers are either attached to the fixtures or installed remotely.
Since the transformers, as well as the lamps and dimmers, emit a slight hum, remote location can be an advantage.
However, locating the transformer too far from the fixtures can result in a loss of power and dimming of the lamps.
When using dimmers with low-voltage lighting, make sure they are specifically designed for low voltage systems and for the specific type of transformer.
Fluorescent Lighting Guide for Indoors
 Fluorescent bulbs or lamps produce light by energizing the
phosphor coating on the inside of a glass envelope. A device
called the ballast regulates the power needed to start
the lamp and keep it going.
Fluorescent bulbs or lamps produce light by energizing the
phosphor coating on the inside of a glass envelope. A device
called the ballast regulates the power needed to start
the lamp and keep it going.
Older magnetic ballasts caused humming and flickering, but new electronic or solid-state ballasts have eliminated these problems.
Fluorescent's produce three to five times the output as incandescent lamps [per watt of energy used], last about ten times as long, and stay very cool.
Because they reduce lighting bills by as much as 75%, and reduce cooling loads as well, they are heavily promoted by model energy codes and mandated in some areas. For example, the California Energy Code requires that the main lighting in kitchens and baths be fluorescent.
The downside of fluorescent's has always been their poor color rendering. Standard fluorescent's emphasize the blue range of the spectrum, giving skin an unflattering, pale appearance. Manufacturers have worked hard over the years to improve the light quality.
So-called “deluxe” fluorescent's offer CRI (color rendering index) values in the 85 to 90 range but with a 25% loss of efficiency.
To achieve CRIs in the high 90s without sacrificing energy efficiency, manufacturers use more expensive rare earth phosphors, creating triphosphor and quad-phosphor lamps.
Fluorescent lamps with high CRIs, and color temperatures within the range of 2700 to 3500K, create pleasing light for skin tones and natural wood and can blend in with incandescent lighting.
 In applications where color accuracy
is important, such as laundry areas, lighting artwork,
and certain hobbies, full-spectrum daylight lamps may be
preferred.
In applications where color accuracy
is important, such as laundry areas, lighting artwork,
and certain hobbies, full-spectrum daylight lamps may be
preferred.
These lamps, which produce light similar to natural daylight, include General Electric’s Chroma 50 and Chroma 75.
Dimming also used to be a challenge with fluorescent's However, using solid-state dimming ballasts and special dimmers designed for fluorescent's can eliminate any humming sounds. These also allow a single dimmer switch to dim groups of fixtures with different length tubes.
Cold Cathode Bulbs
The super-compact fluorescent 120-V bulb shown at left using an Edison base and with a color temperature of around 2700 K is available from TCP, a company offering a wide range of lighting components, bulbs, ballasts. Shown is TCP's "Cold Cathode" 8-watt bulb, item 8G2508CL.[3]
This bulb type emits very little heat and is described by the company as especially suitable for signs, marquees, and accent lighting both indoors and outside. The bulbs are also described as excellent for dimming & flashing applications. Photograph courtesy of our associate Charles Soberman.[4]
Note: these Cold Cathode bulbs are UL approved for wet locations in Base Up Position ONLY.
Guide to Using Compact Fluorescent Lights
 Compact fluorescent lights have created a lot more flexibility,
allowing fluorescent's to be used in recessed downlights,
wall sconces, pendants, and just about any type of
luminaire. Early compact fluorescent's were noisy, slow to
start, and had a limited selection of color temperatures.
Compact fluorescent lights have created a lot more flexibility,
allowing fluorescent's to be used in recessed downlights,
wall sconces, pendants, and just about any type of
luminaire. Early compact fluorescent's were noisy, slow to
start, and had a limited selection of color temperatures.
Newer products, however, are quiet and typically have rapid-start ballasts. Dimmable ballasts are also available for compact fluorescent's, but are costly. As with tube fluorescent's, look for high CRIs and lower (warmer) color temperatures from 2700 to 3500K to blend in with incandescent and halogen lighting.
All compact fluorescent's have a minimum 80 CRI.
While some compact fluorescent's have been introduced that mimic R and PAR-type reflector bulbs, directional lighting is best achieved with incandescent or halogen lamps.
Fluorescent's are better used for ambient lighting, indirect lighting, and lighting of closets and storage areas. Although they cost $5 to $20 per bulb, depending on the wattage and configuration, they generally pay for themselves within two to three years in both energy savings and longevity of the bulbs.
- - Adapted with permission from Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction (Steve Bliss, J Wiley & Sons) .
Guide to LED Light Bulbs
Please see LED BULB & LIGHTING TYPES for details about LED light bulbs used in building lighting & light fixtures.
LED bulb brigtness in lumens and energy costs are at our Table of Current LED Bulb Prices & Features.
Industry Associations for Lighting
- American Lighting Association www.americanlightingassoc.com
- - Adapted with permission from Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction (Steve Bliss, J Wiley & Sons) .
More detail about lamp or bulb types including abbreviations and feature comparisons can be read
at Lamp & Bulb Abbreviations & Types.
Also see LIGHTING, INTERIOR GUIDE our home page for information about all lighting topics relating to building interior There is a vast array of choices in light bulbs, known in the lighting industry as “lamps.”
...
Continue reading at BULB & LAMP ABBREVIATIONS & CODES or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- BULB & LAMP TYPES GUIDE - home
- ANTIQUE LAMPS (BULBS) & CONNECTOR TYPES
- ANTIQUE LAMPS (BULBS) LIGHT OUTPUT - LUMENS
- ASBESTOS in LAMPS & LIGHT BULBS
- BAYONET BASE BULB TYPES
- BULB & LAMP ABBREVIATIONS & CODES
- BULB COLOR TEMPERATURE COMPRARISONS
- BULB COLOR TEMPERATURE U CRI
- BULB CRI SCALE DEFINITION & RATES
- COMPACT FLUORESCENTS INDOORS
- FLUORESCENT LIGHT BULB CODES & TYPES
- FLUORESCENT LIGHT REPAIRS
- FLUORESCENT vs INCANDESCENT BULBS
- HALOGEN LIGHTS INDOOR USES
- INCANDESCENT BULB GUIDE
- LAMPS (BULBS) ANTIQUE CONNECTOR TYPES
- LED BULB & LIGHTING TYPES
- RECESSED & TRACK LIGHT BULB GUIDE
- LIGHTING, EXTERIOR GUIDE - home
- INTERIOR LIGHTING GUIDE - home
Suggested citation for this web page
BULB & LAMP TYPES GUIDE at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to BUILDING LIGHTING
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
Our Comment Box is provided by Countable Web Productions countable.ca
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- Steve Bliss's Building Advisor at buildingadvisor.com helps homeowners & contractors plan & complete successful building & remodeling projects: buying land, site work, building design, cost estimating, materials & components, & project management through complete construction. Email: info@buildingadvisor.com
Steven Bliss served as editorial director and co-publisher of The Journal of Light Construction for 16 years and previously as building technology editor for Progressive Builder and Solar Age magazines. He worked in the building trades as a carpenter and design/build contractor for more than ten years and holds a masters degree from the Harvard Graduate School of Education. Excerpts from his recent book, Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction, Wiley (November 18, 2005) ISBN-10: 0471648361, ISBN-13: 978-0471648369, appear throughout this website, with permission and courtesy of Wiley & Sons. Best Practices Guide is available from the publisher, J. Wiley & Sons, and also at Amazon.com - [3] TCP, 325 Campus Drive, Aurora OH 44202, USA, Tel: 800-324-1496, website: www.tcpi.com
- [4] Charles, Soberman, San Miguel de Allende, Guanajuato, Mexico
- Our recommended books about building & mechanical systems design, inspection, problem diagnosis, and repair, and about indoor environment and IAQ testing, diagnosis, and cleanup are at the InspectAPedia Bookstore. Also see our Book Reviews - InspectAPedia.
- Best Practices Guide to Residential Construction, by Steven Bliss. John Wiley & Sons, 2006. ISBN-10: 0471648361, ISBN-13: 978-0471648369, Hardcover: 320 pages, available from Amazon.com and also Wiley.com. See our book review of this publication.
- "Electrical System Inspection Basics," Richard C. Wolcott, ASHI 8th Annual Education Conference, Boston 1985.
- "Simplified Electrical Wiring," Sears, Roebuck and Co., 15705 (F5428) Rev. 4-77 1977 [Lots of sketches of older-type service panels.]
- "How to plan and install electric wiring for homes, farms, garages, shops," Montgomery Ward Co., 83-850.
- "Electrical System Inspection Basics," Richard C. Wolcott, ASHI 8th Annual Education Conference, Boston 1985.
- "Simplified Electrical Wiring," Sears, Roebuck and Co., 15705 (F5428) Rev. 4-77 1977 [Lots of sketches of older-type service panels.]
- "How to plan and install electric wiring for homes, farms, garages, shops," Montgomery Ward Co., 83-850.
- "Home Wiring Inspection," Roswell W. Ard, Rodale's New Shelter, July/August, 1985 p. 35-40.
- "Evaluating Wiring in Older Minnesota Homes," Agricultural Extension Service, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, Minnesota 55108.
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.



